Embrace unparalleled efficiency with our Sample Employee Sheet Template. Specifically tailored for HR aficionados and managers, this tool redefines excellence in employee data management. Experience heightened accuracy and draw insights effortlessly. Ready to revolutionize your HR processes? Begin your transformative journey with our all-encompassing employee data blueprint.
20+ Employee Sheet Samples
1. Employee Attendance Sheet Template

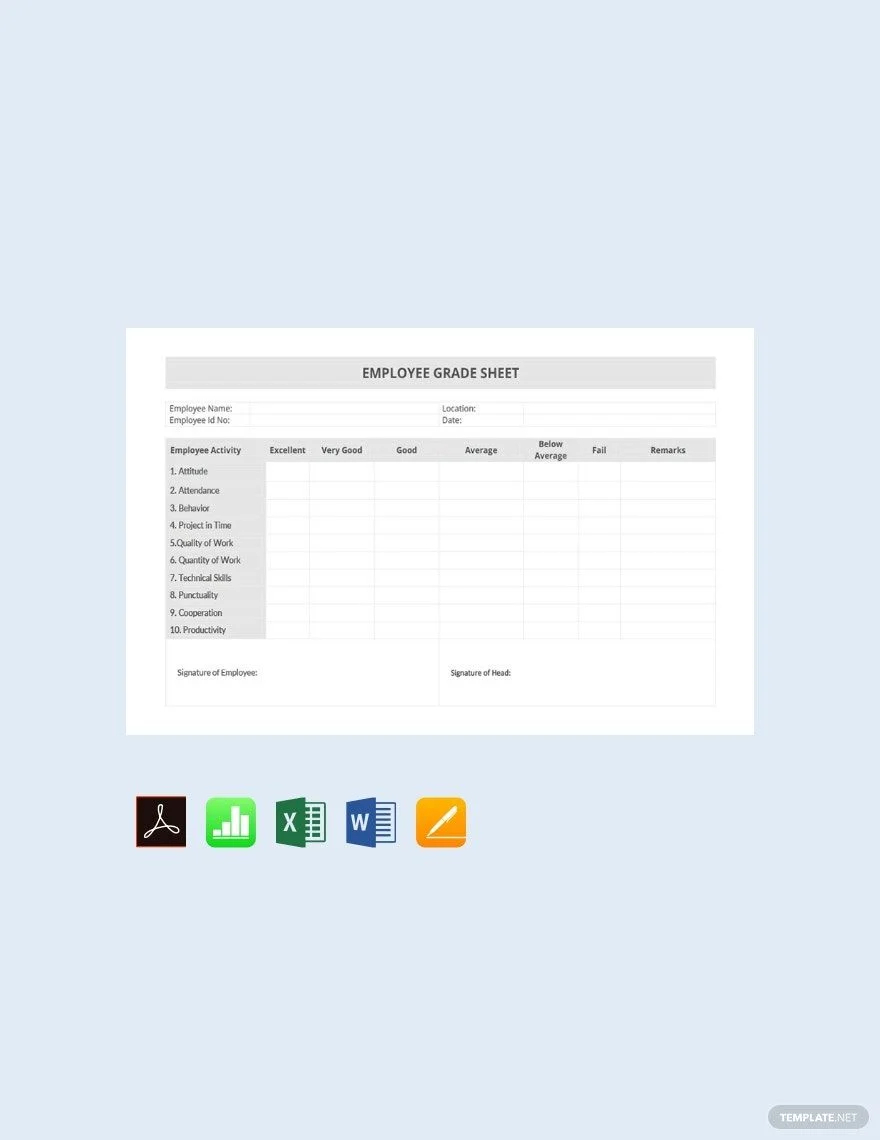
2. Employee Grade Sheet Template
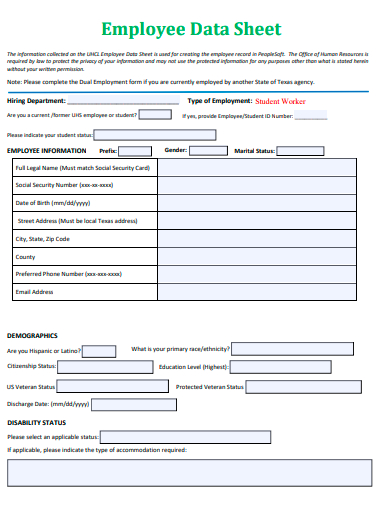
3. Employee Data Sheet Template
4. Sample Employee Information Sheet Template
5. Employee Activity Sheet Template
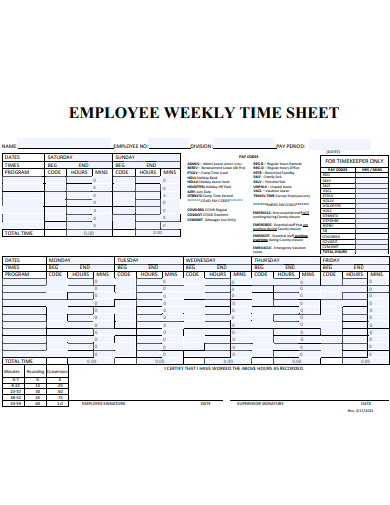
6. Hourly Employee Time Sheet Template
Creating an Employee Spreadsheet: A Comprehensive Guide
Crafting an effective employee spreadsheet is fundamental for businesses aiming to efficiently manage personnel data. Such a spreadsheet aids HR professionals and managers in tracking vital details, observing progress, and discerning trends. Here’s how to go about developing one:
Start by defining your objectives. Understand the core purpose behind your spreadsheet. Is it for tracking attendance, managing payroll, or overseeing performance? This clarity will shape the kind of columns and data you incorporate.
Select your platform wisely. Microsoft Excel might be the default choice for many, but other tools like Google Sheets or LibreOffice Calc can also serve the purpose, especially if collaboration is key.
Initiate with essential employee details. This would typically encompass the employee ID for unique identification, the full name, their position or role, the department they’re affiliated with, and their hiring date.
If the spreadsheet leans towards payroll, it’s prudent to include financial specifics. This would mean details such as the base salary, any allowances or bonuses, necessary deductions (like tax or health insurance contributions), and the net payable amount.
For those keen on monitoring attendance, columns dedicated to the days an employee was present, days they were absent, along with vacation and sick leave details would be pertinent.
Performance metrics are crucial for spreadsheets focusing on performance evaluations. Metrics could range from goals achieved and projects completed to Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) met. It’s also handy to have a section for feedback or comments.
Visualization can enhance comprehension. Incorporate relevant charts or graphs, especially when dealing with trends or comparisons. This not only makes the data more digestible but can also spotlight crucial patterns.
Given the sensitive nature of employee data, security is paramount. Employ password protection or other encryption methods, particularly if dealing with financial data. Access should be restricted to relevant personnel, and always ensure you maintain secure backups.
Keeping the spreadsheet updated is non-negotiable. Establish a routine for timely updates, and periodically review the entire sheet to ensure its relevance as business needs evolve.
Finally, harness the power of filters and sorting features that most spreadsheet software offers. This organization aids in sifting through data swiftly and viewing information in preferred sequences.
In sum, constructing an employee spreadsheet is a blend of planning, organization, and diligent execution. As businesses evolve, such tools become indispensable, making it all the more crucial to ensure their accuracy and relevance. Always prioritize data privacy and security, given the personal nature of the information being handled.
7. Employee Weekly Time Sheet Template
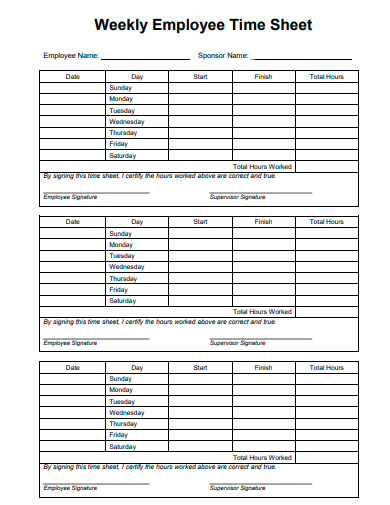
8. Weekly Employee Time Sheet Template
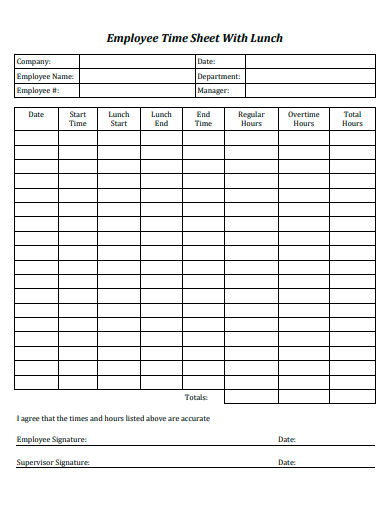
9. Employee Time Sheet With Lunch Template
10. Sample Employee Fact Sheet Template
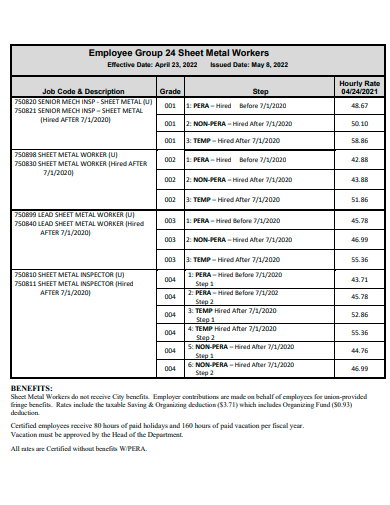
11. Employee Group Sheet Template
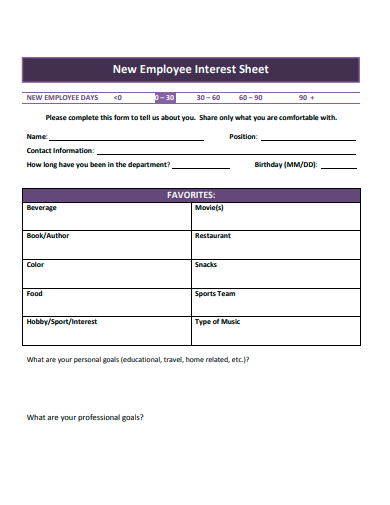
12. New Employee Interest Sheet Template
13. Professional Employee Performance Program Cover Sheet Template
What Should an Employee Sheet Include?
In any organization, an employee sheet is a critical tool for managing and organizing vital personnel data. Its comprehensive nature assists HR professionals and supervisors in making informed decisions, monitoring staff progression, and ensuring efficient workforce management. Here’s an in-depth look into the essential components that should be incorporated into an effective employee sheet:
Basic Personal Information:
Full Name: This acts as the primary identifier, ensuring clarity in communication and documentation.
Employee ID: A distinct identification number, ensuring each staff member has a unique identity within the company.
Date of Birth: This aids in recognizing age-related milestones and ensuring compliance with employment age regulations.
Contact Details: This should cover phone numbers, residential address, email addresses, and potentially emergency contacts.
Professional Details:
Position/Role: Clearly indicates the employee’s role and responsibilities within the organization.
Department: Helps in identifying the team or unit the employee is part of and assists in inter-departmental communications.
Date of Joining: Provides clarity on tenure, crucial for determining benefits, and understanding an employee’s journey within the company.
Reporting To: Details on the supervisory chain help streamline communications and hierarchical understanding.
Compensation and Benefits:
Basic Salary: A clear record of the employee’s foundational pay.
Additional Benefits: This includes bonuses, incentives, and any other perks offered.
Deductions: Details on statutory or optional deductions, such as taxes, insurance contributions, or pension funds.
Net Pay: A calculated column that provides the final monthly or annual take-home amount after considering all additions and deductions.
Attendance and Leave Records:
This section tracks the employee’s daily presence, noting any absences, late arrivals, early departures, and their reasons. It’s also where official leaves—such as vacation, sick leave, or any other form of time-off—are recorded, ensuring a clear record for payroll and other assessments.
Performance Metrics:
This area can encompass a range of metrics, from sales targets achieved and projects completed, to feedback received and professional milestones reached. It aids in both self-assessment and formal performance reviews.
Training and Development:
A section dedicated to the professional growth of the employee, detailing any training sessions attended, certifications earned, or courses completed. This showcases an employee’s commitment to continual learning and skill enhancement.
Miscellaneous Details:
Emergency Contact: Vital information for unforeseen circumstances, ensuring the company can connect with someone close to the employee if needed.
Work Authorization Status: For diverse workforces, especially those with international employees, this confirms if individuals have the legal right to work in a particular country or region.
Notes Section: A flexible space for any additional information or observations, from health considerations to notable achievements.
An employee sheet serves as a comprehensive snapshot of an individual’s professional journey and status within a company. By ensuring it’s detailed, regularly updated, and well-organized, businesses can make the most of this tool, enhancing their human resource management processes. Proper data privacy and security measures are imperative to protect the sensitive information such sheets contain.
14. Employee Personal Data Sheet Template
15. Employee Orientation Acknowledgement Sheet Template
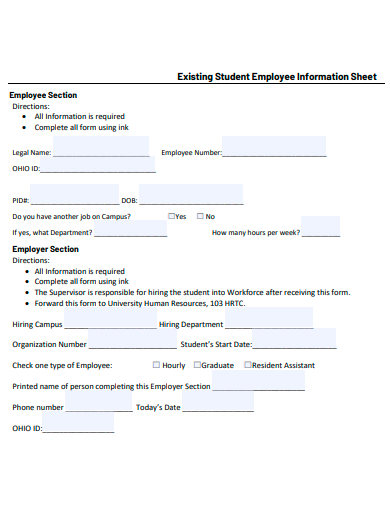
16. Sample Existing Student Employee Information Sheet Template
17. Employee Notification Sheet Template
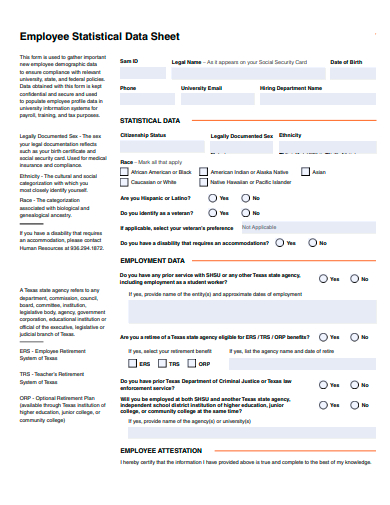
18. Employee Statistical Data Sheet Template
19. Employee Illness Policy Fact Sheet Template
20. Temporary Employee Checklist and Cover Sheet Template
21. Employee Injury Communication Tracking Sheet Template
What to Avoid When Tracking Employee’s Hours
Tracking employees’ hours is a fundamental practice for many businesses, especially those that pay hourly wages or need to manage overtime. While this practice is vital for payroll and productivity assessment, it comes with its pitfalls. Here are some things to avoid when tracking employee hours:
Invasive Monitoring:
While it’s essential to ensure that employees are working the hours they claim, overly invasive monitoring can feel like a breach of privacy. Avoid software that captures unnecessary screen recordings, keylogs, or personal data. Not only can this erode trust, but it may also expose your business to legal complications.
2. Relying Solely on Memory:
Encouraging employees to record their hours at the end of the week or month based on memory can lead to inaccuracies. It’s easy to forget the specifics over time, leading to potential overpayments or underpayments.
3. Ignoring Breaks and Rest Periods:
Not accounting for or discouraging legally mandated rest breaks can lead to burnout and decreased productivity. Moreover, not tracking or compensating for these breaks where required by law can expose businesses to legal challenges.
4. Using Outdated Systems:
Paper timesheets or old software systems are not just inefficient; they’re prone to errors. In today’s digital age, using outdated tracking methods can result in inaccurate reporting and unnecessary administrative burdens.
5. Neglecting to Offer Flexibility:
In a world that’s increasingly leaning towards flexible work hours, rigid tracking mechanisms that don’t allow for variations can demotivate employees. While it’s crucial to ensure accountability, it’s equally vital to respect and accommodate genuine needs for flexibility.
6. Not Reviewing for Accuracy:
Simply having a tracking system in place isn’t enough. Regularly review the data for inconsistencies or anomalies. This can help identify genuine errors or potential cases of time theft.
7. Overemphasis on Quantity Over Quality:
Focusing solely on the number of hours worked without considering the quality of work can be counterproductive. Employees might clock in the required hours but might not necessarily be productive. Balance the importance of hours tracked with performance outcomes.
8. Failing to Communicate Purpose:
If employees don’t understand why their hours are being tracked or believe it’s just a mechanism for excessive scrutiny, they might become resistant or demotivated. Ensure you communicate the reasons, whether it’s for payroll accuracy, fair allocation of work, or other valid business purposes.
9. Not Training Staff on the System:
Implementing a time tracking tool without adequate training can lead to confusion, mistakes, and non-compliance. Ensure every employee understands how to use the system accurately.
10. Ignoring Legal and Compliance Aspects:
Different regions have varied laws regarding work hours, overtime, and employee monitoring. It’s crucial to be aware of these regulations and ensure that your tracking methods are compliant.
In Conclusion:
Tracking employee hours is a delicate balance between ensuring accountability and respecting privacy and autonomy. The key is to approach it with transparency, fairness, and an understanding of both business and employee needs. By avoiding these pitfalls, businesses can create a harmonious work environment where time tracking becomes a tool for mutual benefit rather than a source of contention.
Related Posts
FREE 5+ Construction Bid Sheet Samples in PDF | MS Word | Excel
FREE 15+ Construction Timesheet Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 26+ Construction Sheet Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | Excel
FREE 20+ Continuation Sheet Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 25+ Program Sheet Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | Pages | PDF
FREE 33+ Student Sheet Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 32+ Planning Sheet Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 10+ OC Sheet Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Beat Sheet Samples in PDF
FREE 3+ Paper Sign Up Sheet Samples in PDF
FREE 50+ Summary Sheet Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | Google Sheets | Excel | PDF
FREE 10+ Cleaning Bid Sheet Samples [ Commercial, House, Residential ]
FREE 10+ Group Sheet Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Family Group Sheet Samples in PDF
FREE 5+ Printable Blank Signing in Sheet Samples in PDF