Quality is possibly the most important characteristic to look for in any business or company on the planet. The owner or manager of any type of business is constantly striving for a certain level of excellence. A variety of factors can have an impact on this, ranging from product and service quality to the quality of the resources used to manufacture them. Everyone is concerned with ensuring that their products meet the expectations of their investors, stakeholders, and, most importantly, their customers and clients. There is a responsibility to ensure that high-quality products and services are available when there is a demand for them. They take a number of critical steps to ensure that the product they produce is marketable. Numerous factors must be in place for these stages to run smoothly and to achieve the highest level of consistency in the quality of their product. These parameters are determined by good control plans, which in turn are determined by good control plans.
Meticulous planning is required to ensure that the final product meets quality standards. It saves both time and money by lowering the likelihood of defective items after they have been manufactured or assembled. In this regard, high-quality action plans are also extremely effective. A quality management system not only lays out the actions and rules that, if followed correctly, will ensure that the final product is of the highest possible quality, but it also provides a clear picture of the high level of quality that the company or firm is attempting to achieve. You can learn more about how a quality control inspection form works by reviewing the examples below, which will help you understand what it is and how to use it. You can also use them as a guide to help you create your own quality plan.
10+ Quality Control Inspection Form
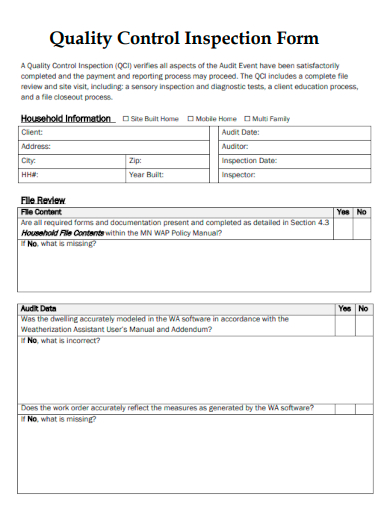
1. Quality Control Final Inspection Form
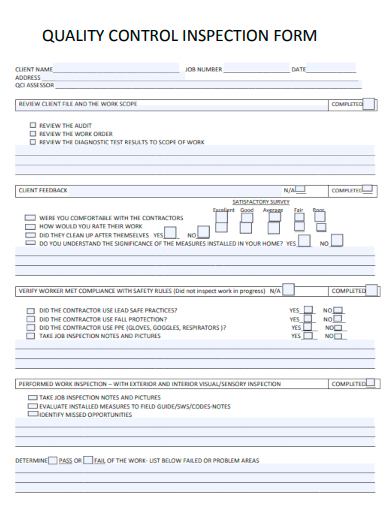
2. Sample Quality Control Inspection Form
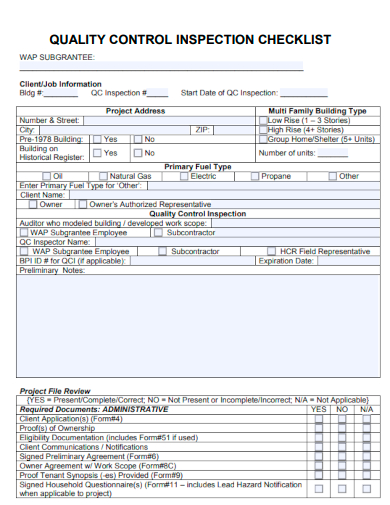
3. Quality Control Inspection Checklist Form
How to Write a Quality Control Inspection Form?
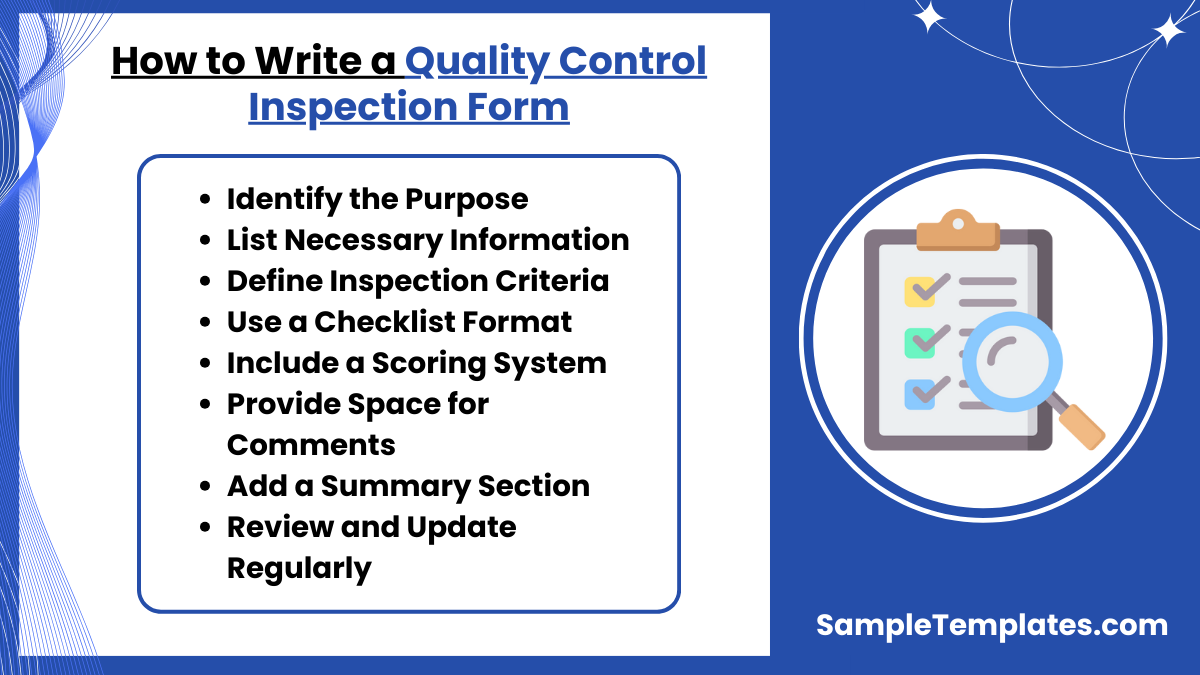
- Identify the Purpose: Clearly define what the form will be used to inspect, whether it’s a product, process, or service. This will guide the overall structure of the form.
- List Necessary Information: Start the form with fields for essential details like the inspector’s name, date, time of inspection, and product batch number or service type.
- Define Inspection Criteria: Outline specific criteria that need to be met for the item or service to pass quality control. These should be measurable and clearly defined.
- Use a Checklist Format: Organize the criteria into a checklist format to simplify the inspection process. This allows inspectors to easily mark each item as compliant, non-compliant, or not applicable.
- Include a Scoring System: Implement a scoring system if applicable, to quantify the results. This can help in deciding whether a product meets the quality threshold set by the company.
- Provide Space for Comments: Allow room for inspectors to add comments or notes on each item. This can be invaluable for addressing issues and implementing improvements.
- Add a Summary Section: Include a section at the end for the inspector to summarize the overall condition of the product or service, including recommendations or final decisions.
- Review and Update Regularly: Ensure the form is kept up-to-date with any changes in quality standards or company policies. Regular reviews can help maintain its relevance and effectiveness.
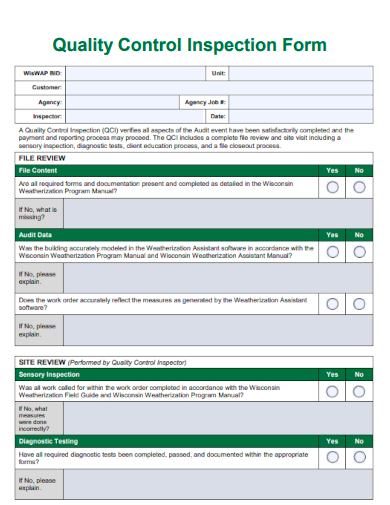
4. Basic Quality Control Inspection Form
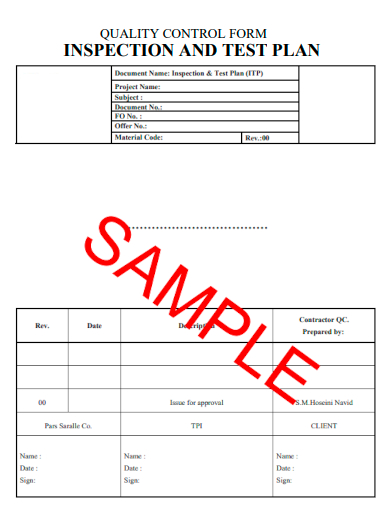
5. Quality Control Inspection & Test Plan Form
How Do I Make a QC Checklist?
- Define Objectives: Start by defining the specific objectives of the QC checklist. What aspects of the product or process are you aiming to assess? This sets the direction for the entire checklist.
- Consult Standards and Regulations: Review industry standards, legal regulations, and internal quality guidelines that the product or process must comply with. This ensures your checklist covers all necessary requirements.
- Identify Key Quality Attributes: List the critical attributes or characteristics that define the quality of the product or process. These can include dimensions, weight, color, functionality, or any other relevant attributes.
- Develop Criteria for Evaluation: For each quality attribute, develop clear, measurable criteria that specify what acceptable and unacceptable outcomes look like. This can include tolerance levels, visual defects, performance benchmarks, etc.
- Structure the Checklist: Organize the checklist in a logical flow that mirrors the production process or sequence of use. Group related attributes together to make the checklist intuitive and easy to follow.
- Choose a Format: Decide on a checklist format—such as a table or series of boxes—that allows for easy marking and offers space for comments or notes. Ensure there is ample room for inspectors to write observations if needed.
- Pilot the Checklist: Test the checklist on a small batch of products or during a trial run of the process. This trial run can help identify any gaps in the checklist and provide insights into its practical application.
- Review and Revise Regularly: After the initial implementation, collect feedback from the users of the checklist and review the outcomes it helped achieve. Regularly update the checklist to refine the criteria, adjust for new standards, or incorporate new quality goals.
6. Formal Quality Control Inspection Form
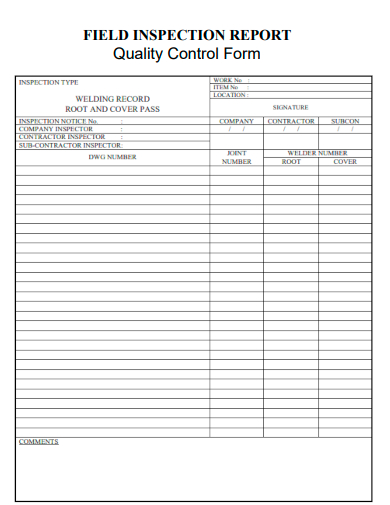
7. Field Inspection Report Quality Control Form
8. Quality Control Daily Inspection Report Form
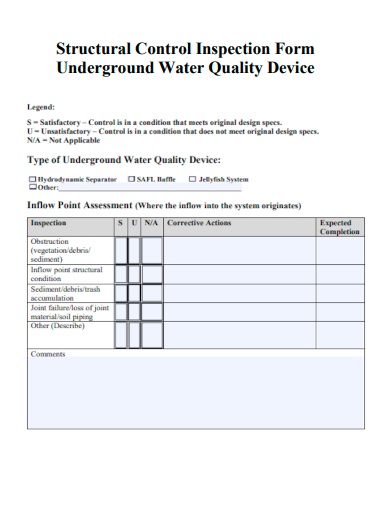
9. Structural Control Inspection Form Underground Water Quality Device
Types of Quality Control?
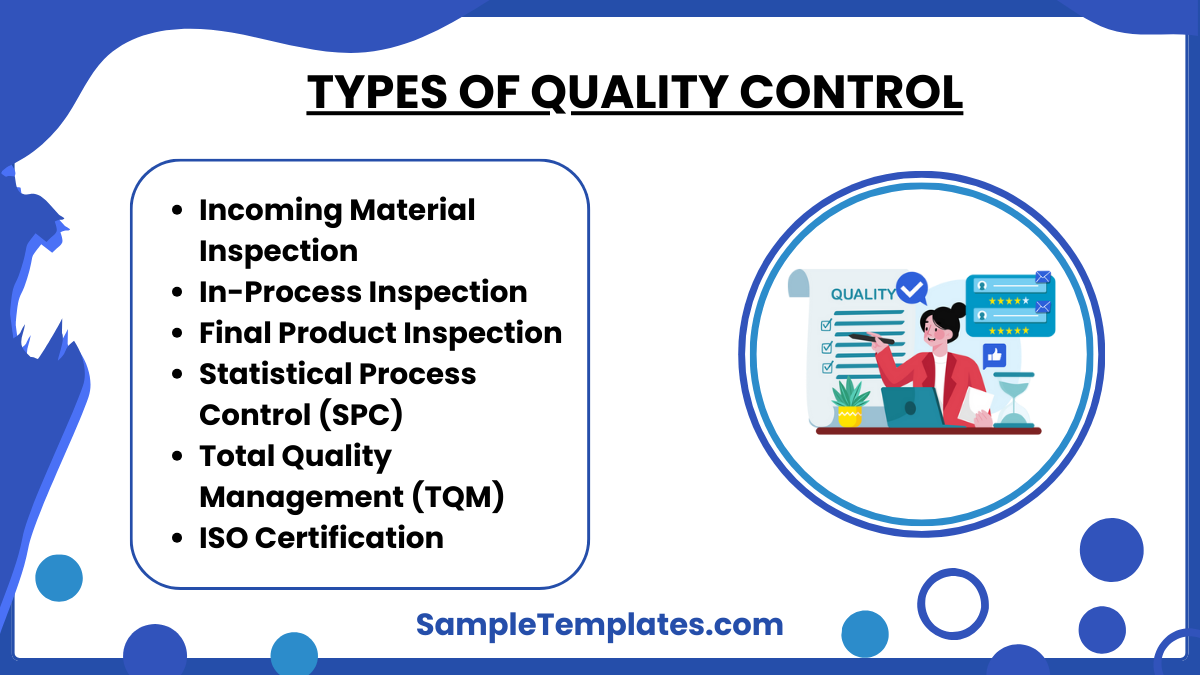
- Incoming Material Inspection: Also known as raw material inspection, this type of quality control involves checking the materials and components that are received from suppliers before they are used in production. This helps ensure that only high-quality inputs are part of the manufacturing process.
- In-Process Inspection: This type of QC occurs during the manufacturing process. It involves checking the products at various stages of production to ensure that they meet the set specifications and identifying issues before the product is completed, which helps in minimizing waste and rework.
- Final Product Inspection: After the manufacturing process is complete, the final product is inspected to ensure that it meets the required standards and specifications. This can involve visual inspections, functional tests, and other checks depending on the product type.
- Statistical Process Control (SPC): SPC uses statistical methods to monitor and control a process. This helps ensure that the process operates at its maximum potential and produces products that meet quality standards. SPC can detect any variances in the process that might lead to defects.
- Total Quality Management (TQM): TQM is a comprehensive approach aimed at improving the effectiveness and flexibility of the whole organization. It emphasizes on quality management as a continuous process that involves every department and employee in the organization.
- ISO Certification: ISO standards are internationally agreed by experts. Think of them as a formula that describes the best way of doing something. Businesses that achieve ISO certification have successfully demonstrated that their operational processes have met the standards of quality management systems, which assures stakeholders of the quality of products and services.
10. Soils Field Laboratory Inspection Quality Control Checklist Form
11. Printable Quality Control Inspection Form
What is a Quality Control Inspection Form?
It is typically the final step before releasing a product into the public domain. Producers perform a variety of tasks to ensure that the goods meet quality standards during this stage of the manufacturing process, including quality checks and corrections.
If the product is finished and ready to ship to the customer, this is a critical step in the process. If you fail to deliver high-quality goods, you risk losing your reputation, losing customers, and increasing returns.
The manner in which a product is manufactured, stored, and distributed is also included in the scope of quality control. The term “defective” is used to describe something that isn’t good enough or is broken. As a result, businesses must develop efficient systems to ensure product safety at all stages of the manufacturing and distribution processes.
If a company operates in a specific industry and sells a specific type of product, internal and external quality control measures may be required to ensure that the products are safe for customers to consume. Internal control mechanisms can be seen in businesses that have their own set of rules. This could range from repairing equipment to evaluating employee performance, as well as everything in between. Upper-level managers are responsible for ensuring that quality assurance procedures are carried out correctly and on time.
External quality control, on the other hand, is required for products intended for general public sale. For example, after food has been produced and distributed, it must be inspected by outside businesses to ensure that it is safe to consume and has not gone bad before it can be sold on the open market.
QCP is an abbreviation for Quality Control Plan in quality control. A Quality Control Plan is a written list of procedures and actions designed to ensure that the goods produced for a project meet or exceed the quality standards specified in the contract, other policies and procedures, and other guidance.
FAQs
What are the action steps?
Action steps are specific steps taken to achieve the objectives outlined in your action plan. In essence, it is about the content of your action plan.
What are the three types of quality?
Quality defects are classified into three types by many professionals: minor flaws, significant flaws, and critical flaws. Minor flaws are those that make up less than 1% of the total. Defects are classified based on their type and severity.
By the end of the day, well-written inspection forms ensure that your company’s or corporation’s, or even your own, goals are met, if not exceeded. It brings your ideas to life. It can help you keep your project on track and avoid problems that may arise during the process. It is essentially the same as developing an effective action plan. It allows you to keep your products and services at a certain level of quality while also allowing for continuous improvement.
Related Posts
FREE 10+ Clinical Quality Management Plan Samples
FREE 10+ Product Checklist Samples
FREE 10+ Site Safety Inspection Checklist Samples
FREE 9+ Sample Quality Reports
FREE 9+ Project Management Quality Control Plan Samples
FREE 7+ Construction Quality Control Plan Samples
FREE 5+ Software Inspection Checklist Samples
How to Create a Checklist
FREE 19+ Delivery Checklist Samples & Templates
FREE 18+ Inventory Checklist Samples & Templates Samples
FREE 14+ Project Management Checklist Samples
FREE 13+ Construction Inspection Report Samples
FREE 12+ Sample Quality Control Plan Templates
FREE 10+ Property Inspection Checklist Samples
FREE 10+ Retail Cleaning Checklist Samples