Evaluations have the freedom to use either the qualitative or quantitative data method. In some cases, it can be applicable to both. These two methods can simply provide information pertaining to the evaluation process and can be used to improve the engagement within the community. It is rarely used alone under certain circumstances. When combined, they would basically produce a great overview of a particular project.
10+ Quantitative Evaluation Samples
1. Quantitative Analysis Evaluation
Quantitative evaluation methods follow a specific criteria in every project evaluation process in cases of: formal acceptance or rejection over a decision of a specific ergonomic project, choosing between the several ergonomic projects that want to achieve the same goal to solve a particular problem, ranking of ergonomic projects due to an instance that the amount of requested capital expenditures would be greater than the funds available, choosing between a particular ergonomic project and a non-ergonomic project, and controlling over the cost of the solutions implemented.
2. Quantitative Data Evaluation
Quantitative data often gives information that answers “how many?”, “who were involved?”, “what is the result?”, and “how much does it cost?” It can be collected through various ways such as having surveys and questionnaires, tests (pretests and posttests), observation method, and reviewing of the existing files and databases. Surveys can be done online or face-to-face. When you are going to analyze a quantitative data, it would usually involve statistical analysis from a basic descriptive statistics to a complex type of analysis.
Quantitative data measures both the depth and breath of the project implementation and is collected either before and after the intervention that would show the outcomes and impact. The limitation in using this type of method of evaluation is that it may include poor response rates coming from the results of the surveys, the difficulty in obtaining needed documents, and the difficulty in every valid measurement.
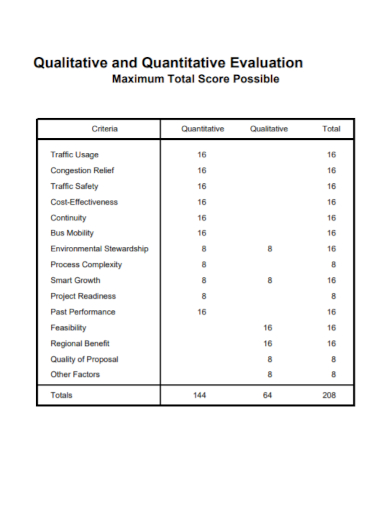
3. Qualitative and Quantitative Evaluation
4. Qualitative Evaluation
In a qualitative evaluation, you are more focused on the questions like “who was responsible?”, “when did it happen?”, and “what value was added?” These type of data are being collected through participant observation, focus groups, interview, and case studies and those that are coming from written documents. The method of analysis would usually comprise of comparing and contrasting, examining, and interpreting various patterns. Also, the analysis would likely to include items like themes, reducing data to essential points, coding, clustering, and other similar approaches.
The strength of having a qualitative data includes providing contexts that would explain certain issues and complementing quantitative data by explaining the reason and process behind the occurrence. The limitations include lack of generalizability, time-consuming, costly, and has a difficult and complex manner of analyzing and interpreting data.
5. Analyzing Quantitative Data Evaluation
6. Reconstructive Surgery Quantitative Evaluation
7. Quantitative Evaluation of Static Analysis
8. Clinical Quantitative Evaluation
9. Summer Awards Quantitative Evaluation
10. Quantitative System Evaluation
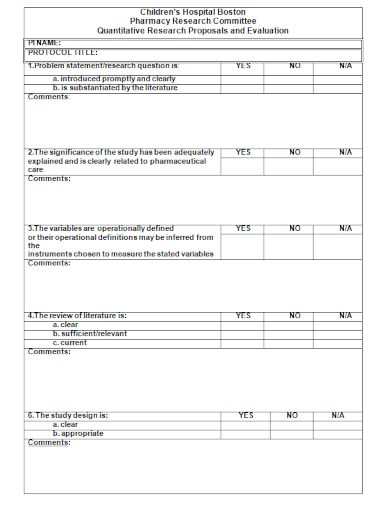
11. Quantitative Research Proposal Evaluation
All About Quantitative Evaluation
Quantitative evaluation is considered as something that is outcome-oriented wherein you basically need to have a predefined outcome of your project. This will test you how your project is doing using the numerical data. It would be wiser if you are going to compare the “pre” with “post” during the duration of the program. You could use a questionnaire that would ask each of the participants to detail their experiences from the program which is included in the “pre” part and try to provide a reflection of their experience before the program started or in the “post” part. This is called a retrospective post-pre survey. It is even preferable to have it compare with the possible changes in the participants with the changes that have occurred in the similar group.
FAQs
When to use quantitative evaluation?
Quantitative evaluations are useful to projects that has a goal to provide an impact into the specific, predefined outcome. The project itself must have a large group of active participants that has a statistical power to detect changes that is related to the program. There have been several factors that influence the calculations in the sample size and statistical power. Calculating the sample size can help you in knowing the population size, confidence level, and the margin of error.
When not to use quantitative evaluation?
Do not use quantitative evaluation when the project does not prefer to predefined outcomes, intrinsic value of the art-making, not interested in having to understand why the program appears to have more effect, have small groups that are not numerous enough to show the significant changes in indicators, and difficult to gather complete or close to complete a specific data.
If you want to see more samples and format, check out some of the quantitative evaluation samples and templates in the article to be guided.
Related Posts
FREE 10+ Employee Self-Evaluation Sample in PDF
FREE 10+ Restaurant Income Statement Samples [ Proforma, Monthly, Projected ]
FREE 10+ Scholarship Evaluation Samples [ Interview, Training, Monitoring ]
FREE 10+ Dependability Evaluation Samples in PDF | DOC
FREE 10+ Quantity of Work Evaluation Samples [ Employee, Self, Performance ]
FREE 10+ Heuristic Usability Evaluation Samples [ Website, Testing, Inspection ]
FREE 10+ Job Knowledge Evaluation Samples [ Employee, Skills, Self ]
FREE 10+ Consultant Performance Evaluation Samples in PDF | DOC
FREE 10+ Job Interview Evaluation Samples [ Teacher, Candidate, Performance ]
FREE 10+ Grant Proposal Evaluation Samples in PDF | DOC
FREE 10+ Faculty Performance Evaluation Samples in PDF | DOC
FREE 10+ Internship Evaluation Samples [ Supervisor, Self, Performance ]
FREE 10+ Resident Evaluation Samples [ Medical, Self, Rotation ]
FREE 10+ Dissertation Evaluation Samples [ Critical, Service, Self ]
FREE 3+ Front Desk Evaluation Samples [ Performance, Receptionist, Employee ]