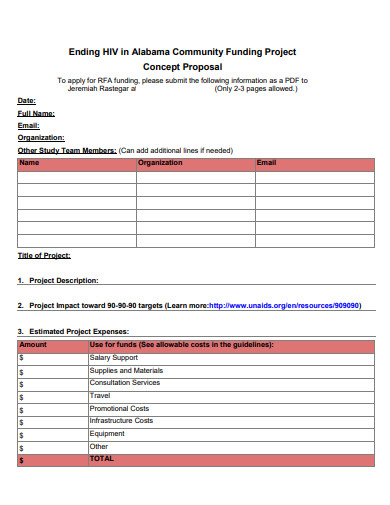
Many organizations have always required a concept paper to be submitted for review prior to the submission of a full proposal.
In recent years businesses and organizations have begun to encourage the use of concept papers as a way for applicants to obtain informal feedback on their ideas and projects prior to preparing a proposal. Some of these agencies now require a concept
paper to be submitted as part of the formal submission process. The purpose of a concept paper, from the funding agency’s point of view, is to help applicants develop more competitive proposals and to save time by eliminating proposals that are not likely
to be funded. The applicant’s purpose in developing a concept paper is to capture the interest of the funding agency and demonstrate that the idea they are proposing is worthy of further consideration.
5+ Project Concept Proposal Samples
1. Project Concept Proposal

2. Funding Project Concept Proposal
3. Sample Project Concept Proposal
4. Simple Project Concept Proposal
5. Sponsored Project Concept Proposal
6. Joint Project Concept Proposal
What is a Project Proposal?
A proposal is the document that facilitates a professional relationship between an organization and outside contributors. Typically, a project proposal is the initial framework for establishing the concept of the project and includes what you want to accomplish, an explanation of objectives, and plans for achieving them. It is common for a project proposal to include a list of activities or tasks that will be associated with the project, illustrate the significance of this specific project idea, and explain the origins of this project.
A proposal is also the marketing document that kicks off a relationship between an organization and outside project stakeholders. Creating a proposal allows an organization to establish a formal, logical presentation to an outside worker or project donor. Proposals are generally drafted during one of the early phases of your project (before detailed plans are made and resources are allocated). Therefore, time and budget estimates are often rough, at best.
Details to Include in a Project Concept Proposal
Executive Summary
The executive summary provides a quick overview of the main elements of your project proposal, such as your project background, project objectives, project deliverables, among other things. The goal is to capture the attention of your audience and get them excited about the project you’re proposing. It’s essentially the “elevator pitch” for the project life cycle. It should be short and to the point.
The executive summary should be descriptive, and paint a picture of what project success looks like for the client. Most importantly, it should motivate the project client; after all, the goal is getting them to sign on the dotted line to get the project moving!
Project Background
The project background is a one-page section of your project proposal that explains the problem that your project will solve. You should explain when this issue started, its current state and how your project will be the ideal solution.
- History: The history section outlines previously successful projects. It also outlines those that could have run more smoothly. By doing so, this section establishes precedents. Namely, how the next project can be more effective using information from previous projects.
- Solution: The solution section addresses how your project will solve the client’s problem. Accordingly, this section includes any project management techniques, skills and procedures your team will use to work efficiently.
Project Approach
Your project approach defines the project management methodology, tools and governance for your project. In simple terms, it allows project managers to explain to stakeholders how the project will be planned, executed and controlled successfully.
- Requirements: Requirements are the items, materials and resources needed for the project. This section should cover both internal and external needs.
- Authorization: This section covers who the decision-makers are on the project team. It also covers which stakeholders have sign-off authority on the client’s side.
- Project Scope: The project scope refers to all the work that will be executed. It defines the work items, work packages and deliverables that will be delivered during the execution phase of your project life cycle. It’s important to use a work breakdown structure (WBS) to define your tasks, subtasks and prioritize them.
- Project Resources: Resources are critical for the execution of your project. The project proposal briefly describes what resources are needed and how they’ll be used. Later, during the planning phase, you’ll need to create a resource management plan that will be an important element of your project plan.
- Project Timeline: Once you’ve defined your project scope, you’ll need to estimate the duration of each task to create a project timeline. Later during the project planning phase, you’ll need to create a schedule baseline, which estimates the total length of your project. Once the project starts, you’ll compare your actual project schedule to the schedule baseline to monitor progress.
- Project Budget: All the resources that you’ll need for your project will have a price tag. That’s why you need to estimate those costs and create a project budget. The project budget will need to cover all your project expenses, and as a project manager, you’ll need to make sure that you adhere to it.
- Financial Statements: If you want to convince internal stakeholders and external investors, you’ll need to show them what are the financial benefits that your project could bring to their organization. You can use a cost benefit analysis and projected financial statements to demonstrate why your project is profitable.
- Appendix: Information not included in the project proposal is part of the appendix. It’s where many of the more interesting details of a project are located. Also, it’s where team members and stakeholders can do a deep dive to learn more.
FAQs
What are the types of project proposal?
- Solicited Project Proposal: A solicited project proposal is sent as a response to a request for proposal (RFP). Here you’ll need to adhere to the RFP guidelines of the project owner.
- Unsolicited Project Proposal: You can send project proposals without having received a request for proposal. This can happen in open bids for construction projects, where a project owner receives unsolicited project proposals from many contractors.
- Informal Project Proposal: This type of project proposal is created when a client asks for an informal proposal, without an RFP.
- Renewal Project Proposal: You can use a renewal project proposal when you are reaching out to past customers. The advantage is that you can highlight past positive results and future benefits.
- Continuation Project Proposal: Sent to investors and stakeholders to communicate project progress.
- Supplemental Project Proposal: This proposal is sent to investors to ask for additional resources during the project execution phase.
What are the advantages of a project proposal?
- Clear proposals prove the viability of a project or program.
- Increase clarity regarding requirements and project roadmap.
- Structure and organization is established up front, reducing the chance for misalignment.
- Successful proposals lead to approved budgets and financial support for organizational growth and project replication.
- Proposals play an integral part in organizational growth, helping in budget approval and new client adoption.
- Reaching out to stakeholders and building alliances increases credibility and exposure in the community at large.
- Having detailed your project’s methods and measurement tools in advance builds accountability into every step of your work.
- Integrating grant writing into day-to-day work turns proposals into useful planning documents and detailed templates for project implementation.
Determine your project proposal type first for an effective presentation. Make sure your proposal targets your audience and clearly defines the problems it will solve.
Related Posts
Proposal Outline Samples & Templates
Title Proposal Samples [ Project, Thesis, System ]
Proposal Samples
Sports Event Proposal Samples
Small Business Proposal Samples
Title Project Proposal Samples [ Community, School, Student ]
FREE 10+ Product Supply Proposal Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages | PDF
FREE 10+ Health Project Proposal Samples [ Public, Mental, Healthcare ]
FREE 11+ Engineering Project Proposal Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 4+ Racing Sponsorship Proposal Samples [ Team, Car, Driver ]
FREE 10+ Nursing Project Proposal Samples [ Community, Health, Clinical ]
FREE 11+ Student Council Proposal Samples in PDF | DOC
FREE 10+ Facilities Management Proposal Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages | PDF
FREE 8+ Joint Venture Proposal Samples [ Commercial, Real Estate, Construction ]
FREE 10+ Scholarship Proposal Samples [ Project, Grant, Sponsorship ]