In the meticulous world of financial sample tracking and accountability, the ‘Missing Receipt Form’ emerges as a safeguard. Designed to document and explain the absence of a physical sample receipt, it maintains financial transparency and ensures accurate record-keeping. From business expenses to personal purchases, a comprehensive Missing Receipt Form provides a backup solution. Explore our guide to understand its structure, significance, and the essential role it plays in financial integrity and compliance.
16+ Missing Receipt Form Samples
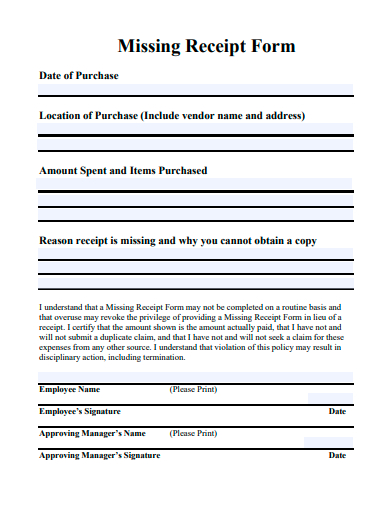
1. Sample Missing Receipt Form Template
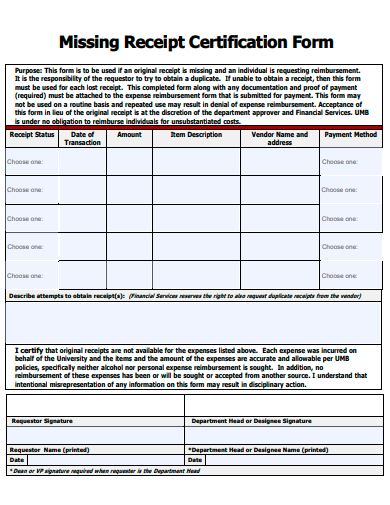
2. Sample Missing Receipt Certification Form Template
3. Sample Missing Original Receipt Form Template
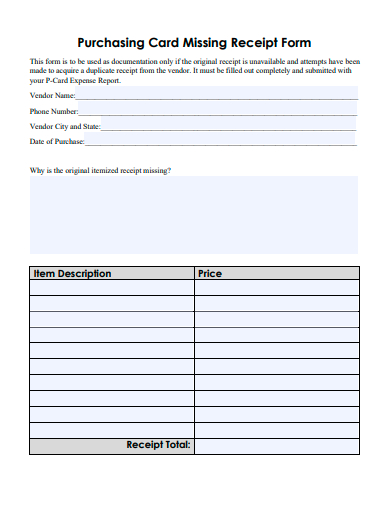
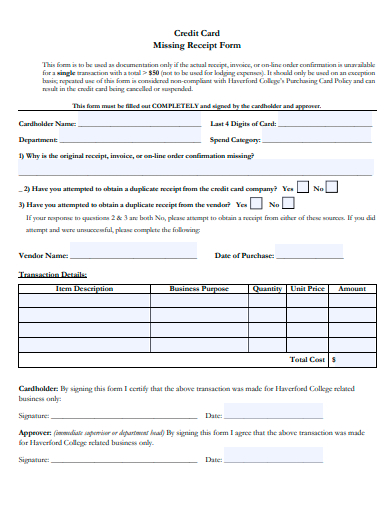
4. Sample Purchasing Card Missing Receipt Form Template
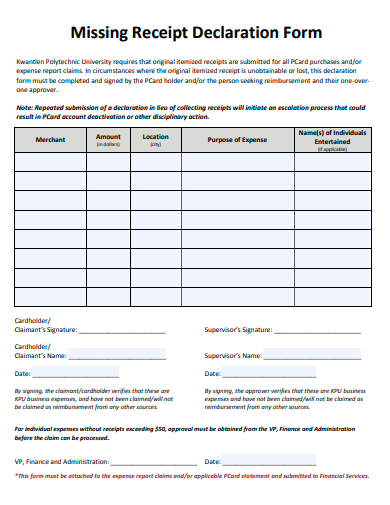
5. Sample Missing Receipt Declaration Form Template
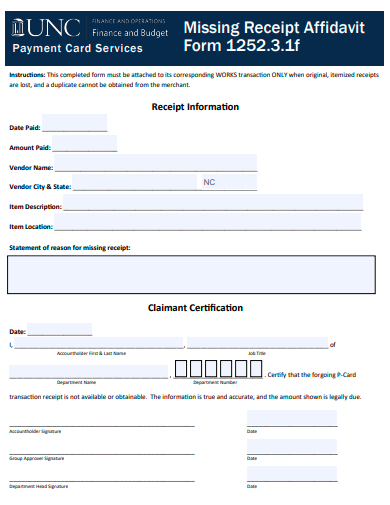
6. Sample Missing Receipt Affidavit Form Template
What is Missing Receipt Form?
Missing Receipt Form: A Comprehensive Guide
When managing finances or keeping track of expenses, documentation is crucial. In the world of business and personal expense management, the general receipt plays an integral role. However, there are instances when receipts are misplaced, lost, or simply not issued. In such cases, a “Missing Receipt Form” comes into play. This guide provides an in-depth look at what a Missing Receipt Form is, its significance, components, and when and how to use it.
Understanding the Need for a Missing Receipt Form
The primary purpose of a receipt is to serve as a tangible record of a transaction. It provides a detailed breakdown of services rendered or products purchased, along with the date, amount, and other pertinent details. But what happens when this crucial piece of evidence goes missing?
Purpose and Significance
Whether it’s for reimbursement purposes in a company or tax deductions, a missing receipt can pose challenges. Without it, one might find it hard to validate an expense. This is where the Missing Receipt Form comes into play. It acts as an alternative process documentation to vouch for the expenses incurred.
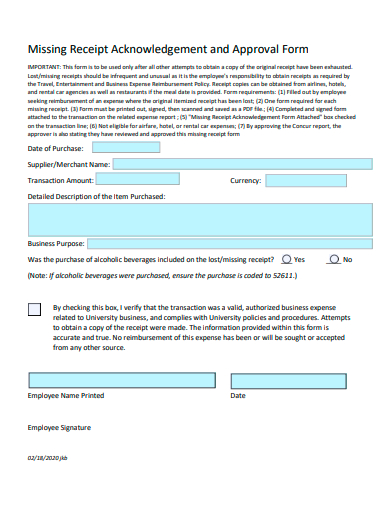
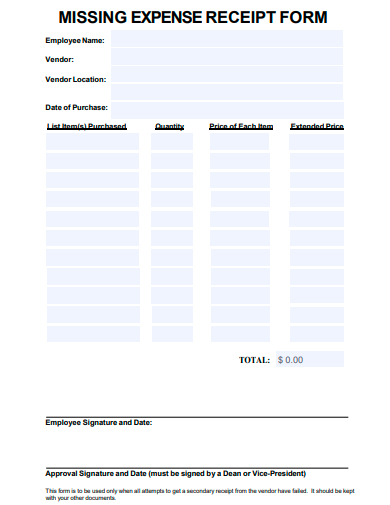
Typical Components of a Missing Receipt Form
- Personal Details: Information about the person claiming the expense – this can include name, designation, employee ID, department, etc.
- Transaction Details: Key data about the transaction such as date, vendor, item/service description, amount, location, etc.
- Reason for Missing Receipt: A section where the individual explains why the original receipt is missing – whether it was lost, never received, damaged, etc.
- Certification or Declaration: A sample statement where the individual certifies that the information provided is accurate and that the original receipt hasn’t been submitted elsewhere for claims.
- Approval Signature: A section for authorities (like managers or finance department personnel) to sign off, acknowledging or approving the claim without the original receipt.
When and How to Use a Missing Receipt Form
- Instances that Call for the Form:
Whether an employee is attending a business conference or a freelancer is accounting for tools purchased, there are various scenarios when this sample form is needed. It’s crucial when the original receipt is missing and a record or reimbursement is necessary. - Procedure:
Once the form is filled, it’s typically submitted to the concerned department, like finance or HR. Some organizations may require additional verification or supporting documents to validate the claim.
Potential Pitfalls and Best Practices
- Avoiding Fraudulent Claims:
Relying solely on a Missing Receipt Form can open doors for fraudulent claims. Implementing a cap on the number or total amount of expenses that can be claimed without a receipt can act as a deterrent. - Digital Backup:
In today’s digital age, taking a quick snapshot of receipts can serve as a backup. Encouraging this practice can reduce the need for missing receipt forms. - Regular Audits:
Conducting periodic checks or audits ensures compliance and helps in identifying and rectifying any discrepancies in the claims.
The Historical Context
While digital transactions and online records have become prevalent in recent times, there was an era where sample paper receipts were the only proof of a transaction. The genesis of the Missing Receipt Form can be traced back to these times.
Evolution with Time:
As businesses grew and operations became more complex, the need for streamlining financial records became evident. The Missing Receipt Form, thus, emerged as a strategic solution to address the gaps created by lost or misplaced paper receipts.
Legal Implications:
Losing a receipt may seem like a minor oversight, but it can have legal ramifications, especially for businesses.
- Tax Audit Concerns:
For companies and self-employed individuals, expenses often translate into tax deductions. In the sample event of a tax audit, the absence of a receipt can pose challenges. A Missing Receipt Form, while not a direct substitute, can provide some leverage during audits, especially if it’s a recognized and accepted practice within the industry. - Reimbursement Disputes:
In the corporate world, disputes over reimbursements are not uncommon. Employees may claim certain expenses which the company might refute in the absence of a tangible receipt. Here, a properly filled Missing Receipt Form can be the bridge that resolves such conflicts.
The Technological Aspect
With the world moving towards digitization, the traditional Missing Receipt Form is also seeing some changes.
- Digital Missing Receipt Forms:
Many modern expense management software now incorporate digital missing receipt forms, allowing users to fill in details electronically, making the process faster and more efficient. - Integration with Expense Tools:
Systems are now available that integrate the Missing Receipt Professional Form feature with other expense tools, enabling automatic flagging of expenses that lack receipts and prompting users to fill in the required details.
Training and Awareness
One of the key challenges with the Missing Receipt Form is a lack of awareness or understanding among employees or stakeholders.
- Regular Workshops:
Companies can conduct workshops and training sessions to educate employees about the importance of maintaining receipts and the correct procedure to fill out a Missing Receipt Form. - Clear Communication:
Ensuring that the guidelines and sample policies related to missing receipts are clearly communicated can reduce discrepancies and misunderstandings.
Who creates a Missing Receipt Form?
A Missing Receipt Form is typically created and provided by the entity or organization that requires proof of transactions for purposes such as reimbursement, financial recording, or tax deductions. Depending on the context, various entities might be responsible for its creation:
- Employers or Companies: In a business setting, the finance or accounts payable department often develops this form. The sample objective is to have a standardized procedure for employees to report and get approval for expenses incurred on behalf of the company when the original receipt is missing. It helps in streamlining the reimbursement process and maintaining proper financial records.
- Educational Institutions: Universities, colleges, or schools might provide these forms for staff and faculty who undertake expenses related to academic activities, research, or other institutional purposes.
- Government Entities: Government officials or employees may need to account for expenses related to their official duties. In the absence of a receipt, a government department might have its own version of a Missing Receipt Form.
- Non-Profit Organizations: NGOs or other non-profit entities often have strict guidelines for financial transparency. These organizations might have Missing Receipt Forms for their members or volunteers to fill out if they incur expenses on the organization’s behalf without a receipt.
- Accounting or Expense Management Software Providers: In the digital age, many organizations use software for expense management. These platforms might have digital versions or templates of Missing Receipt Forms integrated into their systems. Users can fill these out electronically when required.
- Tax Preparers or Accountants: For individuals or businesses seeking to claim tax deductions for which they lack receipts, some tax preparers or accountants might provide a form or template to design document the details of the transaction.
- Freelancers or Self-Employed Individuals: Some freelancers or self-employed individuals create their own Missing Receipt Form templates. This is especially useful when they need to account for business-related expenses to clients or for tax purposes.
Who is authorized to sign a Missing Receipt Form?
The authorization to sign a Missing Receipt Form typically depends on the policies and procedures of the organization or entity that uses the form. However, in general contexts, the following individuals or roles are often authorized to sign:
- Direct Supervisor or Manager: In many organizations, especially businesses, the immediate supervisor or manager of the person incurring the expense is authorized to sign the form. This ensures that the manager is aware of and can validate the authenticity of the expense.
- Finance or Accounts Payable Department: A representative from the finance department, often someone responsible for reimbursements or expense approvals, might be required to sign the form. Their signature indicates that the form has been reviewed and the expense will be processed in lieu of the original receipt.
- Department Head or Director: For larger expenses or in cases where the missing receipt might be under special scrutiny, the head of a department or a higher-ranking official might need to sign off on the form.
- Compliance or Audit Team: In organizations with stringent financial controls, a member of the internal audit or compliance team might need to sample review and sign the form, especially if the expense falls under a category that’s routinely audited.
- The Individual Incurring the Expense: The person who incurred the expense and is submitting the Missing Receipt Form usually has to sign it as well. Their signature acts as a declaration that the information provided is accurate to the best of their knowledge.
- Treasurer or Financial Officer: In smaller organizations, like some non-profits or clubs, the treasurer or the primary financial officer might be the designated authority to approve such forms.
- Government or Regulatory Officials: In specific contexts, especially related to public funds or grants, a government or regulatory official might be required to review and sign the form to ensure accountability.
- Project Leads or Coordinators: For expenses tied to specific projects, the lead or coordinator of that project might have the authority to approve and sign the Missing Receipt Form.
It’s worth noting that in some organizations, multiple signatures might be required. For example, both the direct manager and someone from the finance department might need to sign off. This dual-authorization process adds an extra layer of scrutiny and ensures checks and balances.
Organizations should clearly define and communicate the authorization process for Missing Receipt Forms to prevent any misunderstandings or delays in expense processing. You can also see more templates like Printable Receipt Forms.
7. Sample Procurement Card Missing Receipt Form
8. Formal Missing Receipt Form Template
9. Sample Missing Receipt Claim Form Template
10. Sample Credit Card Missing Receipt Form Template
11. Sample Office of Finance Missing Receipt Form Template
12. Sample Missing Receipt Acknowledgement and Approval Form
13. Sample Expense Reimbursement Missing Receipt Form
14. Sample Missing Receipt Authorization Form Template
15. Sample Missing Expense Receipt Form Template
16. Sample Standard Missing Receipt Form Template
17. Sample College Missing Receipt Form Template
How do you Create a Software Form?
Creating a software form involves understanding the user’s needs, determining the form’s purpose, and designing it in a way that facilitates user interaction and data collection. You can also see more templates like Research Data Collection Forms. Here’s a concise guide on how to create a software form:
Step 1: Determine the Purpose First and foremost, identify what you aim to achieve with the form. Are you registering new users, collecting sample feedback, or maybe entering data for processing? The form’s design and fields will largely depend on its purpose.
Step 2: Sketch and Design Before jumping into coding, it’s helpful to sketch the layout:
- Field Placement: Decide on the order and grouping of input fields. Commonly used fields include text boxes, drop-down lists, checkboxes, radio buttons, and date pickers.
- Form Size and Style: Ensure the form fits well within the overall software interface and is styled consistently.
- Instructions and Labels: Clearly label each input field and provide instructions if necessary.
Step 3: Choose a Development Approach The technology and method you use will depend on the type of software you’re developing:
- Web Forms: For web-based format applications, use HTML forms combined with CSS for styling. You can add interactivity and validation using JavaScript or frameworks like React or Angular.
- Desktop Forms: If you’re developing a desktop application, utilize frameworks specific to your platform, like Windows Forms for .NET or JavaFX for Java applications.
- Mobile Forms: For mobile apps, utilize the UI components provided by the platform SDK, whether it’s Android (XML layouts) or iOS (Storyboard or SwiftUI).
Step 4: Implement Backend Functionality A form is often more than just its frontend appearance. It interacts with a backend to process data:
- Data Handling: Determine how the form data will be captured, validated, and stored. This might involve saving to a database, sending an email, or processing the data for other tasks.
- Error Handling and Feedback: Implement proper error-handling mechanisms. If a user makes an error, such as entering invalid data, provide clear feedback. Also, give feedback upon successful submission.
Step 5: Test the Form Once the form is ready, it’s crucial to test it:
- Usability Testing: Ensure the form is user-friendly and intuitive.
- Functionality Testing: Check that all elements work as expected, from input fields to submission buttons.
- Validation Testing: Ensure that validation rules work, both on the frontend and backend.
- Security Testing: Protect against potential vulnerabilities, especially if collecting sensitive information.
In Conclusion, a missing receipt form, while a useful tool, should not replace the practice of safekeeping original receipts. Instead, it should serve as a last-resort solution when the inevitable happens. By understanding its importance, components, and the best practices surrounding its use, one can ensure transparency, accountability, and smoother financial processes. You can also see more templates like Software Documentation Samples.
Related Posts
Sample Sworn Affidavit Forms
Vehicle Inspection Forms Samples & Templates
Sample Employee Advance Forms
Sample Child Travel Consent Forms
Sample Testimonial Request Forms
Sample Employee Details Forms
Sample Divorce Forms
Sample Attestation Forms
Employee Performance Appraisal Form Templates
FREE 9+ Sample Presentation Evaluation Forms in MS Word
FREE 10+ School Admission Form Samples & Templates in MS Word | PDF
FREE 30+ Patient Consent Form Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 10+ Sample Sign Off Form Templates in PDF | MS Word
FREE 11+ Sample Medical Consultation Forms in PDF | MS Word
FREE 8+ Sample Donation Forms in PDF | MS Word