A solid plan is required for any successful data analysis endeavor. The data analysis project plan depicts several of the project’s core requirements. The plan provides the structure of the data, declares the study’s objectives, describes the data sources, and specifies the study’s procedures. Because it explains the study’s techniques and objectives to supervisors, grant writers, and experts in the field, the plan paper becomes an important aspect of the project. Starting a big data project is fraught with uncertainties. What are the project’s objectives? What should you be aware of when it comes to your data? So, where do you start? As a data analyst or someone who routinely works with data, it’s critical to know how to manage a data analytics project to ensure efficiency and the best results for your clients. Understanding the data analytics lifecycle is one of the first stages.
What is Data Analysis Plan? A data analysis plan is a road map for organizing and analyzing survey data, and it should assist you to accomplish three goals related to the goal you set before you started your survey:
– Provide answers to your most pressing research questions
– To better comprehend the responses, ask more precise survey questions.
– Divide poll respondents into demographic categories to compare their views.
10+ Data Analysis Project Plan Samples
1. Data Analysis Project Plan Template

2. Quality Assurance Data Analysis Project Plan
3. Data Analysis Project Plan
4. Sample Data Analysis Project Plan
5. Data Analysis Session Project Plan
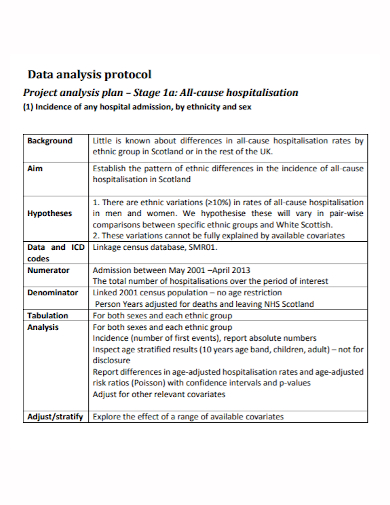
6. Data Analysis Protocol Project Plan
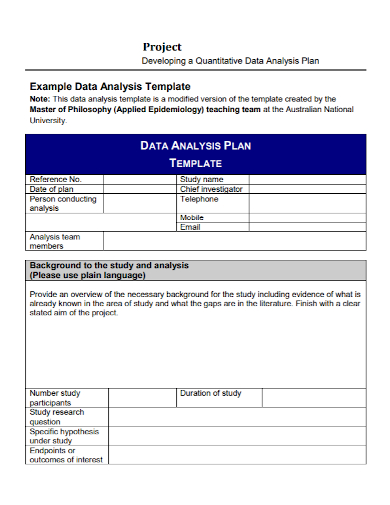
7. Quantitative Data Analysis Project Plan
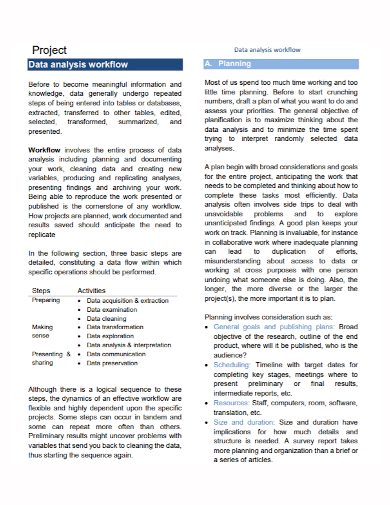
8. Data Analysis Workflow Project Plan
9. Data Analysis Program Project Plan
10. Group Project Data Analysis Plan
11. Data Analysis Summary Project Plan
Writing Data Analysis Project Plan
- Project Objectives – The project’s objectives must be included in the data analysis project plan. These goals show interested parties what the plan’s goals are and what a thorough review of the data should disclose. The project’s goals should be centered on a specific business question, such as “How do changes in raw material prices affect the company’s profits?” or “How do social media posts affect stock prices?”
- Data Sources – The next point the plan should address after establishing the project’s objectives is the sources of the data to be included in the report. Annual sales or stock prices are examples of objective data sources, while observations and opinions are examples of subjective data sources. For example, more objective data sources will be used in financial data analysis plans, but more subjective data sources will be used in marketing and leadership assessments.
- Collection Methods – The data collection methods must also be included in the plan. Annual reports, industry sales numbers, and stock price histories can all provide objective data to analysts. Customer surveys, opinion polls, and face-to-face interviews are all methods for gathering subjective data. The strategy must demonstrate why each method is being used and how it will help the project achieve its goals. If the procedures outlined in the plan do not align with the project’s goals, the project’s request for resources to execute the task may be denied.
- Analysis Methods – After the data collection tasks are accomplished, the project’s next phase is to analyze the data. The methodologies used to analyze the data must be included in the project plan. Quantitative approaches, such as statistical measurements, and qualitative methods, such as assessing sentiments or perceptions, are both available. The type of analysis methodologies to be utilized is frequently dictated by the project’s objectives. For example, a data analysis study with the goal of determining consumer satisfaction with a new product could employ both quantitative and qualitative methods, such as data from customer surveys.
FAQs
Why do you have to understand business issues?
You will be provided a brief description of the expectations when you are assigned a data project. You should be able to figure out what the company’s main goals are based on that outline. You should look at the project’s general scope, business objectives, the information the stakeholders are looking for, the type of analysis they want you to apply, and the deliverables (the project’s outputs).
How do you prepare the data?
You can start cleaning your dataset once you’ve structured and identified all of the variables. In this stage, you’ll fill in any missing variables, create new broad categories to help categorize data that doesn’t fit anywhere else and eliminate any duplicates from your data. The data will be processed more effectively without being skewed if average data scores are computed for categories where there are missing values.
How do you validate the data?
After you’ve created your models, you’ll need to evaluate the data to see if you have all of the information you need for your deliverable. Did the models perform as expected? Is there anything further that needs to be done with the data? Did you get the response the client was looking for? If not, you may need to repeat the preceding procedures. Expect a great deal of trial and error!
If you want to see more samples and formats, check out some data analysis project plan samples and templates provided in the article for your reference.
Related Posts
FREE 9+ 30-Day Marketing Plan Samples in PDF | MS Word | Apple Pages | Google Docs
FREE 3+ Sales Team Action Plan Samples in PDF | MS Word | Apple Pages | Google Docs
Marketing Plan For Small Business Samples
FREE 7+ Fashion Business Plan Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Sprint Planning Samples In MS Word | Google Docs | PDF
FREE 10+ Wedding Planning Samples in MS Word | Apple Pages | Powerpoint | PDF
FREE 9+ Monthly Study Planner Samples in PSD | Illustrator | InDesign | PDF
FREE 9+ Sample Curriculum Planning Templates in PDF | MS Word
FREE 10+ Teacher Development Plan Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages | PDF
FREE 10+ Basketball Practice Plan Samples in PDF
FREE 12+ School Business Plan Samples in PDF | MS Word | Apple Pages | Google Docs
FREE 7+ Client Strategic Plan Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 11+ Trucking Business Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word | Google Docs | Pages
FREE 7+ Small Hotel Business Plan Samples PDF | MS Word | Apple Pages | Google Docs
FREE 14+ Bakery Business Plans in MS Word | PDF | Google Docs | Pages