There are many ways to accomplish a task, meaning you can arrive at the same result by using different methods or means. As a part of their project management work plan, companies utilize alternative analysis to determine how they will approach a project. In system engineering, the analysis of alternatives is one of the effective methods to analyze various system architectures and design decisions related to frameworks on business and technical performance.
10+ Analysis of Alternatives Samples
1. Analysis of Alternatives
2. Decisions Based on Analysis of Alternatives
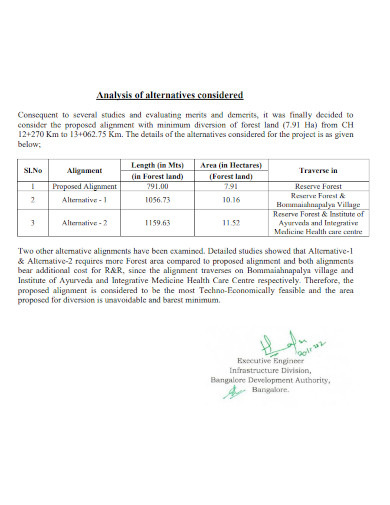
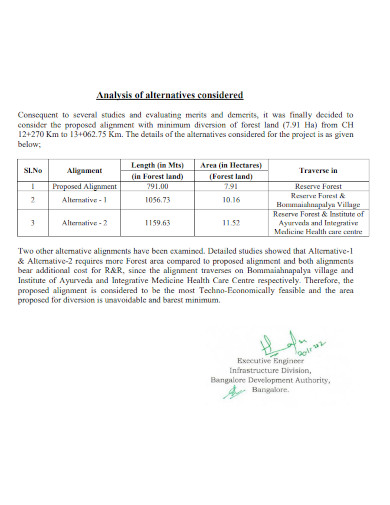
3. Analysis of Alternatives Considered
4. Alternatives to the Proposed Project
5. Summary of Alternative Analysis
6. Analysis of Alternatives to The Project
7. Analysis of Alternatives Development Process
8. Economic Evaluation Analysis of Alternatives
9. Alternatives Analysis and Trade Studies
10. Advancing Alternatives Analysis
11. Sample Alternatives Analysis
What is an Analysis of Alternatives?
An analysis of alternatives or AoA refers to the evaluation of various methods or routes that you can take to achieve your business goals or a certain project management objective. It is an analytical comparison of different operational effectiveness, cost of life-cycle, and suitability of alternatives as well as helps in determining the potential flaws of the operational factors. This analysis usually involves sensitivity analysis, life-cycle costing, utilization of cash flow analysis templates, and cost-benefit analysis. The analysis of alternatives is also a part of the decision-making process which enables you to find the appropriate cost-effective smart action plan and prevent duplication of unnecessary efforts.
How to Write an Analysis of Alternatives
The analysis of alternatives is the process of analyzing and evaluating a number of options before making an investment or business decision. It helps in establishing and standardizing parameters for cost analysis, a schedule management plan, work performance evaluation, and a risk management action plan. This analysis is often performed at the initiation of a project as well as during the entire life cycle of a project. It helps in identifying whether a decision is sound and provides updates during the entire project to strengthen the assessment criteria.
Step 1: Create an Outline for your Plan
In your strategic planning, make sure to define all the different routes or decisions you can take to achieve your objectives and accomplish operational effectiveness. Include the identification of your stakeholders, and the definition of the timing, effort, or funding. You will also need to create a study team and study plan to provide them with guidelines on how to complete their tasks.
Step 2: Establish an Analytical Framework
Provide a definition of your analysis problem statement, the context of the problem, and the scope and framework for the alternative observations and comparisons. Establish the assumptions and ground rules to provide you with an analysis outline. In this step, your study will involve access to data collection, requirements, and sources.
Step 3: Identify and Describe the Alternatives
After identifying the different alternatives you can take from your data source, make sure to choose one as your parameter. The alternatives you have identified will address your problem statement within the context and scope you have provided.
Step 4: Assess and Compare
Evaluate your alternatives against your criteria like cost, risk, life cycle cost-effectiveness, benefits, and likelihood analysis. Perform a sensitivity analysis to determine how a target variable is affected by modifications from an input variable.
Step 5: Report your Results
Document the results of your analysis of alternatives that support the alternative you have selected and how it will provide support to the business or project decisions made by the stakeholders.
FAQs
What are the basic components of an analysis of alternatives?
An analysis of alternatives includes basic components which are the capability need, deficiencies, and opportunities, program description, threats, operational environments, operational concept, operational requirements status quo and alternatives, trade-off analysis, and recommendations and conclusions.
What are the advantages of performing an analysis of alternatives?
Performing an analysis of alternatives enables portfolio, program, and project managers to determine, understand, and analyze the available alternatives to manage a project as well as the best action plan to handle concerns about the project’s costs and risks.
When should an analysis of alternatives be updated or performed?
An analysis of alternatives must be updated and performed in every acquisition phase and during the entire lifecycle of a program to ensure that the appropriate material solution is being established and developed.
The analysis of alternatives is an evaluation of various available options before making an important investment or business decision. It establishes the standard parameters for schedule, cost, risks, and performance. It enables companies to discover and explore multiple alternatives they can take before proceeding to the execution stage of a project proposal while also being knowledgeable and considerate of the potential risks and uncertainties.
Related Posts
FREE 10+ Feasibility Analysis Report Samples [ Financial, Project ...
FREE 8+ Value Analysis Samples in PDF MS Word
FREE 10+ Problem Solving Report Samples in PDF DOC
FREE 9+ Sample Case Analysis Templates in MS Word PDF ...
FREE 10+ Research Paper Proposal Samples in MS Word PDF
FREE 10+ Decision Matrix Samples in MS Word PDF | DOC
FREE 10+ Real Estate/Property Strategic Plan Samples in MS Word ...
FREE 5+ Development Feasibility Study Samples [ Project, Software ...
FREE 11+ Business Case Samples in PDF DOC
FREE 10+ Project Feasibility Report Samples in PDF
FREE 13+ Sample Feasibility Reports in MS Word PDF | Google ...
FREE 10+ Sample Resolution Agreement Templates in PDF MS ...
FREE 10+ School Feasibility Report Samples in PDF DOC
FREE 6+ Construction Profit and Loss Samples in PDF
FREE 9+ Case Study Analysis Samples in PDF MS Word