Analyzing the cost of something is safe way to determine the amount needed to get things done. A cost analysis is defined in economics as a way to measure production costs to help determine if it is profitable or not. A cost analysis can be done both in business and outside of business, like in one’s personal purchases, expenses, and income. Being able to properly conduct a cost analysis for certain things is essential. However, it requires a lot of knowledge and expertise about the field, as well as the appropriate tools to get the job done. Cost analysis samples are great tools to use to help you get by with the task of analyzing costs. Below are some cost analysis samples that you may check out and use as reference.
Analyzing the cost of something is safe way to determine the amount needed to get things done. A cost analysis is defined in economics as a way to measure production costs to help determine if it is profitable or not. A cost analysis can be done both in business and outside of business, like in one’s personal purchases, expenses, and income. Being able to properly conduct a cost analysis for certain things is essential. However, it requires a lot of knowledge and expertise about the field, as well as the appropriate tools to get the job done. Cost analysis samples are great tools to use to help you get by with the task of analyzing costs. Below are some cost analysis samples that you may check out and use as reference.
Cost Analysis Samples
1. Business Cost Analysis Sample
Need help with analyzing costs of your small business? The help that you’re looking for is in this business cost analysis sample. The sample is used specifically for small businesses. It is made available in Word document making it possible for you to use it as your own template instead of just a guide. Just make the necessary changes to make it appropriate for your needs, and it should be good.
2. Sample Cost and Price Analysis Worksheet
This cost and price analysis sample works both as a reference for your cost analysis needs and as a worksheet to help you learn more about how the analysis process is done. The worksheet is made up of five parts and each part provides exercises for you to do to help you learn and acquire knowledge. Important details are highlighted in yellow in each section so that they can easily be distinguished. This is sample worksheet is indeed a great way to learn about cost analysis.
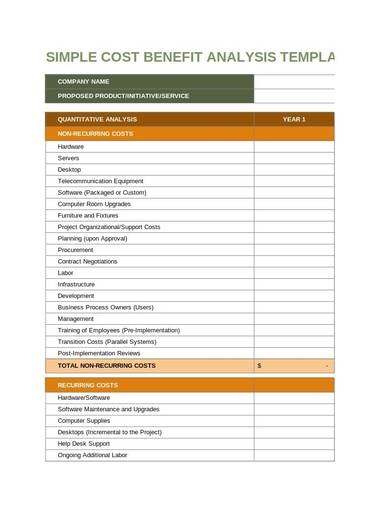
3. Simple Cost-Benefit Analysis Template Sample
This sample cost-benefit analysis template is as simple as it gets. It is also an easy and convenient way to analyze and organize costs and data for analysis. All of the information that you need are listed in different cells and columns under their respective sections in the table created in the spreadsheet. The main rows and columns are colored to be easily distinguished, and each cell is programmed with the appropriate formula for easy computation of data. It is also perfect for organizing and analyzing data for a product cost analysis.
4. Cost-Benefit Analysis Tool Sample
If you need to learn about cost analysis, then you can turn to this cost-benefit analysis tool sample for help. How can it help you? It’s not only a sample, it also includes detailed information about what a cost analysis is, when to use it, how to use it, and an example that will surely be useful to complete beginners. The tool is only two pages long, which means you don’t have to spend a lot of time reading and understanding what it is. It is definitely worth it.
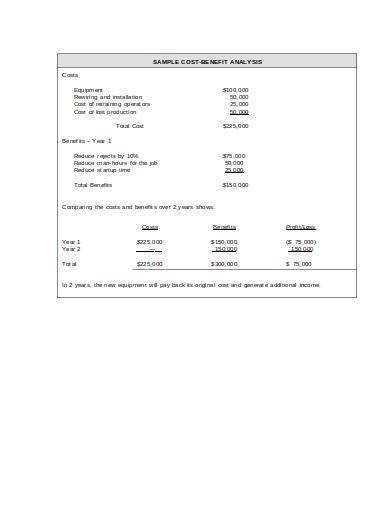
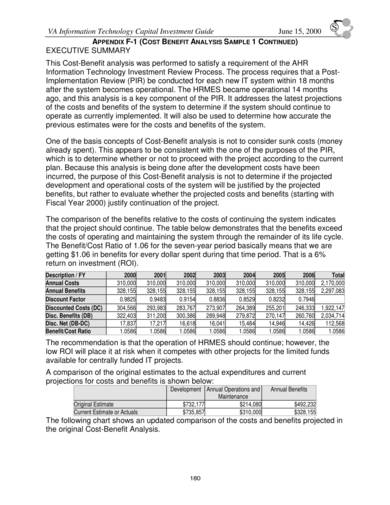
5. Sample Cost-Benefit Analysis Template
The sample cost-benefit analysis template shown above is created and used by the United States Department of Veterans Affairs. If you are looking for a sample template that is guaranteed reliable and useful, then this is the sample template that you should use. The different sections in this document are written in bold letters, and the details or instructions on what to write in each section are written in blue. This way you will be able to make quality and related content and come up with a good analysis.
6. Sample Functional Cost Analysis
What is a functional cost analysis? A functional cost analysis should not be mistaken with that of a functional behavioral analysis. Obviously one is used to examine component costs of a product and the other one is used to examine behavioral characteristics or trends. The functional cost analysis sample shown above includes five useful steps on how a functional cost analysis is done. A functional cost analysis form is also provided at the last page.
7. Undergraduate Cost-Benefit Analysis Sample
The sample above is an undergraduate study about cost-benefit analysis. This is another great tool that one can use to learn about cost-benefit analysis. It includes a definition of cost-benefit analysis, a table providing example details, ways on how to measure current costs, ways on measuring future costs, etc.
8. Cost-Benefit Analysis Practical Samples
In this sample, you will be able to learn about the practical samples about the use, applications, impacts, and techniques on cost-benefit analysis. The sample includes various graphs, charts, and tables to organize data and represent data clearly. This sample provides a great source of information to those who really need it.
9. Sample Cost-Benefit Analysis
This sample cost-benefit analysis is a simple yet detailed analysis document that uses a generic layout similar to the ones used in textbooks. Although it is only 8 pages long, it includes a table of contents so that you can easily look up the specific cost analysis topic or example you want to learn about. Tables are provided to represent data for different operational costs. You can also easily find the different sections and topics in the sample because they are written in bold and capital letters.
10. Meal Cost Analysis Sample
How much does a meal cost? Meal pricing undergoes a cost analysis to ensure that the price is just enough to cover costs and earn a profit. If not priced accordingly, meals may end up overpriced or underpriced, which are both not good for business. Learn the pros and cons, and other related information about meal pricing with the use of the meal cost analysis sample. It covers everything that you need to know about meal cost analysis and how it should be properly done.
Related Posts
FREE 10+ Failure Mode and Effects Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Make or Buy Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Fishbone Root Cause Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 11+ Cost Volume Profit Analysis Samples & Templates in PDF | MS Word
FREE 6+ Corporate Portfolio Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Fault Tree Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Comp Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Fishbone Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Individual Swot Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ 5 Year Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Benefit Costs Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Job Hazard Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Primary Source Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Literary Analysis Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Critical Path Analysis Samples in PDF