A Cash Book is a general document more like a journal that consists of all details about the cash. It can be the cash deposited, withdrawal, disbursement, invoices, receipt, etc. For an organization or an institute, it is a very important document. All the information that is accumulated in this document is afterward are input in the general ledger. Here we have provided different types of Cash Book Samples that can help you deal with the sample receipts. You can choose from the samples and get the one you prefer to work with.
13+ Cash Book Samples in PDF | DOC
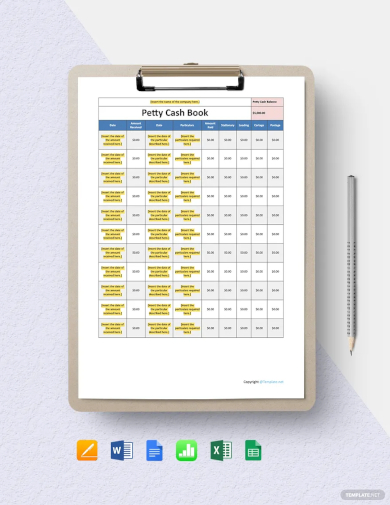
1. Petty Cash Book Template
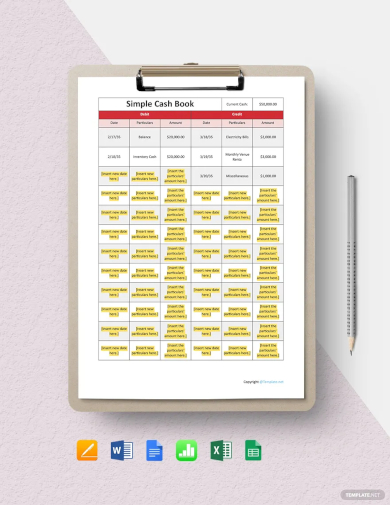
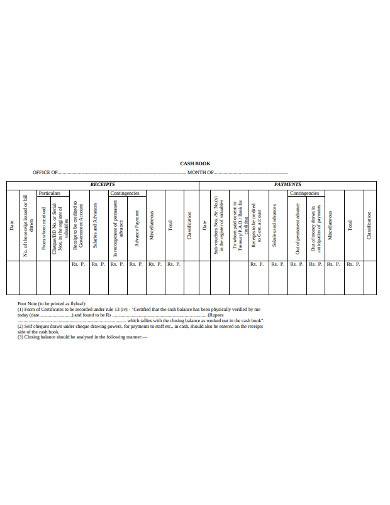
2. Simple Cash Book Template
3. Cash Receipt Book Template
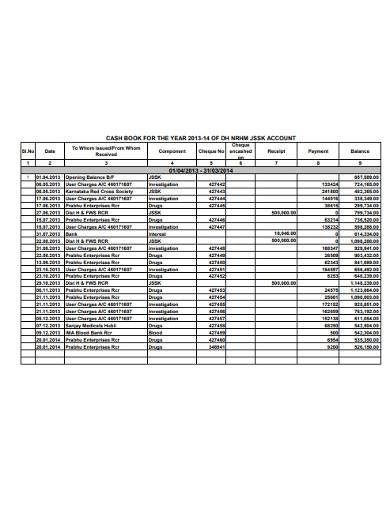
4. Sample Cash Book Template
This is a template of a Cashbook Sample that has different tables as its concrete structure. For example, you can write about the wage payment, someone’s account details, cash payment receipts, etc. This sample has been designed to give you an idea about the structure of a cash book. You can download this structure as a reference for your cash book as per your requirements.
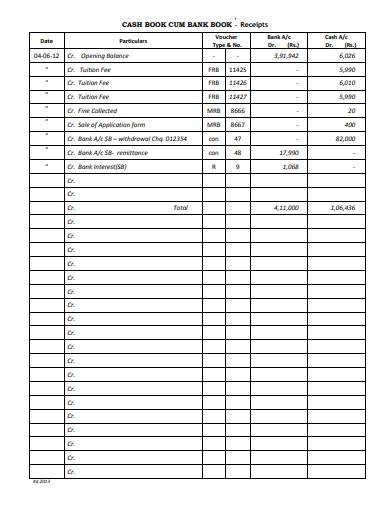
5. Cash Book Receipts Template
A Cash Book Receipts Sample designed professionally can help you to prepare a cash book immediately without any hassle. You can opt for this sample provided here and use the format of this sample as a suitable sample reference to your original document. For your sample payment receipts, this is the best structure that you will find.
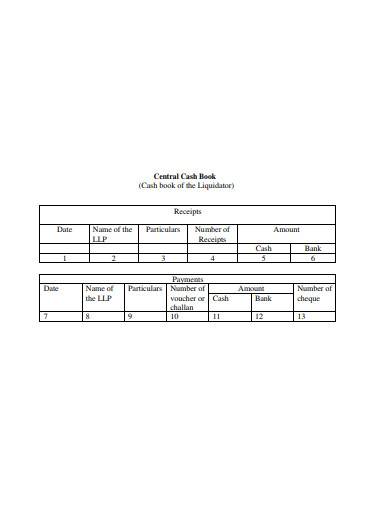
6. Central Cash Book Template
There are two charts that are provided and below that some instructions are mentioned in this Central Cash Book Template. You can download this template if it suits your requirements. We are pleased to tell you that this template is free to download. Therefore you do not have to think about the money, the template is cost-efficient. The rest of the details you can check out after downloading. This might be the one that you think suits the cash flow statements.
7. Maintenance of Cash Book Template
You cannot just leave your cashbook unmanaged and disorganized. You need to do proper maintenance of the journal if you do not want your details to get misplaced. This can be done in the simplest of steps. You can download this Maintenance of Cash Book Sample and go through the instructions that are mentioned and you will be able to manage your cash book entry.
8. Annual Cash Book Template
An annual cash book is necessary for the annual record at the end of every financial year. This helps in the management of the funds and the cash that has been withdrawn and sample receipts of the sales. This Annual Cash Book Template can help you structure a proper cashbook register. You can get this template easily downloaded in any device you use as this template is compatible with both Windows and iOS.
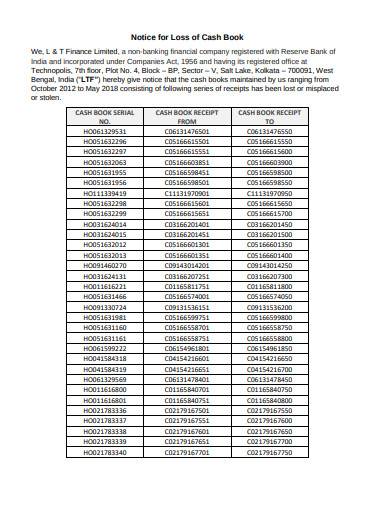
9. Sample Notice for Loss of Cash Book Template
If you have lost some of the data regarding the cash, you can always register a notice to the bank or the finance organization to retrieve the lost data. How will you do so? You need to mention the lost data in an organized way. Download this Notice for Loss of Cash Book Sample and use the structure where you can mention the cash sale receipt that you have lost.
10. Printable Cash Book Template
In case you want to print out the cashbook, we have a compatible structure for that. This Printable Receipt Cash Book Sample has been designed so that you can make your cashbook print-ready. The design of the cashbook that is provided in this sample is very simple. You can easily input the details and then print them out for your comfort.
11. Business Petty Cash Book Template
Petty cash is the amount that is kept separately for the use in small matters. In business, the role of petty cash is very important. Therefore it should also have a proper listing in the cashbook. For that, we have developed this Business Petty Cash Book Template so that you can avail of a simple structure that you can use for the sample listing of petty cash.
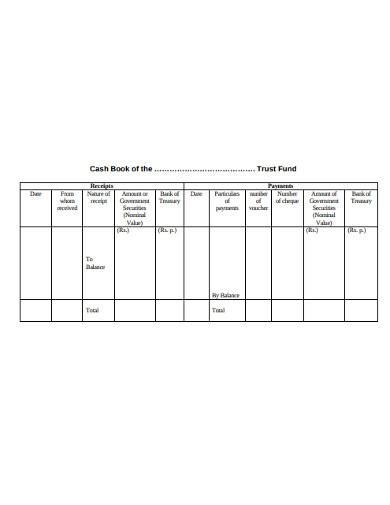
12. Sample Trust Fund Cash Book Template
A Trust Fund Cash Book Sample can be used to draft the cashbook for the proper cataloging of all the transactions related to the trust fund. This will help to keep the important details in a systematic manner. You can get this template downloaded as an example from which you can get the sample plan to craft the cashbook framework.
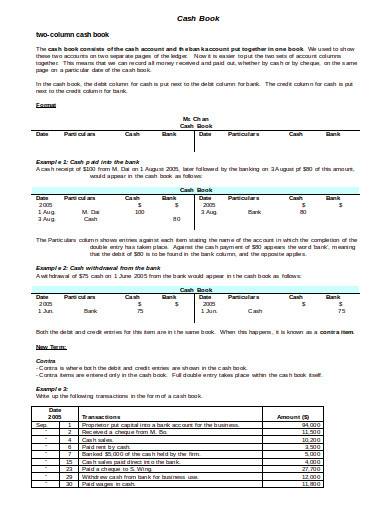
13. Two Column Cash Book Template
You can prepare a cashbook report sample with this Two Column Cash Book Sample where you can mention the transactions and the usage of cash on different dates separating them with columns. This will help you to arrange and categorize it based on your preferences. So, hurry and download now if you want this structure to be the part of your cashbook.
14. Three Column Cash Book in DOC
Three Column Cash Book in DOC is another structure that we have designed for the benefit of the customers and the clients. Like all the samples provided here, you can use this structure in a similar way. This is drafted after taking into consideration the general trend of structuring a cashbook. This sample is available in the editable DOC format, hence you can make your required inputs and changes in the sample itself. Isn’t it a better way for the cash payment receipts to catalog?
Related Posts
10+ Restaurant Invoice Samples & Templates
11+ Daycare Receipt Samples and Templates
11+ Gym Invoice Samples & Templates
10+ Goods Receipt Templates
9+ Jewelry Invoice Samples and Templates
9+Sample Fundraiser Receipt Templates
7+Payment Voucher Sample
6+Sample Bank Statement
10+Sample Statement of Cash Flow
10+ Advance Payment Invoice Templates
8+ Travel Receipt Samples and Templates
7+Free Checkbook Register
7+House Rent Receipt Sample
6+ Parking Receipt Samples
5+ Sample Cleaning Service Receipt