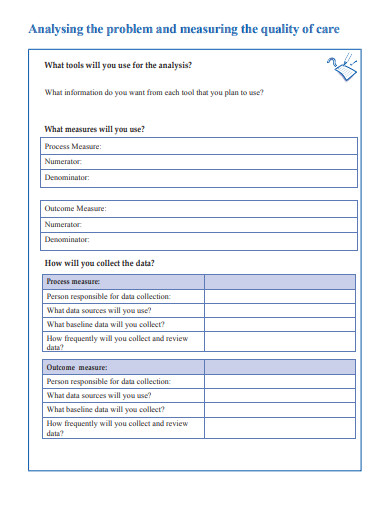
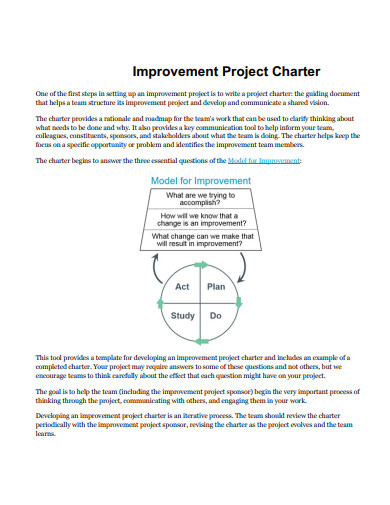
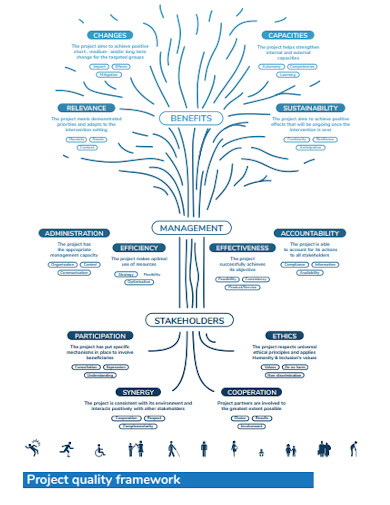
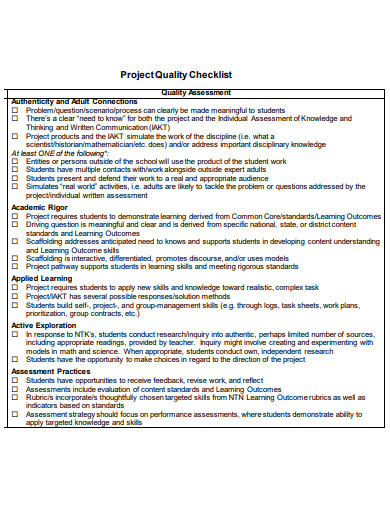
Perhaps the most distinguishing feature of any business or organization on the planet is its dedication to quality. To be successful, any type of business or business owner strives to maintain a consistently high level of quality. The quality of products, services, and resources are just a few examples of what might be considered. Ascertain that all of your output meets the expectations of your investors, stakeholders, and, most importantly, your customers. Additionally, the requirement for high-quality products and services comes with the responsibility of ensuring that those quality standards are met. To ensure that whatever they produce is marketable, the company makes a number of significant efforts. Numerous factors must be established to ensure that these stages are successfully completed and that their product is consistent with the highest possible quality. Effective control plans must be implemented to establish these parameters.
The importance of planning cannot be overstated when it comes to ensuring that the final product meets quality standards. It contributes to time and resource savings by reducing the likelihood of defective items being produced following their design and development. High-quality action plans are particularly effective in this regard. Not only does it paint a clear picture of the high standard of quality that the business or organization aspires to, but it also specifies actions and parameters that, if followed correctly, will ensure the highest possible quality in the end result. Consider the samples below to gain a better understanding of what goes into project quality. You can use them to familiarize yourself with the document and, if you’re feeling particularly creative, to create your own high-quality roadmap.
10+ Project Quality Samples
1. Project Quality
2. Quality Improvement Project Template
3. Quality Improvement Project Charter
4. Project Quality Management
5. Project Quality Framework
6. Project Quality Assurance Plan
7. Project Quality Checklist
8. Project Quality Policy
9. Project Quality Assurance Framework
10. Project Quality Assurance Plan Example
11. Project Quality Management Example
What Is Project Quality?
When it comes to launching a product onto the market, quality control is frequently the final step. Producers perform a variety of operations during this stage of the manufacturing process, such as quality checks and corrections, to ensure that the goods produced meet quality standards.
This stage is critical when it comes to shipping because it establishes whether the product is ready to be delivered to the customer. Inability to deliver high-quality items can tarnish a company’s reputation, reduce customer retention, and increase return requests.
Additionally, quality control involves inspecting the processes used to manufacture, store, and distribute a product. A “defective” product is one that does not meet specified specifications or has been tampered with in some way. As a result, businesses must develop effective systems to ensure the integrity of their products throughout the supply chain.
Internal and external quality control measures may be required of a business, depending on the industry and the products distributed by the business. Internal controls are frequently used by businesses that communicate via internal protocols. This could range from equipment maintenance to performance evaluations of employees, and everything in between. Upper management is responsible for ensuring that quality assurance procedures are carried out properly and on time.
External quality control, on the other hand, is required for products sold to third parties. When food is manufactured and distributed, for example, it must be inspected by third parties to determine its nutritional value and expiration date prior to being sold to market customers.
It is an acronym for Quality Control Plan, and it refers to a written collection of procedures and actions designed to ensure that goods meet the quality objectives specified in contract contracts, other procedures and manuals, and other guidance. In English, QCP stands for Quality Control Plan.
How to Write a Project Quality
- Create an organization chart
To implement each quality assurance method effectively, management must first create an organizational chart that includes job descriptions, business qualifications, and the training necessary to implement each method effectively. These standards must be documented in order to demonstrate that inspectors have received adequate training and are competent. This document should be kept on file and made available to senior management in the event of a problem or error. - Define responsibilities
Following that, management must define all internal employees’ roles and responsibilities, as well as those of external affiliates. Each partner should be aware of the processes for which they are accountable, as well as who will be responsible for quality assurance following the completion of their work. With the exception of a few small businesses, the majority of businesses require a separate group of individuals to perform quality control and verification procedures. Separate documentation is required to ensure that adequate time was allotted to each task, as multitasking may result in an increase in instances of human error. On the other hand, large corporations prefer that different members of the same department review their colleagues’ work in a centralized setting. These quality assurance specifications should be well defined to avoid confusion and to ensure that each step is performed exactly as specified. - Purchase and receive materials
Before ordering materials, management should thoroughly understand the specifications to ensure that the components ordered meet the desired quality standards. While pursuing the lowest vendor rates may save businesses money in the short term, it may result in them falling short of quality assurance criteria in the long run. As a result, prior to initiating the ordering process, it is critical to ascertain the material’s critical characteristics. After receiving the materials, staff should inspect the shipment to ensure that all products meet the specified standards. If the delivery falls short of the company’s expectations, the items must be returned to the supplier. - Verify Supplier’s Qualifications
While an inspection of basic materials is relatively straightforward, performing quality assurance on more complex components and equipment can be time-consuming and challenging. As a result, companies should clearly define their requirements and vendor expectations prior to submitting a bid request. For instance, businesses could request that a third party audit a vendor to ensure that their internal processes comply with applicable regulations. Then, prior to signing a contract, businesses should evaluate the reputation, brand, and qualifications of potential suppliers. - Evaluate Quality Feedback
Quality assurance’s objective is to ensure that products meet specified specifications prior to being distributed to customers. On the other hand, feedback is an invaluable tool for enhancing product performance and overall quality. Businesses can ascertain a product’s advantages and disadvantages by examining online reviews, user complaints, and customer suggestions. Organizations should establish a customer service team that compares evaluations to compliance records to ascertain whether noncompliance caused issues. If an employee discovers that a procedure is in violation of the law, they are required to report the violation. - Develop a process for corrective action
Finally, businesses must develop a corrective action plan to address quality issues such as regulatory violations and noncompliance. When a non-compliant process is reported, the quality control employee is responsible for investigating the circumstances surrounding the occurrence. It could be the result of a system failure or an employee’s negligence. After determining the root cause, the company must take preventative measures to ensure that the event does not recur. This package could include additional quality checks or automated tools, such as inventory ordering systems. Businesses can use quality control plans to ensure that all products meet expected standards and that appropriate corrective actions are taken in the event of a product recall or other consumer complaint. This demonstrates to customers that a business values their feedback and is committed to providing the highest quality products available.
FAQs
What are the four types of quality control?
Process Control. Control Charts. Product Quality Control. Process Control.
What are the three types of quality?
Professionals frequently classify flaws in a product’s quality as minor, major, or critical. Minor flaws are those that constitute less than 1% of the total. A defect’s nature and severity are used to determine the category to which it should be assigned.
What are action steps?
Action steps are specific actions taken to achieve the objectives outlined in your action plan. In essence, it is all about the content of your action plan.
A well-written action plan ensures that the objectives of your business or corporation, as well as your own personal objectives, are met and exceeded. In other words, it transforms your fantasy into a reality. It can help you stay on track with your project and avoid potential roadblocks. Creating a high-quality action plan follows a similar pattern. It enables you to maintain a certain level of product and service quality while also allowing for continuous improvement.
Related Posts
FREE 10+ Project Kickoff Samples in PDF | MS Word
Printing Company Profile
Travel Company Profile
Exemption Letter
News Report
Employee Uniform Form
Self-Declaration Form
To Whom It May Concern Letter
10 FREE Notice To Quit Letter Samples & Templates
Security Company Profile
Written Warning
Event Program
OMR Sheet
Building Inspection Report
Employment Certificate