In the ever-evolving landscape of scientific and academic pursuits, a robust ‘Research Application’ is the cornerstone of groundbreaking discoveries and innovations. This document delineates the essential parameters, sample objectives, and methodologies that drive a research initiative forward. Crafted with precision and adhering to the highest standards, our Research Application template integrates key elements ensuring thoroughness and clarity. Whether embarking on a new journey of inquiry or seeking funding and approvals, this tool is designed to set your research endeavor on a trajectory of excellence.
16+ Research Application Samples
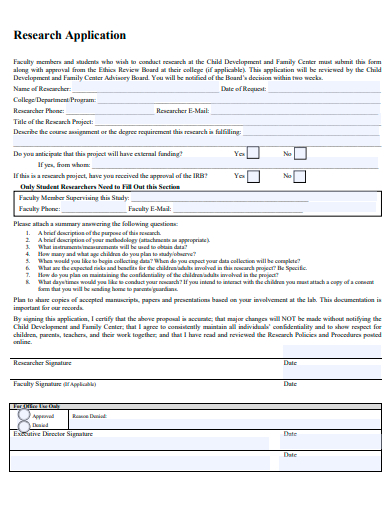
1. Sample Research Application Template
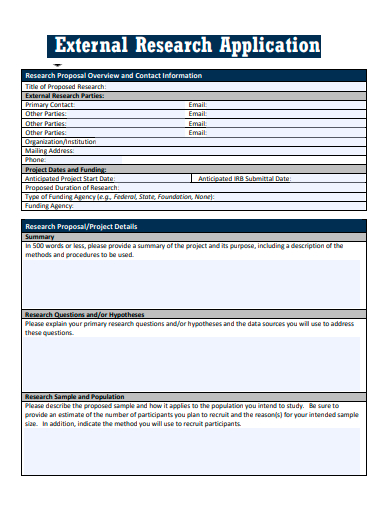
2. Sample External Research Application Template
3. Sample Medical Student Research Application
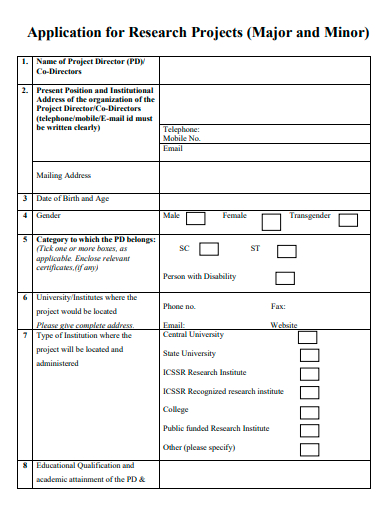
4. Sample Research Projects Application Template
5. Sample Independent Study Research Application
What is a Research Application?
A research application is a formal document used to seek approval or funding for a research project. It articulates the researcher’s objectives, methodology, sample timeline, and other essential details to convince reviewers or funders of the project’s feasibility and significance. Here’s a detailed guide on the components and importance of a research application.
Understanding the Importance of a Research Application
- A Gateway to Funding: Many academic and industry research projects are funded by external organizations. A compelling research application can secure the necessary funds to carry out a project.
- Ensures Research Feasibility: Drafting an application compels researchers to think critically about their methodology, ensuring the research’s viability.
- Acts as a Blueprint: Once approved, the research application serves as a guiding document throughout the research process.
Key Components of a Research Application
- Title and Abstract: A concise representation of the research’s main idea and sample objectives. The abstract should be clear and to the point, providing an overview of what the study aims to achieve.
- Introduction/Background: This section provides context. It sample outlines existing research in the field, identifies gaps or challenges, and explains the significance of the proposed study.
- Objectives: Clearly defined goals and what the research aims to achieve.
- Methodology: A detailed description of how the research will be conducted. This includes the sample research design, participants, tools, and techniques to be used.
- Timeline: A schedule indicating the various phases of the research and their expected completion dates.
- Budget: An itemized list of anticipated expenses. This can include equipment costs, participant incentives, travel expenses, and more.
- Expected Outcomes: This section outlines the anticipated results and their significance.
- References: A list of sources cited in the application.
Drafting a Compelling Research Application
- Understanding the Audience: Tailor the application to the interests and concerns of the reviewers or funders. Know their priorities and address them.
- Clarity is Key: Avoid jargon and ensure the document is readable for non-experts in the field.
- Justify the Budget: Ensure every item in the sample budget is accounted for and justified in terms of the research’s needs.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Vagueness: Being unclear about objectives or methodology can lead to rejection.
- Overambition: While it’s good to aim high, an overly ambitious project can seem unrealistic to funders.
- Neglecting the ‘So What?’: Always highlight the significance and potential impact of the research.
Finalizing and Submitting the Application
- Proofread: Ensure there are no grammatical or factual errors.
- Seek Feedback: Before submitting, have peers or mentors review the application to provide constructive sample feedback.
- Follow Submission Guidelines: Different institutions or funding bodies might have specific submission guidelines. Adhere to them closely to increase the chances of approval.
How to Fill a Research Application?
Filling out a research application requires a systematic approach. It’s not just about providing answers but ensuring that each section is answered with clarity, precision, and coherence. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate through the process:
1. Familiarize Yourself with the Application Form
Before you begin, review the entire application. Understand each section, its requirements, and any guidelines provided. This will give you a clear picture of what’s expected and help you gather the necessary information.
2. Gather All Necessary Information and Documents
Compile the data, references, previous research papers, and any other documentation you might need. This makes the process smoother, as you won’t have to stop and search for information while filling out the sample form.
3. Start with Basic Details
Begin with straightforward sections:
- Personal and Institutional Details: Your name, affiliation, contact information, etc.
- Project Title: Make sure it’s clear and indicative of your research topic.
4. Draft the Abstract or Summary
Though it’s a sample brief section, the abstract is crucial. It provides a snapshot of your entire sample proposal. Ensure it’s concise, clear, and compelling, highlighting the main objectives and significance of the research.
5. Elaborate on the Research Background
Here, delve into the existing literature and current state of knowledge in your research area:
- Highlight the gaps or challenges that exist.
- Detail why there’s a need for your proposed study.
6. Clearly Define Objectives
List down the primary and secondary goals of your research. Ensure they are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
7. Detail the Methodology
This section is crucial:
- Design: Describe the research design, be it experimental, observational, qualitative, or quantitative.
- Participants/Subjects: Detail who will be involved and any selection criteria.
- Tools and Techniques: Outline the methods, apparatus, or software you’ll be using.
8. Provide a Detailed Timeline
Break down the research process into phases or milestones, specifying the expected completion date for each.
9. Outline the Budget
Itemize your expected expenses:
- Equipment and materials.
- Compensation for participants, if any.
- Travel or fieldwork costs.
- Miscellaneous expenses like printing or software purchase.
Remember to justify each budget item and ensure it aligns with the proposed research activities.
10. Mention Expected Outcomes
State clearly what you expect to find or achieve through this research. This will showcase the potential impact and significance of your study.
11. Attach References
Cite all sources and prior research you’ve referred to while filling out the sample application. This not only gives credit but also strengthens your proposal’s credibility.
12. Review and Proofread
Before submission:
- Ensure there’s consistency in your answers.
- Check for any grammatical or typographical errors.
- Ensure you’ve adhered to any word or page limits set by the application form.
13. Seek Feedback
Have a peer, mentor, or supervisor review your application. They might provide valuable insights or catch errors you missed.
14. Submit According to Guidelines
Check the submission method, whether it’s online, through email, or physical copies. Ensure you’re meeting all requirements, such as format, additional documents, or any cover letters.
6. Sample Psychology Research Application Template
7. Sample Research Application Template
8. Sample Directed Research Application Template
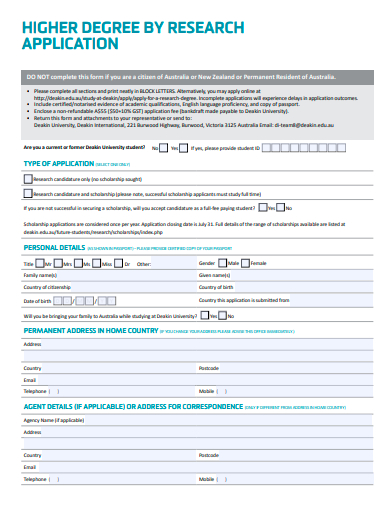
9. Sample Higher Degree Research Application Template
10. Sample Interim Support For Research Application
11. Sample Summer Research Application Template
12. Sample Postgraduate Research Application Template
13. Sample Drug Research Application Template
14. Sample Research Grant Application Template
15. Sample Visiting Research Student Application Template
16. Sample Basic Research Application Template
17. Sample Board Research Application Template
The Legal Importance of a Research Application
Research applications are not just bureaucratic necessities or gateways to funding; they also possess significant legal ramifications. When researchers draft and submit these documents, they are essentially entering into an understanding where they commit to conduct research as outlined. The legal importance of a research application can be better appreciated by examining its various facets:
1. Intellectual Property Rights
- Establishment of Original Ideas: A research application can serve as a record, indicating when a researcher proposed a specific idea or innovation. This can be crucial if there are disputes about the originality or timing of a concept, especially in fields where intellectual property is paramount, such as patent research.
- Protection of Proprietary Methods: If a research methodology is unique, detailing it in an application can provide documentation that might help in future IP claims.
2. Ethical Considerations
- Informed Consent: Many research projects, especially those involving human participants, require informed consent. The details in the research application help review boards ensure that researchers are obtaining consent ethically and legally.
- Protection of Vulnerable Groups: Special considerations are given to research involving vulnerable populations (e.g., children, prisoners, or individuals with cognitive impairments). The application ensures that the researcher is aware of and compliant with these considerations.
3. Accountability and Transparency
- Use of Funds: When researchers receive funding based on their application, they’re legally obligated to use these funds as described. Misappropriation or misuse of funds can lead to legal consequences.
- Adherence to Proposed Methodology: Drastically deviating from the proposed methodology without approval can be grounds for accusations of academic dishonesty or fraud.
4. Data Privacy and Protection
- Handling Personal Data: Research often involves collecting and analyzing personal data. Mismanagement or misuse of this data can have legal repercussions. The research application usually outlines how data will be collected, stored, and protected, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
5. Research with Commercial Implications
- Contracts and Agreements: If the research has commercial partners or implications, the research application might be integrated into contractual agreements. Not delivering on promises or violating terms can have legal consequences.
6. Compliance with Institutional and National Regulations
- Adherence to Guidelines: Most institutions and countries have specific guidelines on conducting research, especially in fields like medicine, environmental science, or animal testing. The research application ensures that researchers are aware of and sample plan to adhere to these regulations, thus avoiding legal pitfalls.
7. Liability and Risk Management
- Disclosure of Potential Risks: Especially in experimental research, there might be risks involved. Detailing these in the application ensures that all stakeholders are aware, and can mitigate potential legal liabilities in case of accidents or unforeseen outcomes.
How do you Create a Research Application?
Creating a research application is crucial for universities, research institutions, and other organizations looking to fund or support research initiatives. A well-designed research application ensures that potential research projects are evaluated on merit, feasibility, and alignment with institutional sample goals. Here’s a step-by-step guide to creating a research application in five comprehensive steps:
Step 1: Introduction and Personal Details
Begin with a section for applicants to provide their personal and institutional affiliations. This includes names, contact information, academic or professional titles, and affiliations. This helps identify the main researchers and ensures there’s a point of contact. Additionally, provide a brief introduction explaining the purpose of the research application, who can apply, and what the evaluation criteria will be.
Step 2: Research Overview and Objectives
Applicants should present a concise sample summary of their proposed research. This abstract should communicate the core idea, importance, and potential impact of the research. Following the summary, ask for detailed research objectives, framed as clear questions or sample statements the research aims to address. Objectives provide a roadmap for the entire research project and help evaluators gauge the project’s scope and potential significance.
Step 3: Methodology and Procedures
This section should allow applicants to describe their research methodology in detail. What methods will they use to achieve their objectives? This could include experimental procedures, data collection methods, and analytical tools. Evaluators look to this section to assess the feasibility and scientific rigor of the proposed research. It’s crucial for researchers to demonstrate a clear link between their objectives and the methods they plan to use, ensuring that the research is grounded in established scientific practices.
Step 4: Budget and Resources
Every research project requires funding and resources. In this section, applicants should itemize expected costs, including equipment, travel, salaries or stipends, software, and other expenditures. They should also detail any resources they already have and those they will need. If collaborations with other institutions or researchers are part of the plan, these should be mentioned here. A well-justified budget demonstrates that the researcher has a realistic grasp of the project’s financial needs and constraints.
Step 5: Expected Outcomes, Deliverables, and Timeline
Conclude the application by asking applicants to outline the expected outcomes of the research. What are the tangible and intangible deliverables? This could range from academic sample papers and conference presentations to software, innovations, or sample policy recommendations. Alongside, a clear timeline should be provided, highlighting major milestones in the research process. This gives evaluators an idea of the project’s duration and the pace at which results or deliverables can be expected. It also shows that the researcher has a structured plan for completing the project within a realistic timeframe.
When disseminating the application, always ensure clear guidelines are provided. The easier it is for applicants to understand what’s expected, the higher the quality of applications you’ll receive. And remember, after receiving applications, a rigorous and transparent evaluation process is key to selecting the most promising research projects.
In Conclusion, a research application is more than just a formality; it’s a testament to the researcher’s dedication, clarity of thought, and thoroughness in planning. By understanding its components and importance, researchers can enhance the chances of their work being recognized and funded. Investing time and effort into drafting a compelling research application can pave the way for groundbreaking research.
Related Posts
FREE 29+ Student Application Form Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 21+ Administrative Application Samples in MS Word | Apple Pages | PDF
FREE 21+ Teacher Application Samples in MS Word | Apple Pages | Outlook | PDF
FREE 25+ Transfer Application Samples in MS Word | Apple Pages | PDF
FREE 23+ Participation Application Samples in MS Word | PDF
FREE 14+ Patient Application Samples in MS Word | PDF
FREE 21+ Eligibility Application Samples in PDF
FREE 20+ Travel Application Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 25+ Sponsor Application Sampales in MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages | PDF
FREE 23+ Candidate Application Samples in PDF
FREE 33+ Committee Application Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 37+ Supplemental Application Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 37+ Product Application Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 33+ Visiting Application Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 34+ Refund Application Samples in PDF | MS Word