In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, the ‘Patient Application’ emerges as a vital instrument. Serving as an initial touchpoint for medical services, it gathers crucial health and personal data to ensure tailored care. Whether for clinical consultations, specialized treatments, or plan of wellness programs, a comprehensive Patient Application sets the stage for informed medical decisions. Dive into our guide to understand its design, importance, and the integral role it plays in fostering optimal patient outcomes.
14+ Patient Application Samples
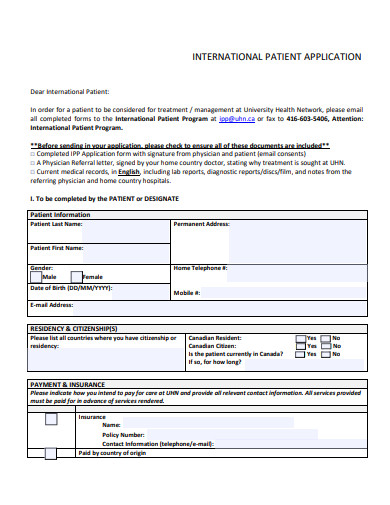
1. Sample International Patient Application Template
2. Sample Patient Registration Application Template
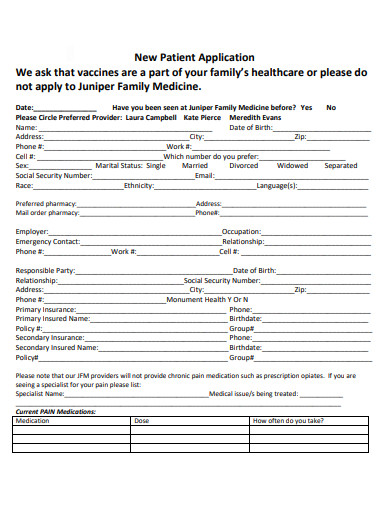
3. Sample New Patient Application Template
4. Sample Patient Assistance Program Application Template
5. Sample Basic Patient Application Template
6. Sample Medical Patient Application Template
What is a Patient Application?
A Patient Application, refers to a sample form or paperwork that individuals fill out when seeking medical services from a healthcare provider or institution. This application typically captures essential personal information, medical history, current health complaints, insurance details, emergency contacts, and any existing medications or allergies. The primary purpose of a Patient Application is to provide healthcare professionals with a comprehensive overview of the patient, ensuring informed and safe medical decisions. It also streamlines administrative processes, enabling effective communication between patients and healthcare providers, and ensuring appropriate billing and insurance procedures.
The Essence of a Patient Application
At its core, a Patient Application is a digital platform designed to cater to a patient’s healthcare needs. It offers a convenient space for patients to access, manage, and understand their health information.
Key Features of Patient Applications
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): Digital versions of a patient’s traditional paper sample charts, allowing for quick access to medical histories, diagnoses, medications, and more.
- Telehealth: Virtual consultation with healthcare providers, reducing the need for physical visits.
- Medication Management: Alerts and reminders to ensure timely medication intake.
- Test Results: Direct access to laboratory and diagnostic test results without waiting for a doctor’s call.
- Billing and Insurance: Manage payments, view insurance coverages, and even chat with financial counselors.
- Health Trackers: Monitor various health metrics, from heart rate and blood pressure to sleep patterns and nutrition.
Purpose of the Patient Application
In the healthcare ecosystem, the Patient Application plays an integral role. Serving as the foundational document for patient interaction with healthcare providers, its importance cannot be overstated. This piece elucidates the multifaceted purposes of the Patient Application. You can also see more templates like Sample Patient Registration Forms.
Data Collection
At its core, the Patient Application serves as a primary tool for collecting essential patient information. This includes:
- Personal Details: Such as name, age, gender, contact information, and address.
- Medical History: Chronic illnesses, past surgeries, known allergies, medications, and family medical history.
- Insurance Information: Details regarding the patient’s health insurance provider, coverage, and sample policy specifics.
Facilitating Accurate Diagnoses and Treatment
A detailed Patient Application aids healthcare providers by:
- Offering a snapshot of the patient’s health background.
- Highlighting potential health risks or hereditary conditions.
- Ensuring the safe prescription of medications by cross-checking with existing medications and known allergies.
Streamlining Administrative Processes
In the administrative sphere of healthcare:
- The application format assists in billing by providing necessary insurance and personal details.
- It helps in coordinating care by offering insights into the patient’s medical history, specialists involved, and past treatments.
- The document ensures smooth transitions between departments or healthcare facilities by providing a consistent data source.
Legal and Consent Purposes
- It serves as a record of the patient’s sample acknowledgment of certain facility practices, such as privacy policies.
- The application may include consent forms for specific treatments, interventions, or data sharing practices, providing legal protection to both the patient and the healthcare provider.
Enhancing Patient-Provider Communication
- By centralizing critical patient data, the application fosters efficient communication between the patient and healthcare provider, ensuring all discussions are rooted in the most recent and relevant information.
- It aids in tailoring health education and counseling based on the individual’s health background.
Emergency Situations
In emergencies:
- The Patient Application serves as a rapid source of critical information, especially when the patient is unresponsive. Details about known allergies, chronic conditions, or current medications can be lifesaving.
- Emergency contact details can be swiftly accessed to notify loved ones or make critical decisions.
Benefits of Using a Patient Application
Adopting patient applications can offer a range of advantages:
- Empowerment and Autonomy: Patients gain better control over their health and medical decisions.
- Improved Health Outcomes: Access to real-time data can lead to better-informed decisions and prompt interventions.
- Convenience: Centralizing health information can save time and reduce administrative hurdles.
The Future of Patient Applications
As technology continues to evolve, so will the capabilities of patient applications:
- Integration with Wearable Tech: Continuous health monitoring through devices like smartwatches.
- AI-Powered Insights: Predictive analytics to offer personalized health advice.
- Virtual Reality & Augmented Reality: Potential tools for therapy, training, and patient education.
Understanding Interoperability in Patient Applications
Interoperability refers to the ability of different systems, devices, and applications to connect, exchange, and interpret data seamlessly. In the realm of patient applications:
- Data Sharing Across Platforms: Patients can access their records even if they switch healthcare providers or use multiple clinics.
- Unified Health Record: A comprehensive view of the patient’s medical history from various sources, ensuring every health care provider has the same holistic view.
Security Protocols in Patient Applications
Protecting sensitive medical data is paramount:
- End-to-End Encryption: Ensuring that data is unreadable if intercepted during transmission.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Extra layers of security to ensure that only the rightful user accesses the data.
- Regular Audits and Updates: Continuously checking for vulnerabilities and updating the system to ward off potential threats.
Enhancing Patient Autonomy and Engagement
Patient Applications empower individuals by:
- Educating: Offering information on conditions, treatments, and preventive measures.
- Encouraging Active Participation: Patients become partners in their care, making informed decisions based on real-time data.
- Fostering Communication: Easier and more efficient channels to connect with healthcare providers. You can also see more templates like Sample Medical Consultation Forms.
Why is Patient Application Necessary?
In the age of digitization, where almost every aspect of our lives is intertwined with technology, healthcare is undergoing its transformation. At the forefront of this change is the Patient Application, which has become indispensable for modern healthcare. But what makes it so essential?
Immediate Access to Health Records
Gone are the days when patients had to carry bundles of medical documents for every doctor’s visit or hospitalization. Patient applications store electronic health records (EHR) that can be accessed anytime, anywhere, ensuring that crucial medical data is available when needed.
Empowerment of Patients
Knowledge is power. With comprehensive access to their health information, patients no longer remain passive recipients of care. They can actively understand their health status, recognize patterns, and make informed decisions.
Seamless Communication with Healthcare Providers
Whether it’s clarifying doubts about a medication or discussing symptoms, patient applications offer direct channels to communicate with doctors, nurses, or other healthcare professionals. This not only reduces potential misunderstandings but also fosters a stronger patient-provider relationship.
Efficient Management of Appointments
Scheduling, rescheduling, or canceling appointments can be done with a few taps. Automated reminders ensure that patients remember their upcoming visits, reducing the number of missed appointments.
Remote Monitoring and Telehealth
For those with chronic conditions or those living in remote areas, frequent trips to the hospital or clinic may not be feasible. Patient applications can integrate with wearable devices to monitor vital stats, while telehealth features allow consultations without physical visits.
Medication Adherence
Forgetting to take medicine or confusion about dosages can impact treatment efficacy. Patient applications send reminders, ensuring that patients adhere to their medication regimen.
Educational Resources
Patient applications often provide valuable resources, including writing articles, videos, and interactive tutorials about diseases, treatments, and health practices. This educates patients, making them more proactive about their health.
Cost-Efficiency
By reducing administrative burdens, unnecessary tests, and missed appointments, patient applications can lead to significant cost savings for both healthcare providers and patients.
Enhanced Data Security
Contrary to sample paper records that can be easily misplaced, stolen, or damaged, digital records in patient applications have robust encryption and security measures. This ensures that sensitive health data remains confidential.
Interoperability and Comprehensive Care
Patient applications can integrate data from various sources, from primary care physicians to specialists, ensuring all healthcare providers have a unified and comprehensive view of a patient’s health.
Key Sections of the Patient Application
1. Personal Information:
This section captures the patient’s name, address, contact details, date of birth, and other identifying data.
2. Emergency Contacts:
Details of individuals to contact in emergencies, including their relationship to the patient and contact numbers.
3. Insurance Details:
Information about the patient’s health insurance provider, policy numbers, coverage details, and any secondary insurance if applicable.
4. Medical Background:
Comprehensive data collection including:
- Past medical history (chronic diseases, surgeries, hospitalizations)
- Family medical history (genetic predispositions or common ailments)
- Current medications and dosages
- Allergies, if any
5. Preferred Pharmacy:
Information about the patient’s preferred pharmacy for ease of sample prescription processing.
6. Consent Forms:
Acknowledgments and consents related to treatment, data usage, privacy policies, and any other pertinent permissions.
7. Billing and Financial Responsibility:
Declaration of the individual responsible for any financial obligations, including uninsured portions.
Advantages of a Patient Application
- Data Consistency: Ensures uniform data collection across all patients.
- Easy Integration: Seamless integration into Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems, reducing redundant data entry.
- Security: Enhanced data protection measures compared to paper-based records.
- Accessibility: Enables easy retrieval and updates of patient data.
Challenges and Considerations
- Data Privacy: Digital formats must comply with regulations such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) to ensure data security.
- Usability: The design should be user-friendly, ensuring patients of all ages and tech proficiencies can complete it without hurdles.
- Updates: Continuous updates may be needed to keep the professional form relevant with changing medical and regulatory landscapes.
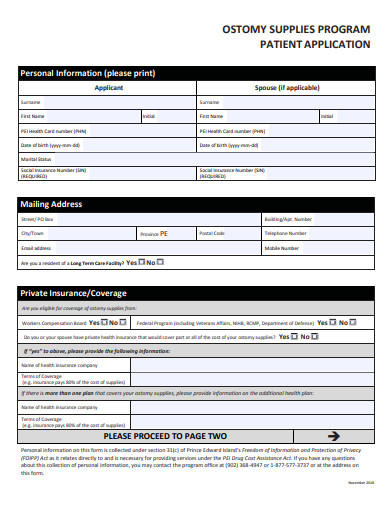
7. Sample Supplies Program Patient Application Template
8. Sample Prospective Patient Application Template
9. Sample Patient Application Template
10. Sample Patient Support Program Application Template
11. Sample Patient Access Application Form Template
12. Classified Patient Information Application Template
13. Sample Standardized Patient Application Template
14. Sample Medical Registry Patient Application Template
15. Sample Patient Online Access Application Template
How do you Create a Patient Application?
Certainly! Creating a patient application is crucial for gathering necessary details and ensuring streamlined medical care. Here’s a step-by-step guide to creating one:
Step 1: Define the Purpose
Determine the primary use of the application: new patient registration form, medical history collection, or treatment consent. The purpose dictates the data you’ll gather and the form’s overall structure.
Step 2: Personal and Contact Information
Begin with fields for the patient’s full name, date of birth, gender, address, email, and phone number. This information ensures proper identification and effective communication for appointments or follow-ups.
Step 3: Medical History
Incorporate sections for past illnesses, surgeries, allergies, and medications. Also, ask about family medical history, as it can provide insights into potential hereditary conditions. Ensure fields are structured for clarity and ease of data entry.
Step 4: Insurance and Payment Details
Gather information on the patient’s insurance provider, policy number, and primary cardholder details. If applicable, include payment preferences and billing information to facilitate financial processes.
Step 5: Current Health Status and Chief Complaint
Provide space for patients to describe their current health concerns or reasons for visiting. This aids medical professionals in diagnosing and directing patients appropriately.
Step 6: Consent and Privacy Acknowledgment
Include a section for patients to give consent for treatments and acknowledge they understand privacy practices. A signature field is essential here to validate the patient’s agreement and understanding.
Step 7: Emergency Contact Information
Request details of a person to contact in emergencies, including their name, relationship to the patient, and contact number. This ensures that medical staff can quickly connect with someone familiar to the patient if necessary.
Step 8: Design and Layout
Ensure the form is well-organized, with clear headings, logical flow, and adequate space for answers. Use checkboxes or drop-down sample lists where applicable for ease of completion.
Step 9: Review Legal and Ethical Considerations
Ensure the form meets healthcare laws and regulations in your jurisdiction, especially concerning patient privacy and data storage. Consider consulting with a legal professional experienced in healthcare laws.
Step 10: Implement Feedback and Testing
Before finalizing, test the form with a small group. Gather sample feedback from both patients and staff to identify areas for improvement. Adjustments based on real-world testing ensure the form is user-friendly and efficient.
Once the form is completed and reviewed, it can be implemented in your medical practice, either as a physical form or a digital application.
In Conclusion, patient applications are undeniably shaping the future of healthcare. They present a harmonious blend of technology and healthcare, aimed at providing optimum patient care. By understanding their capabilities and potential, both patients and providers can harness these tools for a healthier tomorrow.
Related Posts
FREE 20+ University Application Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | PDF
FREE 29+ Student Application Form Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 21+ Administrative Application Samples in MS Word | Apple Pages | PDF
FREE 21+ Teacher Application Samples in MS Word | Apple Pages | Outlook | PDF
FREE 25+ Transfer Application Samples in MS Word | Apple Pages | PDF
FREE 23+ Participation Application Samples in MS Word | PDF
FREE 21+ Eligibility Application Samples in PDF
FREE 20+ Travel Application Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 25+ Sponsor Application Sampales in MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages | PDF
FREE 23+ Candidate Application Samples in PDF
FREE 33+ Committee Application Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 37+ Supplemental Application Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 37+ Product Application Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 33+ Visiting Application Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 34+ Refund Application Samples in PDF | MS Word