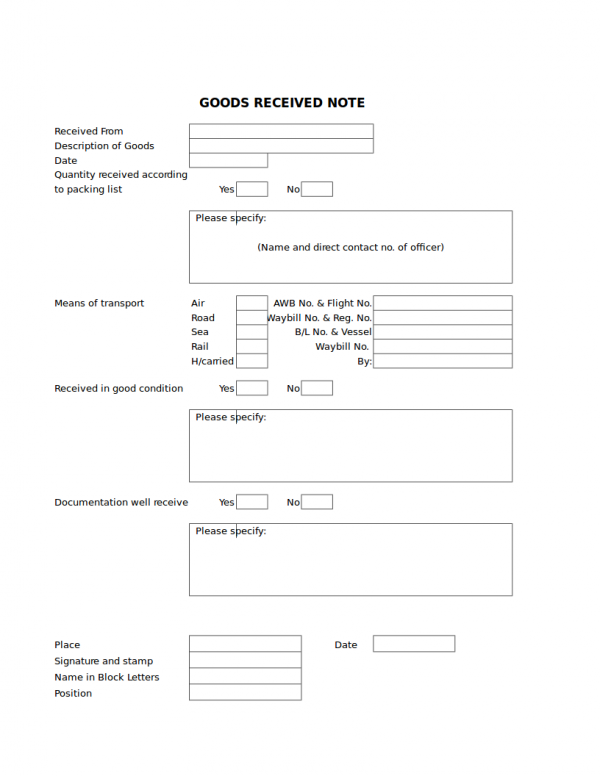
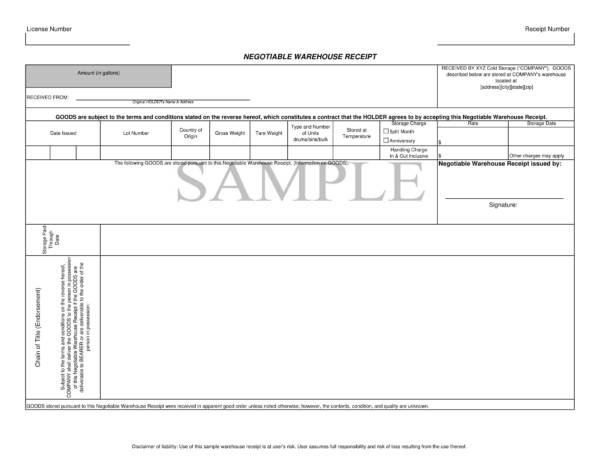
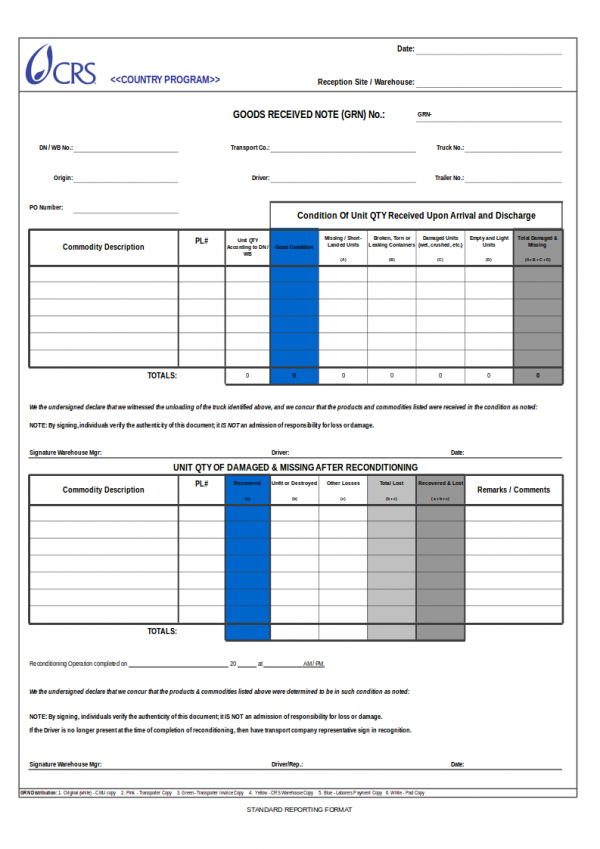
Receipts are those little sheets of sample paper that are handed by the cashier after payment has been made for the purchased products or goods. There are plenty of uses of a receipt and other uses that are specific to what type it is. A receipt sample is primarily used as proof of purchase that payment has been made by the buyer and is acknowledged by the seller or the representative of the seller.
Goods Receipt Template
In this article, we will discuss about a certain type of receipt called a goods receipt. What is this receipt and what is it used for. We will get to answer these questions and more as we go through the topic. Also, goods receipt samples and templates are provided to serve as one’s reference list and may be used as one’s own receipt. You may check them out below.

Goods Receipt Purchase Order
Goods Receipt Purchase Order (GRPO)
Vendor Information
- Vendor Name:
- Address:
- Contact Information: (Phone Number, Email)
Purchase Order Information
- Purchase Order Number:
- Purchase Order Date:
- Delivery Date:
- Payment Terms:
Ship To Information
- Company Name:
- Delivery Address:
- Contact Person:
- Contact Information: (Phone Number, Email)
Goods Receipt Details
- Goods Receipt Number:
- Goods Receipt Date:
Item Details
| Item No. | Description | Quantity Ordered | Quantity Received | Unit Price | Total Price | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Item Description 1 | |||||
| 2 | Item Description 2 | |||||
| … | … |
Additional Information
- Received By:
- Inspection Notes:
- Additional Remarks:
Approval
- Approved By:
- Date:
- Signature:

Download In
Goods Receipt in Procurement
Goods Receipt Note (GRN)
GRN Number: [Unique GRN Identifier]
Date of Receipt: [DD/MM/YYYY]
Delivery Note Number: [If applicable]
Supplier Information
- Supplier Name: [Supplier’s Full Name]
- Address: [Supplier’s Address]
- Contact Number: [Supplier’s Contact Number]
Purchase Order Details
- Purchase Order Number: [PO Number]
- Date of Order: [DD/MM/YYYY]
- Expected Delivery Date: [DD/MM/YYYY]
Receiver Details
- Received By: [Receiver’s Name]
- Position: [Receiver’s Position in the Organization]
- Department: [Receiving Department]
Delivery Information
- Carrier Name: [Name of the Delivery Service]
- Vehicle Number: [Delivery Vehicle Registration Number]
- Time of Receipt: [Time when goods were received]
Goods Received
| Item No. | Description of Goods | Ordered Quantity | Received Quantity | Unit of Measure | Condition on Arrival | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [Item Description] | [Number] | [Number] | [Unit] | [Good/Fair/Poor] | [Any remarks] |
| 2 | [Item Description] | [Number] | [Number] | [Unit] | [Good/Fair/Poor] | [Any remarks] |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
Inspection and Acceptance
Inspection Report: [Brief summary of inspection findings, confirming the quality and quantity of the received goods.]
Accepted By:
Name: [Inspector’s Name]
Position: [Inspector’s Position]
Signature: _________
Date: [DD/MM/YYYY]
Additional Comments or Observations
[Any additional comments regarding the delivery, condition of goods, discrepancies noted, or any other observations.]
Authorization
Authorized By:
Name: [Authorizer’s Name]
Position: [Authorizer’s Position]
Signature: _________
Date: [DD/MM/YYYY]

Download In
Goods Receipt Process
Introduction
The Goods Receipt Process is a critical stage in the procurement cycle, where received items are verified against purchase orders to ensure accuracy in quantity, quality, and specifications. This process ensures that the inventory is updated, and the organization is only invoiced for the items correctly received. A systematic approach to the goods receipt process can significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of inventory management and supplier payments.
Step-by-Step Process
- Receiving Notification: The procurement or warehouse department is notified about the imminent arrival of goods. This notification might come from the supplier or the shipping company.
- Preparation for Receipt: The receiving department prepares for the arrival of goods by ensuring that space is available for unloading and that the necessary tools and personnel are ready.
- Physical Receipt of Goods: Goods are physically received at the designated receiving area. The receiving team verifies the delivery against the shipping note or delivery note to ensure that the shipment corresponds to the expected delivery.
- Inspection and Verification:
- Quantity Check: The quantity of the items received is checked against the purchase order to ensure the correct amount has been delivered.
- Quality Inspection: The quality of the goods is inspected to ensure they meet the required standards and specifications. Any damaged or defective items are noted.
- Documentation Verification: The shipment is checked against the purchase order and shipping documentation for accuracy, including the correct product codes, descriptions, and any other relevant details.
- Recording in Goods Receipt Note (GRN): A Goods Receipt Note (GRN) is created, documenting the details of the received goods. This includes date of receipt, GRN number, supplier information, purchase order number, descriptions of goods, quantities received, condition of goods, and inspection report.
- Updating Inventory Records: The inventory management system is updated with the new stock. This involves adjusting inventory levels to reflect the received goods.
- Notification of Discrepancies: If there are discrepancies or issues with the received goods, the procurement department is notified. This could involve short shipments, damaged goods, or quality issues.
- Approval and Processing for Payment: Once the goods are verified and accepted, the goods receipt is approved. The finance department is then notified to proceed with supplier payment according to the terms of the contract.
- Archiving Documentation: All relevant documentation, including the purchase order, delivery note, GRN, and inspection reports, are filed and archived for future reference and audit purposes.
Best Practices
- Automate the Process: Use procurement and inventory management software to streamline the goods receipt process, reducing manual errors and increasing efficiency.
- Train Staff: Ensure that all staff involved in the goods receipt process are properly trained in inspection techniques and the use of any relevant software.
- Clear Communication: Maintain clear and open communication channels with suppliers to quickly resolve any discrepancies or issues with delivered goods.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits of the goods receipt process to identify areas for improvement and ensure compliance with internal policies and external regulations.
Conclusion
The Goods Receipt Process is essential for maintaining accurate inventory records, ensuring quality control, and validating supplier payments. By following a structured process and employing best practices, organizations can minimize errors, reduce fraud, and improve supply chain efficiency.

Download In
Goods Receipt Journal Entry
When goods are received but not yet paid for (purchased on credit), the journal entry to record the receipt of goods typically looks like this:
Date: [Date the goods were received]
| Account Title | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory or Expense | XXXX | |
| Accounts Payable | XXXX |
Explanation:
- Inventory or Expense: If the purchase is for goods that will be resold, it is debited to the Inventory account. If the purchase is for goods or services used as supplies or for operational purposes, it is debited to the appropriate Expense account.
- Accounts Payable: Represents the credit entry, indicating the company’s obligation to pay the supplier in the future.
Example Journal Entry
Suppose a company receives $3,000 worth of inventory on credit from a supplier on March 15, 2023. The journal entry to record this transaction would be:
Date: March 15, 2023
| Account Title | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory | 3,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | 3,000 |
Narration: Recorded receipt of inventory worth $3,000 on credit from [Supplier Name].
Key Points to Remember
- Debit Entry: The debit entry increases the Inventory or Expense account, reflecting the acquisition of new assets or the consumption of resources.
- Credit Entry: The credit entry increases the Accounts Payable account, reflecting an obligation to pay the supplier.
- Narration/Description: Always include a brief explanation of the transaction, mentioning the nature of the goods received and the name of the supplier. This is crucial for clarity and future reference.
This format ensures that the goods receipt is accurately recorded in the company’s books, reflecting both the increase in assets or expenses and the corresponding increase in liabilities.

Download In
Browse More Templates On Goods Receipt
Goods Delivery Receipt Template
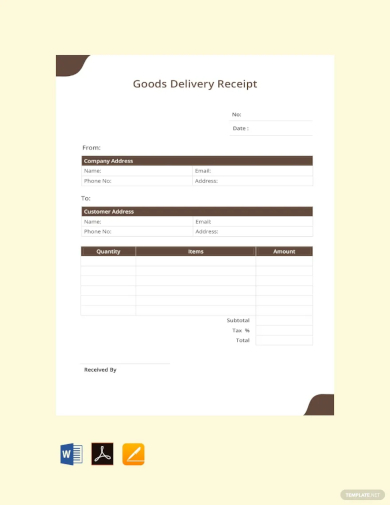
Receipt for Goods or Services Template
Uses of Goods Receipt Note
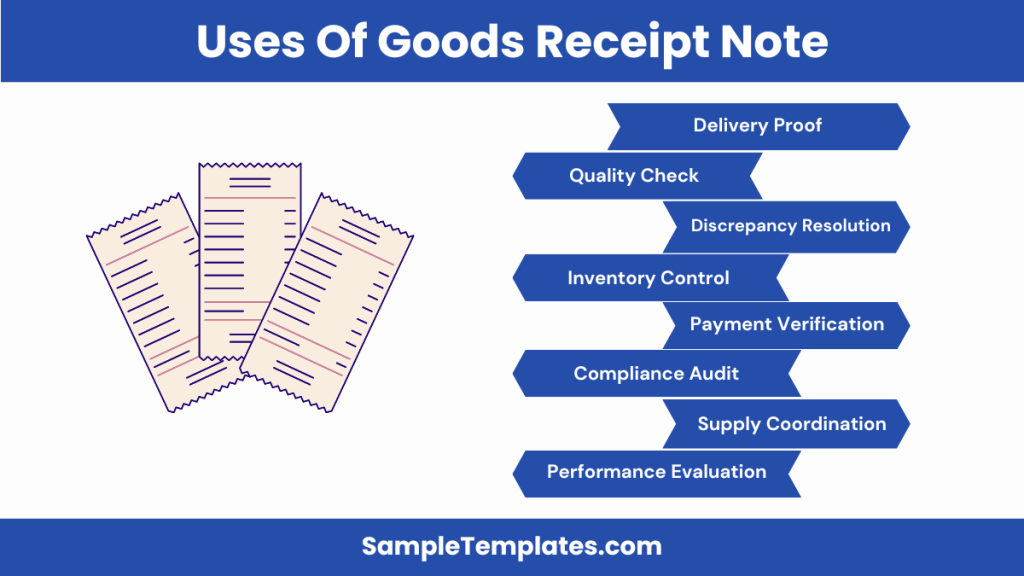
A Goods Receipt Note (GRN) plays a vital role in the inventory and supply chain management processes of a business. Here are some of its key uses:
- Proof of Delivery:
- Acts as documented evidence that goods have been received from a supplier, confirming the completion of a delivery.
- Quality Assurance:
- Enables the inspection of received goods for quality and condition, ensuring they meet the agreed specifications and standards before acceptance.
- Inventory Management:
- Facilitates accurate record-keeping and updating of inventory levels, helping businesses maintain optimal stock levels and manage reordering processes efficiently.
- Payment Processing:
- Serves as a basis for verifying and authorizing supplier payments by matching the goods received with purchase orders and supplier invoices.
- Discrepancy Resolution:
- Helps in identifying and resolving discrepancies between ordered and received quantities or any damage issues, providing a clear basis for returns or claims.
- Compliance and Audit Trail:
- Contributes to regulatory compliance by maintaining an audit trail of goods coming into the business, which is essential for audits, internal controls, and financial reporting.
- Supply Chain Coordination:
- Enhances coordination and communication within the supply chain by providing clear and documented communication regarding the receipt and status of goods.
- Performance Evaluation:
- Assists in evaluating supplier performance over time, based on the accuracy, timeliness, and quality of delivered goods, informing future procurement decisions.
The GRN is a crucial document that helps streamline operations, minimize errors, and enhance the efficiency of supply chain and inventory management practices.
Goods Receipt Note Template
Certificate Of Receipt Sample
Basic Delivery Conformation Receipt Template
Goods Received Note Format Download
Steps Involved in Goods Receipt Process
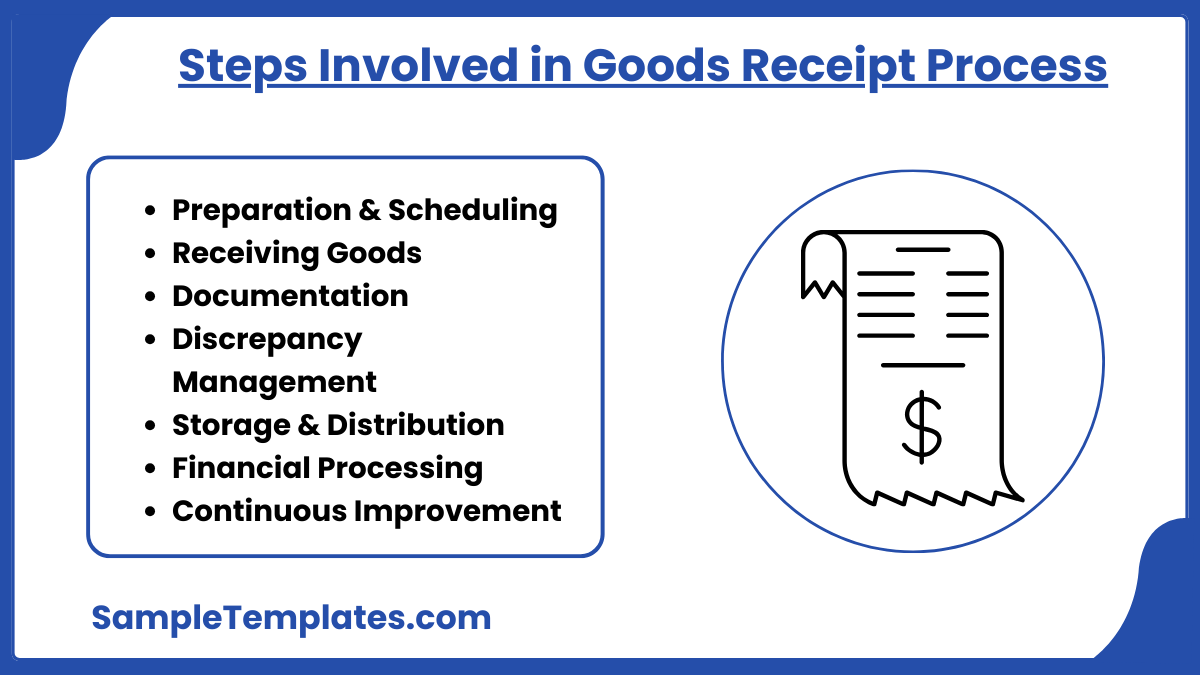
The goods receipt process is a critical component of supply chain management, ensuring that products delivered by suppliers are accurately received, inspected, and documented. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps involved in this process:
1. Preparation and Scheduling
- Coordinate with Suppliers: Schedule delivery times to manage receiving capacity effectively.
- Prepare Receiving Area: Ensure the receiving area is ready and equipped to handle the incoming goods, including space allocation and necessary equipment.
2. Receiving Goods
- Verify Delivery: Check the delivery against the shipping notice for correctness in terms of supplier, items, and quantities.
- Inspect Goods: Perform a quality inspection to verify that the goods meet the required specifications and are free from damage.
3. Documentation
- Record in Goods Receipt Note (GRN): Document the receipt of goods on the GRN, including details such as product name, quantity, condition, and any discrepancies noted during the inspection.
- Update Inventory Records: Adjust inventory levels in the management system to reflect the newly received goods.
4. Discrepancy Management
- Report Discrepancies: Any discrepancies between the goods received and the purchase order (e.g., short shipments, quality issues) should be documented and reported to the supplier for resolution.
- Handle Returns: Arrange for the return of defective or incorrect items, if necessary.
5. Storage and Distribution
- Store Goods Appropriately: Based on the nature of the goods (e.g., perishable, hazardous), store them in the appropriate location and conditions.
- Internal Distribution: Distribute goods to the relevant departments or locations within the organization as required.
6. Financial Processing
- Invoice Reconciliation: Match the goods receipt documents with the purchase order and the supplier’s invoice to verify that the delivery and billing are accurate.
- Authorize Payment: Once the reconciliation is complete and satisfactory, authorize payment to the supplier.
7. Continuous Improvement
- Review Processes: Regularly review the goods receipt process for efficiency and effectiveness, identifying areas for improvement.
- Supplier Feedback: Provide feedback to suppliers on their performance regarding delivery accuracy, product quality, and adherence to schedules.
By following these steps, businesses can ensure that the goods receipt process is efficient, accurate, and effective, thereby maintaining optimal inventory levels, minimizing errors, and fostering strong supplier relationships.
Goods Received Note Template
Goods Delivery Receipt Template
What Is a Goods Receipt?
You would probably think that a goods receipt is similar to those receipts that we get from convenience stores or grocery stores. Who would suspect that it isn’t? Just the name itself would lead you to believe that it is another type of sample receipt that we use and encounter on a daily basis. Receipts are generally issued to acknowledge that one has received something in exchange of something of the same value. So when you make store purchases, your store receipt is an acknowledgement that the store has received the right amount of payment for the good that has been purchased.
A goods receipt is also issued for the purpose statement of acknowledgement, but it does not really involved money or the receipt of money. It acknowledges the receipt of goods that are listed in a document issued by a warehouse, port terminal, shipping operator, etc. The items are inspected to ensure that they match those that are listed on the document. This is one way of legally conducting an inspection of the said products to know if they are really what they are declared to be. It is important that a goods receipt be secured, especially if is for business purposes as this is going to be part of the business inventory. The items or goods listed in the document are also covered under specific terms and conditions.
Other related articles you mat find useful are Loan Receipt Templates, Receipt Templates in Word, and Credit Card Receipt Templates.
The Difference Between a Receipt and An Invoice
Receipts are often referred to as invoices and vice versa. This is because both of them are so similar that it would be hard to really find their differences just by looking at both pieces of paper. Well, if you just take a look at them you will really not find any defining differences. But if you try to learn a little bit about them, you will surely fins that little ray of light which sets them apart. Of course, we want to make things easier for you so we have here a list of the differences between a receipt and an invoice.
- Exactly when do you receive a receipt and an invoice? This is the most obvious difference that you surely won’t find out by just looking at it. Invoices are issued before payment for the sale transaction has been made, while receipts are issued after payment has been made.
- So if an invoice is issued before payment has been made, that is because it is use primarily to request for the payment form of goods or services that has been consumed. What about receipts? as mentioned above, receipts are pretty much the acknowledgement that payment has been made.
- Because invoices are used to request for payment, you will probably not see the mode of payment used for the sale transaction, but you will have there the name, signature, age and even the date of the birth of your client. Of course that is on a case to case basis and largely depends on the seller and the type of business.
- While you are able to get see the mode of payment in a receipt, if it through cash, debit or credit card, or gift card, you will not be able to acquire such information as the address and age of the client or buyer.
- A receipt has its own receipt number that is unique and recognized by the store or establishment. Invoices also have their own set of invoice number known only to the business who uses them. Both receipt number and invoice number serve to determine if the products or goods purchased are from their store in case of a refund or repair.
- Invoices are not always paid right after they are issued to the buyer or client. There are certain payment terms that can be applied when it comes to paying invoices. Depending on what the buyer and seller has agreed upon as well as the total amount to be paid, payment terms can last a couple of weeks to a year. This type of sample agreement is not applicable to transactions done with a receipt.
Can you see clearly now how receipts are different from invoices? There are a lot, but they are not as hard as you think they are. These difference can easily be spotted if you pay attention to the details. If you want to know more about receipts and invoices, you are welcome to visit our website. We have their articles with samples and templates, like Purchase Receipt Templates, Grocery Payment Receipt Samples & Templates, and Construction Receipt Templates.
Receipt Of Goods Template
Formal Goods Delivery Receipt Template
Types of Goods Receipts in SAP
In SAP, the Goods Receipt process is a crucial part of materials management that documents the receipt of products from a supplier into the warehouse, triggering updates in inventory management, financial accounting, and cost accounting. SAP supports various types of goods receipts, catering to different scenarios in supply chain and inventory management. Here are some of the primary types of goods receipts in SAP:
1. Goods Receipt for Purchase Order
- Transaction Code: MIGO or MB1C
- This is the most common type of goods receipt, used to record the arrival of materials ordered through a purchase order (PO). It updates inventory quantities and values and is essential for matching invoices.
2. Goods Receipt into Unrestricted Use
- Materials received are directly placed into the warehouse as unrestricted stock, available for use. This is typically used for standard inventory items that have no special handling or storage requirements.
3. Goods Receipt to Blocked Stock
- Transaction Code: MIGO with Movement Type 103
- In this scenario, materials are initially received into a “blocked” status, meaning they are not available for use or sale. This might be used for items that require inspection or quality checks before they can be moved to unrestricted stock.
4. Goods Receipt for Stock Type Change
- Transaction Code: MIGO with appropriate Movement Type
- This involves changing the stock type of existing inventory, such as moving items from quality inspection to unrestricted use after they have passed inspection.
5. Goods Receipt for Subcontracting Order
- Transaction Code: MIGO with Movement Type 101
- This goods receipt is used when receiving finished goods from a subcontractor who has provided a service or added value to supplied materials. The process accounts for the consumption of components sent to the subcontractor and the receipt of the finished product.
6. Goods Receipt for Consignment Stock
- Transaction Code: MIGO with Movement Type 101 K
- Goods are received into consignment stock, meaning they are stored at the company’s premises but remain the property of the vendor until they are used or consumed, at which point the company becomes liable to pay for them.
7. Goods Receipt for Returnable Transport Packaging
- Transaction Code: MIGO with appropriate Movement Type
- This is used to manage the receipt of transport packaging materials that are to be returned to the supplier. It helps in tracking these items to ensure they are returned or accounted for.
8. Goods Receipt without a Purchase Order
- Transaction Code: MB1C with Movement Type 501
- In certain cases, goods might be received without a prior purchase order, such as in the case of unsolicited samples. This type of goods receipt allows for the material to be received into inventory without matching it to a PO.
Each of these types of goods receipts in SAP is designed to accommodate the diverse needs of inventory and supply chain management, ensuring accuracy in stock levels, financial records, and compliance with business processes and policies.
Goods Received Note Sample
Goods Receipt Note Format
Benefits of Having an Efficient Goods Receipt Process
An efficient goods receipt process is crucial for any business that manages inventory, as it serves as the entry point for materials into an organization. Here are the key benefits of having an efficient goods receipt process:
1. Improved Inventory Accuracy
- Accurate recording of received goods ensures that inventory levels are always up-to-date. This accuracy is essential for effective inventory management, preventing stockouts and overstocking, and enabling better demand forecasting.
2. Enhanced Supplier Relationships
- Efficient processing of goods receipts allows for timely payment to suppliers, fostering trust and reliability. It also facilitates better communication regarding discrepancies or quality issues, leading to improved supplier performance and collaboration.
3. Increased Operational Efficiency
- Streamlining the goods receipt process reduces manual data entry, minimizes errors, and speeds up the workflow from receiving goods to making them available for sale or production. This efficiency can significantly impact overall operational productivity.
4. Effective Quality Control
- An efficient process includes checks for quality and compliance with purchase orders. Early detection of defects or discrepancies allows for prompt action, such as returning faulty goods or adjusting inventory records, ensuring that only products meeting quality standards enter the supply chain.
5. Better Financial Management
- Accurate and timely recording of goods receipt affects financial reporting and budgeting. It ensures that liabilities (accounts payable) are accurately recorded, and inventory values are correctly reflected on the balance sheet, contributing to more reliable financial statements.
6. Compliance and Traceability
- Maintaining a thorough record of goods received helps comply with regulatory requirements, especially in industries where traceability of materials is essential for safety or quality assurance, such as food, pharmaceuticals, and electronics.
7. Reduced Inventory Shrinkage
- Efficient receipt processes help minimize losses due to theft, damage, or administrative errors. By accurately tracking goods from the point of receipt, companies can reduce instances of inventory shrinkage, protecting their bottom line.
8. Optimized Warehouse Management
- Knowing exactly what inventory is coming in and when it helps warehouse operations prepare for storage and distribution, optimizing space utilization and reducing handling costs.
9. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
- Ultimately, an efficient goods receipt process contributes to better stock availability, quality control, and order fulfillment speed, all of which are crucial for meeting customer expectations and maintaining high service levels.
By investing in the efficiency of the goods receipt process, businesses can achieve a competitive advantage through improved inventory management, operational efficiencies, financial accuracy, and customer satisfaction.
Warehouse Good Delivery Receipt Template
How to Create a Goods Receipt Template?
A goods receipt template can take on many sample forms and may contain a variety of different things. A good goods receipt template is one that appropriate for the types of goods listed and applicable for use for that particular transaction. Here are some simple steps that you can follow to create a simple yet useful goods receipt template.
- The first thing that you need to do is make an outline of the things that you will be including on your goods receipt. Goods receipt samples and other templates can help you with gathering the details that you need.
- The next thing to do is to decide whether how you want to make your template. You can have it computerized using Word and Excel application, or create one manually with a pen, paper, and ruler.
- Prepare the things or the equipment that you need.
- Set the paper size, paper orientation and margin of your working document. make sure that the margin is the same size for all of the four sides of your working sheet. This will make your document look neat and framed.
- Start with adding the header or the logo of the company or institution who owns the goods and then followed by all the other important contents, such as the list of items, the date when the goods are received, the date when the invoice was received, the invoice number and the name of the vendor.
- Make sure to provide an are where both senders and receivers can affix their signatures and write their full names.
- Also include other important statements, terms and conditions in the receipt template.
- Mention any attachments or other documents that come the goods receipt.
- Proofread your work to make sure that there are no spelling or grammar errors, and so that the details you have are complete.
- When you are satisfied with your work, have it saved with your desired file name and keep for future use.
Existing goods receipt samples and templates will be a great help to guide you on what things you will need to include on your goods receipt template. You may check other receipt samples and templates on our website, namely Parking Receipt Samples, Petty Cash Receipt Samples & Templates, and Work Receipt Templates.
What Things Are Included in a Receipt?
There are pretty much a lot of things that you can find in a receipt and all of them are equally important as all the other parts. The list below shows the things that are included in a receipt.
- The heading which, includes the name of the store or establishment, their address and contact number. The name of the company which the store is under is also provided.
- The date when the purchase was made as well as the date of payment is also listed.
- The list of items, products or services purchased or consumed are also included in the receipt together with their quantity, retail price and any promotions or discounts that are applicable to the said products.
- The receipt number or transaction ID is also indicated, which appears as a system generated set of numbers.
- The mode of payment of the transaction, if it is paid with cash, through credit or debit card or with a gift card. There are other acceptable modes of payment aside from the one’s mentioned, which depends on the store.
- The tax breakdown, including the tax percentage, and the total tax amount.
- The total amount to be paid.
- The applicable discounts and promotions.
- Statement that tells about how long the receipt is valid.
- The name of the cashier and the checker, and their employee number.
- The time when the payment was made.
Try checking out any receipts that you have and you will see the listed items above are in it. Some receipts may have less, and others may have more inclusions than the list which is normal as every receipt is unique. But you don’t really have to memorize all of them. Getting familiar with them works best. You may also check out other related articles, like Bill Receipt Samples and Templates, Store Receipt Templates, and Expense Receipt Templates.
General FAQs
How do you write a goods receipt?
To write a goods receipt, document details such as the date, supplier name, description of received items, quantity, quality, and any discrepancies. Include the receiver’s signature for confirmation.
What is GRN and MRN?
GRN (Goods Receipt Note) and MRN (Material Receipt Note) are documents used in inventory management. GRN confirms receipt of goods, while MRN is specific to materials, detailing their reception and use.
Who sends the goods receipt?
The goods receipt is typically prepared and sent by the receiving department or personnel within a company. This document confirms the physical receipt of goods from a supplier.
What is a GRN process?
The Goods Receipt Note (GRN) process involves documenting the physical receipt of goods ordered from a supplier. It includes verification, inspection, and recording relevant details to update inventory records.
What is a good receipt without invoice?
A goods receipt without an invoice occurs when a company receives goods from a supplier, but the corresponding invoice has not been received or processed. It’s a record of the received items.
In conclusion, this goods receipt signifies the successful and accurate receipt of the specified items. Thorough inspection ensures compliance with order details, guaranteeing the quality and quantity of goods. This record serves as confirmation of a seamless transaction, providing clarity and accountability in our supply chain process.
Related Posts
FREE 16+ Printable Hotel Receipt Templates in PDF | MS Word
FREE 6+ Sample rent receipt form in MS Word | PDF
FREE 10+ Sample Receipt Voucher Templates in PDF | MS Word
FREE 10+ Fee Receipt Samples in PDF | MS Word | Google Docs | Excel | Apple Numbers | Apple Pages
FREE 7+ Vehicle Sales Receipt Samples in MS Word | PDF
FREE How to Create a Car Rental Receipt [9+ Samples]
FREE 13+ Taxi Receipt Templates in PDF | Google Docs | Google Sheets | Excel | MS Word | Numbers | Pages
FREE 10+ Receipt Book Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Online Receipt Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | Google Sheets | MS Excel | PDF
FREE 10+ Personal Analysis Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | Pages | PDF
FREE 5+ Non Profit Receipt Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Advance Receipt Samples in PDF | DOC
FREE 3+ Investment Receipt Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | Google Sheets | MS Excel | PDF
FREE 3+ Enterprise Receipt Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Tenant Receipt Samples in PDF | MS Word | Google Docs | Google Sheets | Excel