As a student, you are very familiar with the different activities you do in school. You might already have done poetry reading, writing, and analysis essay in your literature classes, or perhaps you have done equations in your math and science classes, or maybe some cut outs for your arts.
One of the most common activities for students is writing reports, specifically for your science project. Although it’s already pretty common, writing reports still is not that easy. That is why we are going to help you out. Check out our free Sample Reports below so that you can get a picture on what you can do for your report.
Download Science Project Report Bundle
Science Fair Research Paper 7th Grade
Science Project Report: The Effects of Sunlight on Plant Growth
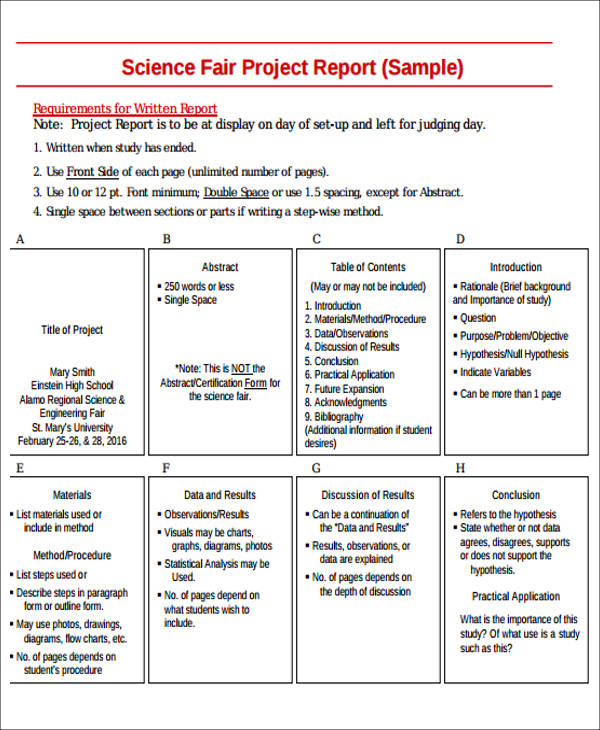
Title Page
- Project Title: The Effects of Sunlight on Plant Growth
- Student’s Name: Jane Doe
- Teacher’s Name: Mr. John Smith
- Class: 7th Grade Science, Section B
- School Name: Riverside Middle School
- Date: October 5, 2024
Abstract
- This experiment investigates how different amounts of sunlight affect the growth of bean plants. Over a period of 30 days, bean plants were exposed to varying durations of sunlight: 4, 8, and 12 hours per day. Growth was measured by the height of each plant and the number of leaves. The results indicate that plants receiving 8 hours of sunlight per day achieved optimal growth, suggesting a moderate amount of sunlight maximizes plant health.
Table of Contents
- Abstract …………………………….. 2
- Introduction ……………………… 3
- Materials and Methods …………. 4
- Results …………………………….. 5
- Discussion ………………………… 6
- Conclusion ………………………… 7
- References ………………………… 8
- Appendices ……………………….. 9
Introduction
- Background Information: This project explores plant biology, focusing on the importance of sunlight for plant health and growth. Sunlight is crucial for photosynthesis, the process by which plants make their food.
- Research Question: How does the amount of daily sunlight exposure affect the growth of bean plants?
- Hypothesis: It is hypothesized that bean plants exposed to moderate amounts of sunlight (8 hours per day) will show optimal growth compared to those receiving less or more daily sunlight.
Materials and Methods
- Materials:
- Bean seeds (Phaseolus vulgaris)
- Potting soil
- Plant pots (15 cm diameter)
- Ruler
- Watering can
- Light timer
- Procedure:
- Fill three pots with equal amounts of potting soil and plant five bean seeds in each pot.
- Place the pots in locations where they can receive 4, 8, and 12 hours of sunlight respectively.
- Water the plants equally to keep the soil moist.
- Measure the height of each plant and count the number of leaves every 5 days for 30 days.
Results
- Data Presentation: Graphs illustrating plant heights and leaf count over time show clear trends. A table summarizing the average growth metrics for each light exposure group.
- Observations: Plants with 8 hours of sunlight displayed the most vigorous growth, both in height and leaf production.
Discussion
- Analysis: The data supports the hypothesis that moderate sunlight exposure (8 hours) is optimal for the growth of bean plants.
- Limitations: Some plants showed signs of wilting which may have affected growth measurements. Future experiments could control for soil quality and watering consistency.
- Future Work: Further research could explore the effects of different light qualities (e.g., light spectrum) on bean plant growth.
Conclusion
- The experiment confirmed the hypothesis that bean plants grow best with moderate sunlight exposure. This finding can help inform gardeners and farmers about optimal sunlight conditions for growing bean plants.
References
- Doe, J. (2024). Effects of Light on Plant Growth. Riverside Science Fair Reference Materials.
- Smith, J. (2024). Introduction to Botany. Riverside Middle School Resources.
Appendices
- Appendix A: Raw Data Tables
- Appendix B: Experiment Setup Photos
This format will help you present your science project in a professional and organized manner. If you have any more specific needs or questions about your project, feel free to ask!

Science Project Reports For Students
Science Project Report: The Effect of Organic vs. Chemical Fertilizers on Plant Growth
Title Page
- Title of the Project: The Effect of Organic vs. Chemical Fertilizers on Plant Growth
- Student’s Name: Emily Johnson
- Teacher’s Name: Mrs. Lisa Green
- Class: 7th Grade Science, Section 1
- School Name: Maplewood Middle School
- Date: November 10, 2024
Abstract
This experiment aimed to compare the effects of organic and chemical fertilizers on the growth of tomato plants. Over a period of six weeks, two groups of tomato plants were grown under controlled conditions, one with organic fertilizer and the other with chemical fertilizer. Growth was measured weekly in terms of plant height and number of leaves. The plants with organic fertilizer showed more consistent and healthier growth, suggesting that organic fertilizers may be more beneficial for tomato plants.
Table of Contents
- Abstract …………………………….. i
- Introduction ……………………… 1
- Materials and Methods …………. 2
- Results …………………………….. 3
- Discussion ………………………… 4
- Conclusion ………………………… 5
- References ………………………… 6
- Appendices ……………………….. 7
Introduction
- Background Information: Interest in sustainable agriculture has prompted comparisons between organic and chemical fertilizers. Organic fertilizers are believed to improve soil health and long-term plant vitality.
- Statement of the Problem: How do organic fertilizers compare to chemical fertilizers in promoting plant growth?
- Hypothesis: Tomato plants grown with organic fertilizer will exhibit more robust growth compared to those grown with chemical fertilizers.
Materials and Methods
- Materials:
- 10 tomato plants
- Organic fertilizer (compost)
- Chemical fertilizer (NPK 15-15-15)
- 10 planting pots
- Ruler
- Notebook for observations
- Procedure:
- Label five pots as ‘Organic’ and five as ‘Chemical.’
- Plant one tomato plant in each pot.
- Apply organic fertilizer to the ‘Organic’ group and chemical fertilizer to the ‘Chemical’ group according to package instructions.
- Water the plants equally.
- Measure and record the height and number of leaves of each plant every week.
Results
- Data Presentation: Graphs showing the weekly growth in height and leaf count for each group.
- Observations: Plants in the ‘Organic’ group generally exhibited more consistent growth and appeared healthier with greener leaves.
Discussion
- Interpretation of Results: The hypothesis was supported; organic fertilizer led to better overall plant health and growth.
- Limitations: Small sample size and limited duration of the experiment.
- Suggestions for Future Research: Future studies could extend the duration of the experiment or test different types of plants to see if results are consistent across species.
Conclusion
The experiment demonstrated that organic fertilizers might be more beneficial for tomato plants than chemical fertilizers, supporting the hypothesis and suggesting broader applications in gardening and agriculture.
References
- Johnson, E. (2024). School Science Textbook, Maplewood Middle School Library.
- Green, L. (2024). “Fertilizers and Plant Growth,” Science Journal for Middle School.
Appendices
- Appendix A: Raw Data Tables
- Appendix B: Photos of Plants Weekly
This structured format ensures the report is thorough and covers all aspects of the scientific process, making it a valuable document for evaluation at a science fair. If you have specific requests or need more examples, just let me know!

Project Report For Computer Science
Computer Science Project Report: [Title of Your Project]
Title Page
- Project Title: Should clearly reflect the main objective or technology used.
- Student’s Name: Full names of all project members if it’s a group project.
- Supervisor’s Name: Name of the faculty or teacher guiding the project.
- Course Title: If applicable, e.g., “Introduction to Programming”, “Advanced Databases”.
- Institution Name: Name of the school or university.
- Date of Submission: The complete date when the report is submitted.
Abstract
- A brief (200-300 words) summary of the project that includes the problem statement, methodology, key findings, and conclusion. This should provide a snapshot of the entire project.
Table of Contents
- Lists the major sections of the report and their page numbers for easy navigation.
List of Figures and Tables
- If your report includes multiple figures, diagrams, or tables, list them with their page numbers.
Introduction
- Background Information: Discuss the background or context of the problem you are addressing.
- Problem Statement: Clearly define the problem you aim to solve.
- Objectives: List the objectives and goals of the project.
- Scope: Outline the scope of the project, specifying what is included and what is not.
Literature Review
- Review of existing solutions or similar projects and their limitations. This section should demonstrate understanding of the project’s domain.
Methodology
- Design: Describe the system architecture and design decisions.
- Development Tools: List programming languages, software tools, and frameworks used.
- Implementation: Detail the implementation process, including algorithms, databases, and other technical components.
Results and Discussion
- Testing and Validation: Describe how the system was tested (unit tests, integration tests, etc.). Include any validation processes.
- Results: Present the results of the testing phase. Use screenshots, code snippets, and diagrams to illustrate.
- Discussion: Analyze the results, discussing how they meet the objectives or solve the problem.
Conclusion
- Summarize the project outcomes and state whether the initial objectives were met.
- Discuss the implications of your findings for future projects or further development.
Future Work
- Suggest improvements and potential future enhancements or directions for further research.
References
- Cite all the sources, documentation, and external codes referenced in your project following a standard citation style (APA, MLA, IEEE).
Appendices
- Include additional material such as code listings, detailed algorithms, and user manuals.
Example Section: Methodology
Design: The project implements a three-tier architecture consisting of a client, a server, and a database. The client interface was developed using React, while the server-side logic was implemented in Node.js with Express.
Development Tools:
- Frontend: React.js
- Backend: Node.js, Express
- Database: MongoDB
- IDE: Visual Studio Code
- Version Control: Git and GitHub
Implementation: The system employs a RESTful API for client-server communication. User authentication is managed using JWT tokens, and data is stored in a NoSQL database (MongoDB) which provides flexibility and scalability.
This format provides a comprehensive guide to creating a detailed and professional computer science project report. Adjust the sections as needed to better fit your specific project requirements. If you need further explanations or additional examples, feel free to ask!

Data Science Project Report
Data Science Project Report: Analysis of Weather Conditions on EV Battery Performance
Title Page
- Project Title: Analysis of Weather Conditions on EV Battery Performance
- Student’s Name: Emily Johnson and Raj Patel
- Supervisor’s Name: Dr. Alan Thompson
- Course Title: Data Science for Sustainable Energy
- Institution Name: City University of Science
- Date of Submission: December 15, 2024
Abstract
This project explores how different weather conditions affect the performance of electric vehicle batteries. Using data from over 1,000 EVs across North America, we applied machine learning models to predict battery degradation under varying temperatures and humidity levels. Key findings suggest that extreme cold significantly impacts battery efficiency and lifespan. This report outlines our methodology, data analysis, model performance, and conclusions about the implications of weather on EV battery technology.
Table of Contents
- Abstract …………………………….. i
- Introduction ……………………… 1
- Data Collection ………………….. 2
- Data Preparation ………………… 3
- Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) …… 4
- Methodology …………………….. 5
- Results …………………………….. 6
- Discussion ………………………… 7
- Conclusion ………………………… 8
- Future Work ……………………… 9
- References ………………………… 10
- Appendices ……………………….. 11
List of Figures and Tables
- Figure 1: Temperature Distribution among EVs ……….. 4
- Table 1: Summary Statistics of Battery Performance ….. 4
- Figure 2: Battery Degradation vs. Temperature ………. 6
Introduction
- Background Information: Interest in electric vehicles is growing; however, battery performance under different environmental conditions remains a concern.
- Problem Statement: There is limited understanding of how weather conditions, specifically temperature and humidity, affect EV battery life and performance.
- Objectives: To analyze existing data to predict how weather impacts EV battery efficiency and lifespan.
- Scope of the Project: This study focuses on temperature and humidity data from North America over the past five years.
Data Collection
- Data Sources: Battery performance data was sourced from a major EV manufacturer’s database, which included telemetry from vehicles.
- Data Description: The dataset includes daily weather conditions, battery charge levels, and mileage for 1,000 EVs from 2019 to 2024.
Data Preparation
- Data Cleaning: Removed entries with missing battery performance metrics.
- Feature Engineering: Created new variables for average daily temperature and humidity.
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
- Statistical Analysis: Computed mean, median, and standard deviation of battery efficiencies.
- Visualization: Produced scatter plots to observe the relationship between battery efficiency and temperature ranges.
Methodology
- Model Selection: Chose linear regression and random forest models for initial predictions.
- Model Building: Developed models using Python’s scikit-learn library.
- Validation Techniques: Employed k-fold cross-validation to validate model accuracy.
Results
- Model Performance: Random forest model had an R-squared of 0.82, indicating a strong fit.
- Interpretation of Results: Clear trend showing decreased battery performance in temperatures below -10°C.
Discussion
- Key Findings: Extreme cold has a detrimental effect on battery performance, reducing efficiency by up to 20%.
- Implications: These results could influence future EV battery designs and consumer information systems.
- Limitations and Assumptions: Analysis assumes uniform battery age and usage patterns, which may not hold universally.
Conclusion
Our analysis confirms that lower temperatures adversely affect EV battery performance. This insight is crucial for manufacturers and consumers, particularly in colder climates.
Future Work
Future studies could expand to global data and incorporate other factors like wind speed and solar exposure.
References
- Johnson, E., & Patel, R. (2024). Journal of Sustainable Energy.
- Thompson, A. (2024). Data Science Applications in Renewable Energy.
Appendices
- Appendix A: Code for Data Analysis and Models
- Appendix B: Extended Data Tables and Graphs
This detailed example provides a clear framework for reporting on a Data Science project, covering all essential aspects from data collection to conclusions and future directions. If you need help with specific parts or more examples, just let me know!

Browse More Templates On Science Project Reports
Science Project Synopsis PDF
Science Project PDF Free Download
Science Project Report Example
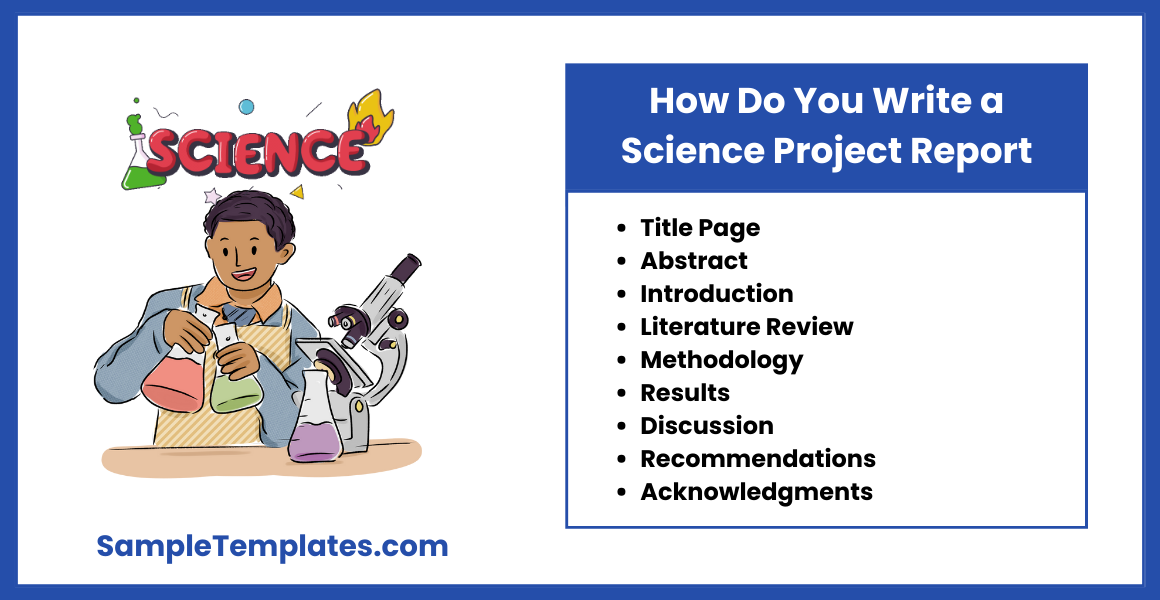
How Do You Write a Science Project Report?
Writing a science project report involves presenting your research, methodology, results, and conclusions in a clear and structured format. Here’s a guide on how to write a science project report:
1. Title Page:
- Include the title of your project, your name, school, and date.
2. Abstract:
- Provide a brief summary of your project, including the purpose, methods, results, and conclusions. Keep it concise but informative.
3. Introduction:
- Clearly state the purpose of your project and the research question or hypothesis you aim to address. Provide background information to contextualize your study. You can also see more on Science Research Report.
4. Literature Review:
- Discuss relevant scientific literature and studies related to your project. Explain how your project contributes to existing knowledge.
5. Methodology:
- Detail the methods and procedures you used to conduct your experiment or research. Include materials, experimental design, and the step-by-step process.
6. Results:
- Present your findings using tables, graphs, charts, or visuals. Clearly label and describe each element. Avoid interpretation at this stage. You can also see more on Research Project Reports.
7. Discussion:
- Interpret your results and discuss their significance. Compare your findings with existing literature. Address any unexpected outcomes and offer possible explanations. Summarize the key findings and the implications of your research. Restate your hypothesis and discuss whether it was supported by the results.
9. Recommendations:
- Suggest areas for further research or improvements to the experimental design. Highlight any limitations of your study.
10. Acknowledgments:
- Acknowledge individuals, organizations, or resources that contributed to your project. List all the sources you cited in your report, following a consistent citation style (e.g., APA, MLA). You can also see more on Scientific Research Report.
Acknowledgement Science Project Report Template
Science Project Report Sample
Doing experiments and projects are recurrent in a science class. One of the things that you need to do in doing both of these activities is to make a report. A project report is a document that contains the information of a project work you made. It contains the following details:
- The title page – the name of your project.
- The abstract – you can actually write this last. This contains the summary of your report—the questions you needed answers to, the methods, processes, and your results.
- The introduction – this will have a background of your sample study schedule, the questions that you needed answers to, and some hypothesis. You can also express the objective of your inquiry.
- Materials – these are the tools and equipment relevant in the experiment.
- Procedures – the methods and processes.
- Discussion of data and analysis – this is the part where you are going to convey the results or the things you find out in your experiment and project.
- Conclusion – this is the executive summary of your study. This may include statements whether your results support or are in conflict with your initial hypothesis.
- Bibliography – do not forget to cite your sources.
Do not forget that you have to sound objective and formal in writing your reports. And always remember that you have to be mindful of your processes; after all, you have to collect your data as systematic and factual as possible.
If you need more information regarding scientific reports, you may check our Sample Scientific Reports and Sample Lab Reports.
Science Project Writing Format
Science Project PDF Download
Tips For Science Project Report
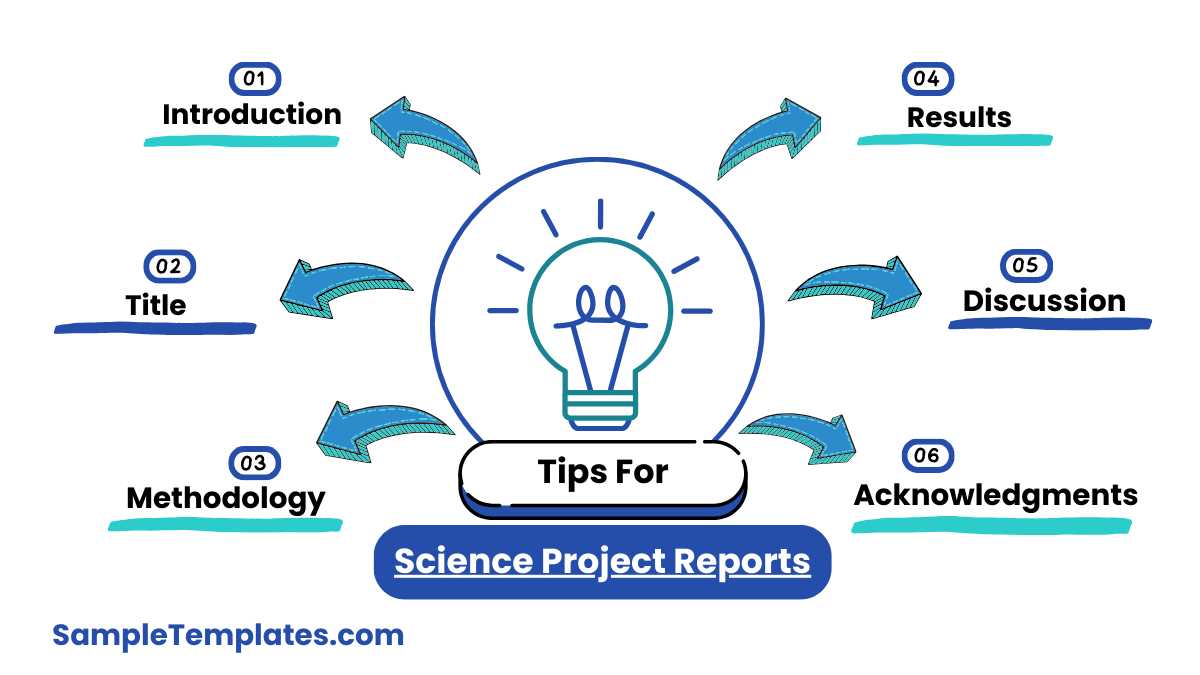
- Start with a Clear Title: Ensure your title is descriptive and reflects the main focus of your project. It should give readers an immediate understanding of what the project entails.
- Organize Your Report Logically: Structure your report with clear sections such as Introduction, Hypothesis, Materials and Methods, Results, Discussion, Conclusion, and References. This helps in maintaining clarity and flow. You can also see more on Manufacturing Project Reports.
- Write a Compelling Introduction: Provide background information on your topic, state the problem you are investigating, and explain why it is important. Clearly state your hypothesis.
- Detail Your Methodology: Describe the materials and methods used in your experiment. Be specific enough that someone else could replicate your study. Include any controls and variables.
- Present Your Results Clearly: Use tables, graphs, and charts to present your data. Make sure they are labeled correctly and referenced in the text. Summarize your findings without interpreting them. You can also see more on Project Completion Reports..
- Interpret Your Findings: In the Discussion section, explain what your results mean. Discuss whether they support your hypothesis, how they relate to other research, and any anomalies or unexpected results.
- Conclude Effectively: Summarize the main findings of your project, the implications of your results, and suggest possible future research or applications. Keep it concise and focused.
- Proofread and Edit: Review your report for clarity, coherence, and correctness. Check for grammatical errors, typos, and ensure all references are correctly cited. Consider having someone else read it to catch any mistakes you might have missed. You can also see more on Project Progress Reports.
Sample Science Project Progress Report Template
Science Project Report
Science Project Sample
Learning is the best part of education. In the case of writing reports, it’s where you can apply what you already learned, learn some more in the process, and share your knowledge to others. Reports are where you can express the knowledge you have acquired. Take sample note, though, that a report can actually be read by others, either your teachers or your classmates or those who are simply seeking to gain information, thus, it is important that you write clearly. But with our samples, I’m sure you will be successful at writing your report.
Science could hardly be science without the help of scientists who performed their own experiments and recorded their findings. The things you read and know now are products of experiments and project making. So have fun with your science project. By doing that, it shows that you might be a scientist in the making. If you have other reports for school, we have a lot more samples, such as Sample Book Reports. They are also for free.
What is a topic for a science project?
Choosing a science project topic depends on your interests, grade level, and the specific requirements of your assignment. Here are some general science project topic ideas across different scientific disciplines:
- Biology:
- Investigate the effects of different fertilizers on plant growth.
- Explore the impact of light intensity on photosynthesis in plants.
- Study the behavior of ants in response to different types of food. You can also see more on Project Proposal Reports.
- Chemistry:
- Test the acidity levels of various household substances.
- Examine the chemical reactions involved in baking soda and vinegar.
- Investigate the factors affecting the rate of a chemical reaction.
- Physics:
- Explore the relationship between the angle of a ramp and the speed of a rolling object.
- Investigate the factors affecting the oscillation of a pendulum.
- Study the effects of different surfaces on the bouncing height of a ball.
- Earth Science:
- Explore the impact of soil erosion on plant growth.
- Investigate the effects of different types of water on seed germination.
- Study the relationship between temperature and the rate of evaporation.
- Environmental Science:
- Examine the effects of pollution on water quality.
- Investigate the impact of different types of packaging materials on the environment.
- Study the effectiveness of natural alternatives to chemical pesticides. You can also see more on Scientific Review Report.
- Astronomy:
- Explore the phases of the moon and their impact on tides.
- Investigate the effects of light pollution on stargazing visibility.
- Study the relationship between solar activity and weather patterns.
- Psychology:
- Explore the impact of music on concentration levels.
- Investigate the effects of color on mood and productivity.
- Study the relationship between sleep duration and cognitive performance.
- Engineering:
- Design and build a simple machine to perform a specific task.
- Investigate the efficiency of different insulation materials.
- Explore the principles of aerodynamics by designing and testing paper airplanes. You can also see more on Short Research Report.
Remember to choose a topic that aligns with your interests and allows for a feasible and controlled experiment. Consult with your teacher or mentor for guidance and approval of your chosen science project topic.
What is a science fair report?
2. What makes a good Science Fair Report?
A good Science Fair Report is clear, concise, and follows a logical structure. It should effectively communicate the purpose, process, and findings of your experiment.
3. What should be included in the Abstract of a Science Project Report?
The Abstract should provide a brief overview of your project, including the problem addressed, methods used, key results, and conclusions. You can also see more on Chemistry Lab Reports.
4. How do I choose a topic for my Science Fair Project?
Choose a topic that interests you, poses a clear research question, and allows for a feasible experiment. Consider its relevance and potential contribution to existing knowledge.
5. What is the significance of the Literature Review in a Science Project Report?
The Literature Review provides context by reviewing existing scientific literature related to your project, supporting the rationale behind your experiment.
6. What citation style should I use in a Science Project Report?
Follow a specific citation style (e.g., APA, MLA) for references in your Science Project Report. Check guidelines or preferences provided by your teacher or institution.
7. Can I include an Acknowledgments section in my Science Project Report?
Yes, the Acknowledgments section allows you to acknowledge sample, organizations, or resources that contributed to your science project.
In conclusion, this Science Project Report encapsulates a meticulous exploration of [topic]. The systematic approach in designing, conducting experiments, and analyzing results revealed valuable insights. The findings contribute to our understanding of [topic] and underscore the importance of continued exploration in this scientific domain, paving the way for future research.
Related Posts
Business Report Samples & Templates
Survey Reports Samples & Templates
Sample Feasibility Reports
Psychological Assessment Report Samples [ Clinical, Child, Intake ]
Report Format Samples & Templates
Acknowledgement for Internship Report Samples [ Hotel, Hospital, Teaching ]
Field Trip Report Samples [ Agriculture, Educational, Environmental ]
Student Counseling Report Samples
Narrative Accomplishment Report Samples [ Science, Teacher, Reading ]
Sample Acknowledgment Report Templates
Internship Narrative Report Samples
Interview Summary Report Samples
Sample Medical Reports
Accomplishment Report Samples
Acknowledgement for Project Report Samples [ MBA, Engineering, Internship ]