An accounting ledger is a must in the business world. No company can ever survive or become successful without the a financial ledger to record all of the business’ transactions. It is considered as the backbone of the financial system any business because it is where all account data from different legers are stored. In the present, general ledger samples have evolved from physical books into digital Excel spreadsheets. Featured in this article are downloadable Excel ledger samples for different business purposes statement. We’ve also included tips on how you can effectively make an Excel ledger below.
FREE 13+ Excel Ledger Samples & Templates in MS Excel
1. Ledger Format in Excel Free Download

2. Ledger Excel Format

3. Account Ledger Format in Excel

4. Ledger Template Excel

5. Company Ledger Account Format Excel
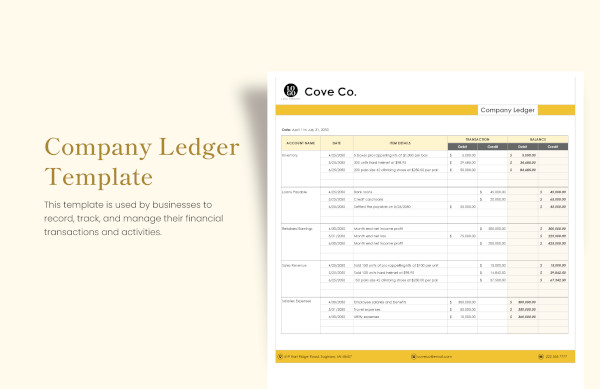
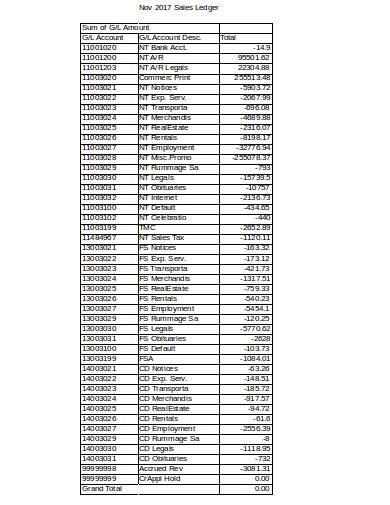
6. Sales Ledger Format in Excel
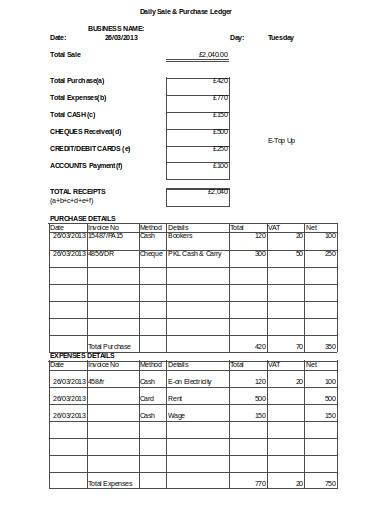
7. Daily Ledger Excel Template
8. Download Ledger Format in Excel
9. Simple Ledger Format in Excel
What Does a Ledger Do?
A ledger serves as the core financial accounting tool for individuals, businesses, and organizations of all sizes. It plays a pivotal role in sample tracking, recording, and organizing financial transactions, enabling the accurate management of financial resources and providing a historical record of financial activities.
Key Functions of a Ledger
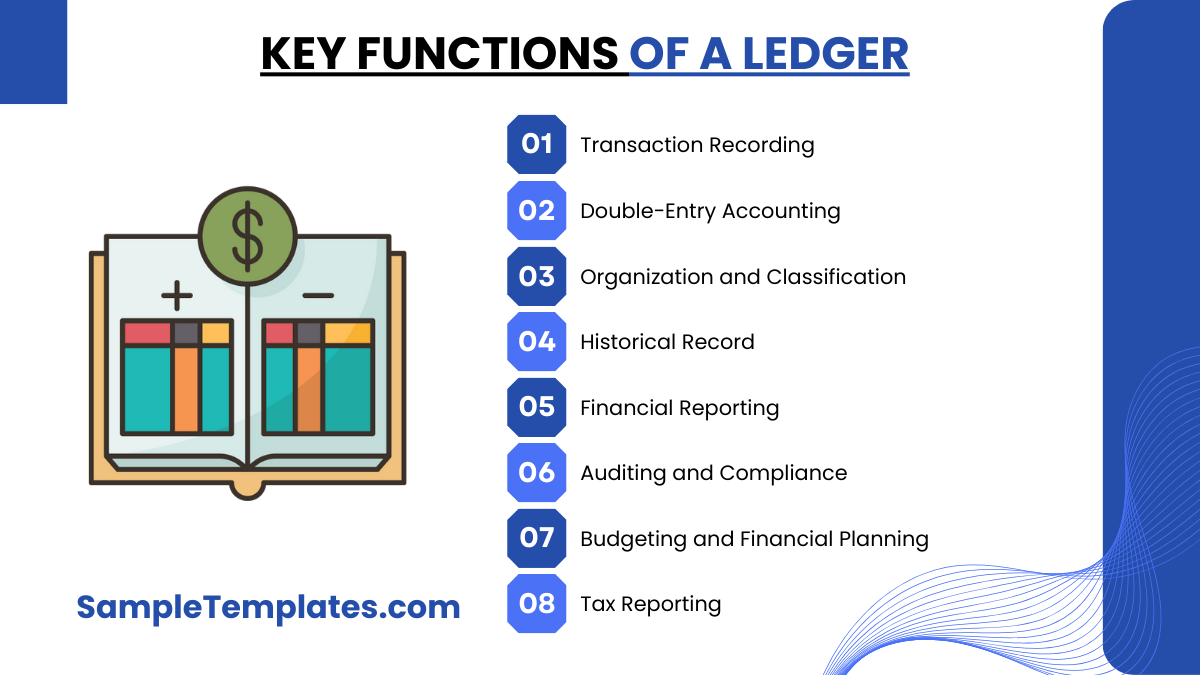
- Transaction Recording: A ledger is primarily used to record and document financial transactions. These transactions can include both inflows (income) and outflows (expenses) of money. Each entry in the ledger typically contains details such as the date, description, amount, and the category of the transaction.
- Double-Entry Accounting: One of the fundamental principles of ledger accounting is double-entry bookkeeping. This means that every transaction is recorded twice: once as a debit and once as a credit. Debits represent an increase in assets or expenses, while credits represent an increase in liabilities or income. This system ensures that the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) remains balanced.
- Organization and Classification: The ledger categorizes transactions into different accounts, making it easier to track and manage financial activities. Common accounts in a ledger include cash, accounts receivable, accounts payable, income, and various expense categories. This categorization allows for a clear overview of different financial aspects.
- Historical Record: Ledgers create a historical record of financial activities. This historical data is essential for tracking the financial progress and performance of a business or individual over time. It serves as an invaluable resource for analysis, financial planning, and decision-making.
- Financial Reporting: The ledger is a foundational element for generating financial reports such as income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements. These reports provide a comprehensive view of an entity’s financial health, profitability, and liquidity.
- Auditing and Compliance: Ledgers play a crucial role in auditing and ensuring compliance with financial regulations. They provide a clear and transparent trail of financial transactions that auditors can review to assess financial accuracy and compliance with accounting standards.
- Budgeting and Financial Planning: A well-maintained ledger aids in budgeting and financial planning. It helps individuals and businesses monitor their expenses, analyze financial trends, and make informed decisions regarding future financial activities.
- Tax Reporting: Ledgers are essential for tax purposes. When filing taxes, individuals and businesses rely on the information contained in their ledgers to report income, expenses, deductions, and other relevant financial data accurately.
10. General Ledger Excel Template
11. Sales Ledger Template Excel
12. Ledger Format Excel Download
13. General Ledger Template Excel Free Download
14. Ledger Excel Sheet
Why is Ledger Important?
Ledgers are essential in accounting and financial management for several reasons:
- Financial Record-Keeping: Ledgers serve as the primary tool for recording and organizing financial transactions. They provide a detailed account of every financial event within an organization, ensuring that nothing is overlooked.
- Accuracy and Accountability: Ledgers use double-entry bookkeeping sample, where every transaction has both a debit and a credit entry. This system promotes accuracy and accountability by ensuring that financial records remain balanced.
- Financial Statements: Ledgers are the foundation for preparing key financial statements like the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. These statements are crucial for assessing a company’s financial health, performance, and compliance.
- Tracking Transactions: Ledgers allow for the tracking of individual transactions, making it easier to monitor who owes the company money (accounts receivable) and whom the company owes (accounts payable). This aids in efficient cash flow management.
- Budgeting and Planning: Ledgers help in creating and managing budgets by tracking income and expenses. They assist organizations in making informed financial decisions and projecting future financial needs.
- Auditing and Compliance: Maintaining a ledger is critical for auditing purpose statement. It provides a clear, detailed record of all financial transactions, making it easier to verify the accuracy of financial statements and ensuring compliance with financial regulations.
- Performance Evaluation: Ledgers help assess a company’s financial performance over time. By comparing data from different periods, organizations can identify trends, areas for improvement, and successful strategies.
- Tax Reporting: Accurate ledgers are essential for tax reporting and compliance. They ensure that income and expenses are properly recorded and can be used as the basis for preparing tax returns.
- Legal Documentation: In case of legal disputes or financial investigations, ledgers serve as valuable legal documentation. They provide a transparent and detailed account of a company’s financial activities.
- Transparency and Investor Confidence: For publicly traded companies, maintaining clear and accurate ledgers is crucial to gaining the trust and confidence of investors and stakeholders. Reliable financial records enhance transparency and credibility.
Types of Ledgers
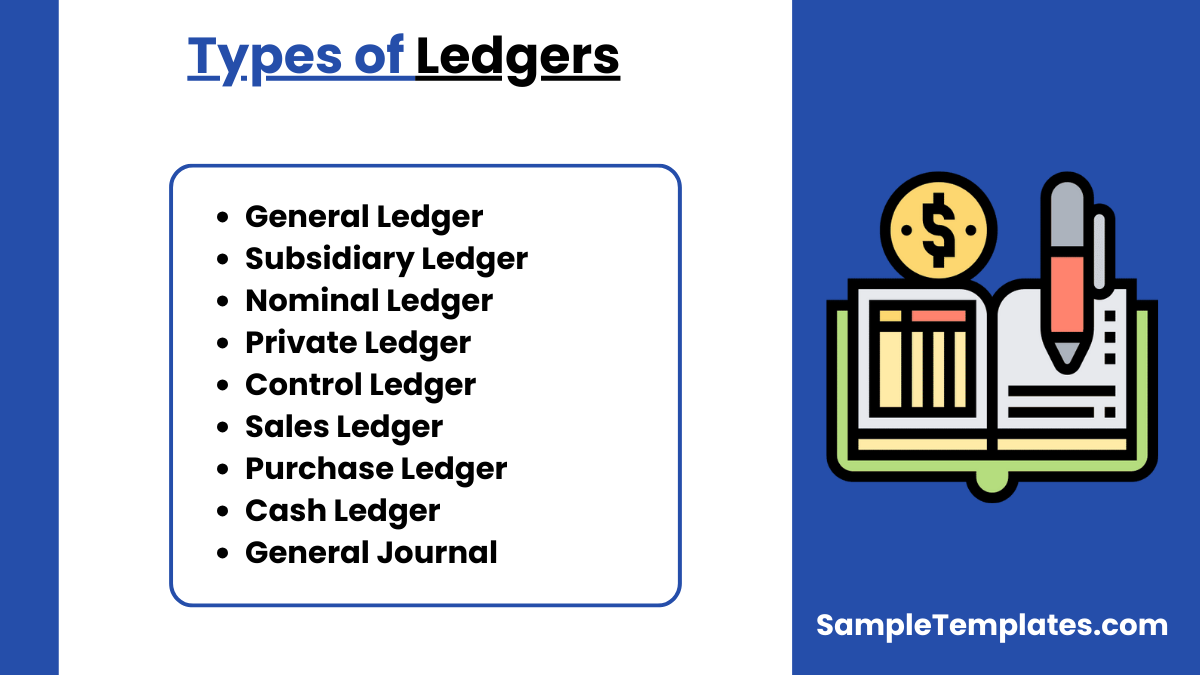
Ledgers are essential tools in accounting, used to record and manage financial transactions. They come in various types, each serving specific functions in financial record-keeping. Let’s explore the common types of ledgers:
1. General Ledger:
- The general ledger is the backbone of accounting. It contains all financial transactions of a business and is organized into various accounts. Each account corresponds to a specific category, such as assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, or expenses. The general ledger uses double-entry bookkeeping, ensuring that debits and credits balance for each transaction. It provides a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial position and is the foundation for creating financial statements.
2. Subsidiary Ledger:
- Subsidiary ledgers are supplementary to the general ledger. They break down specific accounts found in the general ledger, offering more detailed information. Common subsidiary ledgers include:
- Accounts Receivable Subsidiary Ledger: This ledger tracks individual customer accounts, detailing transactions like sales, payments, and outstanding balances.
- Accounts Payable Subsidiary Ledger: It records detailed transactions with suppliers, including invoices, payments, and outstanding balances.
- Inventory Subsidiary Ledger: Used by businesses to track individual inventory items, their purchase and sale transactions, and current quantities in stock.
- Fixed Asset Subsidiary Ledger: This ledger records details about a company’s fixed assets, such as buildings and equipment, including acquisition cost, depreciation, and disposal.
3. Nominal Ledger:
- The nominal ledger, also known as the nominal accounts or income statement, focuses on accounts related to revenue, expenses, gains, and losses. Unlike the general ledger, which encompasses all financial transactions, the nominal ledger specifically compiles accounts relevant to the income statement. It highlights a company’s financial performance over a specific period, summarizing revenue and expense accounts to calculate net profit or loss. The nominal ledger is instrumental in generating financial statements, especially the income statement.
4. Private Ledger:
- A private ledger is used by organizations to maintain confidentiality and privacy regarding specific financial transactions or information. It may contain sensitive data that is restricted to certain personnel or departments, ensuring that unauthorized individuals do not have access to these records.
5. Control Ledger:
- Control ledgers are often employed in larger organizations to monitor and control multiple subsidiary ledgers. They help ensure that subsidiary ledgers align with the general ledger and maintain accuracy and consistency across the financial records of the entire organization.
6. Sales Ledger:
- A sales ledger, often part of the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger, tracks all sales transactions and customer balances. It includes details about customer invoices, credit sales, and payments. It is crucial for managing the sales and credit operations of a company.
7. Purchase Ledger:
- The purchase ledger, often part of the accounts payable subsidiary ledger, records all purchases and outstanding payment obligations to suppliers. It includes information about supplier invoices, credit purchases, and payments, aiding in effective procurement management.
8. Cash Ledger:
- A cash ledger specifically tracks all cash transactions, including cash receipts and disbursements. It ensures a clear record of cash flow within an organization.
9. General Journal:
- While not a traditional ledger, the general journal is worth mentioning. It is used to record transactions initially before they are posted to specific ledger accounts. The general journal captures the debits and credits of individual transactions in chronological order.
15. Account Ledger Template Excel
16. Accounts Ledger Book in Excel
17. Excel Ledger Template with Debits and Credits
What Is an Excel Ledger?
A ledger is a document mainly used to record bookkeeping entries, as well as a balance sheet and income statement transactions. Unlike journal entries where you record transactions by date, a general ledger is a central location where account data is stored. Ledgers used to be recorded in actual books. In the present, ledgers get saved in Excel format, which makes the recording process easy and convenient. What you see in the traditional ledger book is basically the same as that of an Excel ledger. The only difference is that Excel ledgers are saved in computer files allowing for safer storage and retrieval of bookkeeping records.
Excel ledgers record accounts receivable, accounts payable, investment details, debit/credit, accrued expenses, inventory, etc. It is the main document used for generating business financial statements such as balance sheet samples, income statement samples, and cash flow statements. Excel ledgers are also used as a daily ledger, employee payroll ledger, project ledger, etc.
How To Make an Excel Ledger?
There’s a lot of simple self-employment ledger or double-entry journal templates in Excel that you can download online for free. Getting a hold of Excel ledger samples is pretty easy nowadays because of the availability of online templates. And to make your ledger making journey even better, here are some tips that you’ll find useful.
1. Use an Excel Template That Is Compatible with Your Computer Software
Indeed, you can easily download Excel templates online for free. But you can’t just choose the templates randomly because it may not work. The Excel template you download should be compatible with that of your computer’s software. If it’s not, then there may be restrictions on what you can do with the template, or you may not be able to open it at all.
2. Customize the Template as Needed
Downloadable Excel templates, like bookkeeping templates for self-employed, may tend to be generic. They sometimes lack the information that you’ll need for your work. So you shouldn’t use it as it is. It is best to customize the template by adding all the necessary tabs, columns, rows, sample charts, and graphs before you enter data. This way, you can easily ad quickly enter data into your ledger spreadsheet without stopping to add certain parts. It makes the task quicker.
3. Apply Excel Formulas Correctly
What makes Excel spreadsheet samples an excellent tool for accounting is that you can sample program specific cells with the appropriate formula to make the calculations for you automatically. It allows accurate computation results at all times. However, the accuracy of the computation will still depend on the data entered. A single mistake will affect the entire ledger, which requires you to start over.
4. Ensure That Data Entered Is Accurate
Having errors is possible if data is entered manually. Human mistakes are normal, but it doesn’t really mean that they’re acceptable. So you’ll need to be extra careful with everything you put in the ledger sample. Th accuracy of the ledger’s contents relies solely on the accuracy of the data added.
5. Always Check Your Work
And to ensure that your work is indeed accurate, you’ll need to check it a lot of times. Checking is time-consuming, but it will all be worth it if your work is error-free. Nothing beats an organized and error-free general ledger, so you should never take it for granted.
FAQs
What is Meant by Original Entry and Final Entry?
Journals and ledgers go together. Journals are referred to as the book of original entry simply because it is where financial report information comes from. Once all financial transactions get posted in the journal, they will be transferred to the general ledger. From there, key financial statements are made. That is why we refer to ledgers as the book of final entry.
What Is a Ledger?
A ledger is a record-keeping book or digital document used in accounting to track financial transactions. It includes detailed entries of credits (money received) and debits (money spent) for each account or category. Ledgers help maintain accurate financial records and enable the creation of financial statements like balance sheets and income statements.
How to Make a Ledger in Excel?
To create a ledger in Excel, open a new sample spreadsheet, label columns for Date, Description, Income, Expenses, Amount, and Running Balance. Enter financial transactions and use formulas for balance calculations.
Can I Use Excel for Tally?
Yes, you can use Excel for basic accounting and ledger keeping, similar to Tally software. While Tally is specialized accounting software, Excel can serve as a simple and versatile tool for maintaining financial records and ledgers for smaller businesses or personal use.
Can I Convert Excel to Tally?
Yes, you can convert data from Excel to Tally by exporting Excel data analysis in the appropriate format (e.g., CSV) and then importing it into Tally using Tally’s data import features. The exact process may vary depending on your specific needs and the version of Tally you’re using.
All the lines and numbers that you see in an Excel ledger will surely make you feel intimidated. Who wouldn’t? Just imagine the work needed if you make a single mistake. The best thing that you can do is to practice and familiarize Excel ledger formats. It’s possible with the use of the downloadable samples we’ve provided above. Make sure to check them out!
In conclusion, a ledger is the bedrock of financial record-keeping, ensuring accuracy, accountability, and informed decision-making in both personal and business finances. It’s an indispensable tool in the world of finance and accounting.
Related Posts
FREE 11+ Account Reconciliation Samples & Templates in PDF | MS Word
FREE 11+ Trial Balance Samples & Templates in PDF | MS Word
FREE 10+ Writing Journal Entry Samples and Templates in MS Word | PDF
FREE 10+ Double Entry Journal Samples and Templates in MS Word | PDF
FREE 10 + Revenue Recognition Samples & Templates in PDF | MS Word
FREE 11+ Liability Insurance Application Samples and Templates in MS Word | PDF
FREE 11+ Petty Cash Reconciliation Samples and Templates in MS Excel | PDF
FREE 10+ Reconciliation Statement Form Samples and Templates in MS Word | PDF | MS Excel
FREE 10+ Annuity Disclosure Form Samples & Templates in PDF
FREE 9+ Absorption Costing Samples & Templates in PDF | MS Word
FREE 10+ Prepaid Expenses Samples and Templates in PDF | MS Excel
FREE 7+ Depreciation Worksheet Samples & Templates in PDF | MS Word
FREE 10+ Turnover Ratio Analysis Samples and Templates in PDF
FREE 11+ Cost Volume Profit Analysis Samples & Templates in PDF | MS Word
FREE 10+ Bank Reconciliation Statement Samples and Templates in PDF | MS Word