A RAID Log is a project manager’s best ally, serving as a dynamic document that identifies and tracks Risks, Assumptions, Issues, and Dependencies. It’s a cornerstone in project management that ensures transparency and control, allowing teams to mitigate potential pitfalls while streamlining communication. By maintaining a detailed RAID Log, project leaders can proactively address challenges, align expectations, and navigate the complexities of project dynamics with confidence and clarity.
8+ RAID Log Samples
1. Sample Risk Management RAID Log Template

2. Sample Project RAID Log Template

3. Sample Program RAID Log Template

4. Sample Agile RAID Log Template

5. Sample RAID Log For Project Management Template

6. Sample RAID Log Analysis Template

What is RAID Log?
Introduction to RAID Log
In project management, staying organized and proactive is crucial for success. A RAID Log is a simple yet effective tool used by project managers to track and mitigate potential risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies throughout the life cycle of a project. It serves as a central record, ensuring that any concerns which could impact the project’s trajectory are managed with due diligence. You can also see more templates like Assumption Log Samples.
The Components of a RAID Log
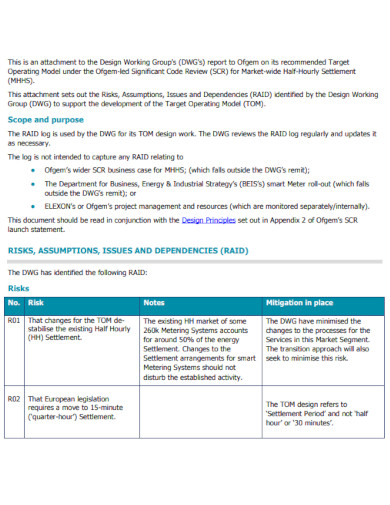
Risks Risks are potential future events that could have adverse effects on the project if they occur. Identifying risks early allows for the development of mitigation strategies to either prevent the risk from happening or to reduce its impact if it does.
Example: A software development project might identify a risk such as “key personnel availability.” The mitigation strategy could involve cross-training team members or hiring temporary contractors.
Assumptions Assumptions are statements about the current or future state of affairs assumed to be true in the absence of proof. They are necessary for sample planning but need to be validated to avoid unexpected impacts on the project.
Example: An assumption might be that “third-party APIs will remain stable throughout the project.” To manage this, the project team would regularly check for updates from the third-party provider.
Issues Issues are current problems that need to be addressed. Unlike risks, which are potential problems, issues are actively impacting the project and require immediate attention.
Example: An issue could be that “the project is currently over budget.” The project manager would need to analyze the budget, identify areas to cut costs, and adjust the project plan accordingly.
Dependencies Dependencies are the relationships between tasks that determine the order in which activities need to be performed. Understanding dependencies is key to developing a realistic project schedule.
Example: A dependency in a construction project could be that “the foundation must be laid before the framing can begin.” The project schedule would reflect this sequence to ensure timely completion.
The Significance of a RAID Log in Project Management
A RAID Log is not just a document; it’s a strategic approach to project management that emphasizes foresight, preparedness, and continuous monitoring. It’s a living document that evolves with the project, ensuring that every potential hiccup is anticipated and planned for. By keeping a RAID Log, project managers can maintain a bird’s-eye view of the project landscape, identifying potential pitfalls before they become problematic.
Implementing a RAID Log in Project Management
To effectively implement a RAID Log, it should be:
- Accessible: Keep the log where all stakeholders can view and contribute. This could be a shared document or a project management software tool.
- Reviewed Regularly: Update and review the RAID log in regular project meetings to ensure that it remains a live document and an integral part of the project management process.
- Integrated: Ensure that the RAID log is integrated with other project documents and processes, such as the risk management plan or the project schedule.
Benefits of Using a RAID Log
- Enhanced Communication: It provides a platform for discussing concerns related to risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies.
- Improved Preparedness: By identifying and tracking potential problems, teams can develop strategies to address them before they escalate.
- Better Decision Making: With a clear understanding of the project’s uncertainties, project managers can make more informed decisions.
Deep Dive into the Elements of a RAID Log
Risks: Navigating Project Uncertainties
Identifying risks is an ongoing process. Project managers must engage with their teams, stakeholders, and other project environments to identify and assess new risks regularly. Each risk is evaluated based on its likelihood and impact, allowing for prioritization and resource allocation to manage it effectively.
Assumptions: The Building Blocks of Project Planning
Assumptions should be documented with as much detail as possible and regularly revisited. They form the foundation upon which project plans are built. When an assumption changes, it can have a ripple effect on the project scope, timeline, and budget, necessitating quick adjustments to the project plan.
Issues: Tackling Project Realities
When issues arise, they are logged with specific details, including who is responsible for resolving them and by when. This clarity ensures that issues are addressed promptly and do not evolve into larger problems that could jeopardize project success.
Dependencies: Orchestrating Project Flow
Dependencies must be carefully managed to ensure that delays do not propagate through the project timeline. Project managers must work closely with team leads to understand the intricacies of task interdependencies and to adjust the project schedule dynamically as things change.
Strategies for Effective RAID Log Management
Consistency and Visibility: The Cornerstones of RAID Log Efficacy
For a RAID Log to be effective, it must be consistently updated and made visible to all project stakeholders. This transparency fosters trust and ensures that everyone is aligned on the project’s status and potential obstacles.
Integration with Project Lifecycle: Ensuring RAID Log Relevance
The RAID Log should be reviewed at each phase of the project lifecycle, from initiation through to closure. This ensures that the log is always relevant and that any new risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies identified during the project are captured and managed. You can also see more templates like Sample Logs.
Leveraging Technology: Enhancing RAID Log Accessibility
Project management software can be used to maintain the RAID Log, providing features such as automated reminders, easy updates, and real-time visibility. This technological integration can significantly enhance the utility and effectiveness of the RAID Log.
The Impact of RAID Log on Project Outcomes
Proactive Problem-Solving: The Hallmark of RAID Log Utilization
By proactively managing the elements of the RAID Log, project managers can prevent many issues from occurring and quickly resolve those that do arise. This proactive approach is key to maintaining project momentum and achieving objectives.
Stakeholder Confidence: The Byproduct of Transparent RAID Management
A well-maintained RAID Log can build stakeholder confidence by demonstrating that the project team is in control and prepared to handle uncertainties. This confidence can be crucial for project support and funding.
7. Sample Fillable Project RAID Log Template
8. Sample RAID Log Template
9. Sample Printable RAID Log Template
How can I Collect RAID Logs?
To collect RAID logs effectively, follow these steps:
1. Establish a RAID Log Framework:
- Create a template that includes sections for Risks, Assumptions, Issues, and Dependencies.
- Ensure that the template allows for the recording of details such as description, impact, probability, mitigation strategies, owner, and status.
2. Engage Your Team:
- Conduct brainstorming sessions with your project team to identify initial entries for each section of the RAID log.
- Encourage team members to contribute to the tracking log based on their expertise and project experience.
3. Consult Stakeholders:
- Interview key stakeholders to gather their insights on potential risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies.
- Stakeholders can provide a different perspective that might be overlooked by the project team.
4. Review Project Documentation:
- Analyze existing project documents such as the project plan, risk management plan, and communications plan for potential entries.
- Previous project reports and post-mortem analyses can also be valuable sources of information.
5. Regularly Update the Log:
- Make updating the RAID log a regular part of team meetings and project reviews.
- Assign responsibility to team members for updating specific sections relevant to their work.
6. Integrate with Project Management Tools:
- Use project management software that includes RAID log functionality or allows for integration.
- This ensures that the RAID log is accessible and can be updated in real-time.
7. Monitor and Review:
- Schedule regular reviews of the RAID log to ensure it remains up-to-date and relevant.
- Use these reviews to track the progress of risk mitigation, assumption validation, issue resolution, and dependency management.
By following these steps, you can collect and maintain a comprehensive RAID log that will serve as a valuable tool for managing your project’s challenges and uncertainties.
What is a Risk in a RAID Log?
A risk in a RAID Log represents a potential problem that, if it materializes, could cause project delays, increase costs, or lead to other negative outcomes. It is a future event with a certain degree of uncertainty and is identified through a process of risk assessment.
Why do we need RAID Log?
We need a RAID Log to systematically track and manage potential risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies in a project, ensuring that each is addressed proactively to minimize negative impacts on the project’s success.
What is the Main Advantage of RAID Log?
The main advantage of a RAID log in project management is that it provides a clear and organized way to monitor and control potential risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies that could impact the project, thereby enhancing decision-making and increasing the likelihood of project success.
In conclusion, a RAID Log is a dynamic tool that supports the management of uncertainties in projects. By systematically tracking risks, assumptions, issues, and dependencies, project teams can enhance their ability to deliver successful outcomes. As with any tool, its effectiveness is dependent on its consistent application and integration into the project management process. With diligent use, a RAID Log can become an indispensable part of any project manager’s toolkit, paving the way for smoother project execution and management.
Related Posts
FREE 10+ Cleaning Log Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Daily Work Log Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Sworn Affidavit Samples in PDF
FREE 10+ Tracking Log Samples in PDF | MS Word
FREE 10+ Receiving Log Samples in PDF
FREE 4+ Assumption Log Samples in PDF | DOC
FREE 10+ Issues Log Samples in PDF | DOC
News Report
Employee Uniform Form
Self-Declaration Form
To Whom It May Concern Letter
10 FREE Notice To Quit Letter Samples & Templates
Security Company Profile
Written Warning
Event Program