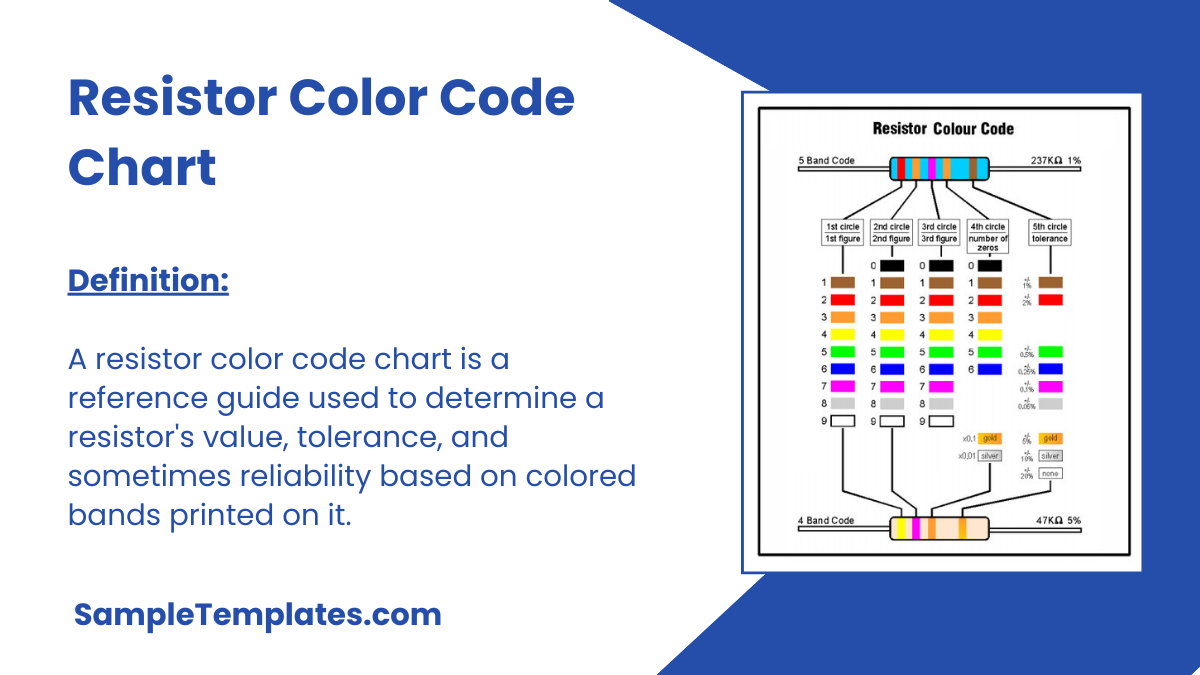
Did you think reading and decoding the information on resistors is tough? Well, let us tell you it’s a cakewalk now with Resistor Color Code Chart. Well resistors have standard colors for the purpose of identification of their resistance. You can easily calculate the resistance by using the chart and applying the formula given along with. Resistor color code charts , HTML Color Code Chart Templates are quite helpful for young students pursuing Electronics Engineering as well as companies dealing in chip designing or VLSI design. Resistor and in excel and word formats Free samples of these templates can be downloaded here and printed for further use.
Resistor Color Code Chart Pdf
How To Read Resistor Color Code?
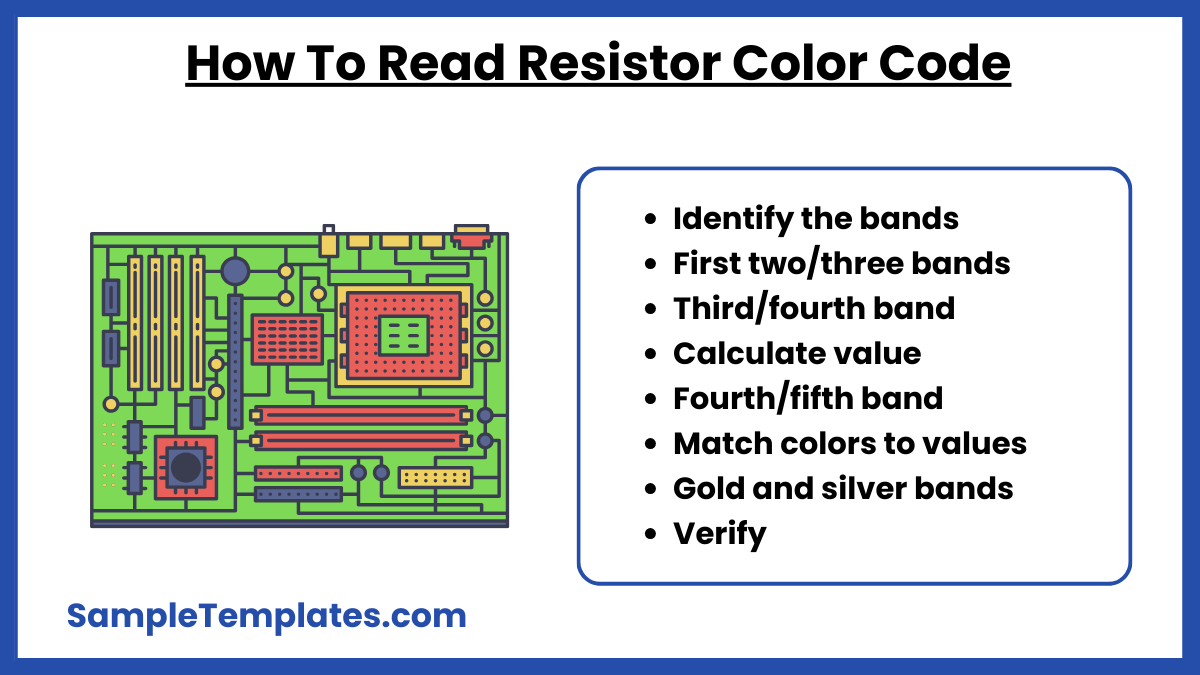
- Identify the bands: Most resistors have 4, 5, or 6 color bands printed on them. You can also see more on Color Chart.
- First two bands (or three in 5-band): These represent the significant digits of the resistance value.
- Third band (or fourth in 5-band): This represents the multiplier (power of 10).
- Calculate value: Multiply the significant digits by the multiplier to get the resistance value.
- Fourth band (or fifth in 5-band): This indicates the tolerance, showing the accuracy of the resistor.
- Match colors to values: Use a resistor color code chart to decode the bands. You can also see more on GPA Chart.
- Gold and silver bands: These indicate lower multipliers (0.1 for gold and 0.01 for silver) or tolerance.
- Verify: Double-check the calculation to ensure accurate reading for circuit design.
Resistor Color Code Table
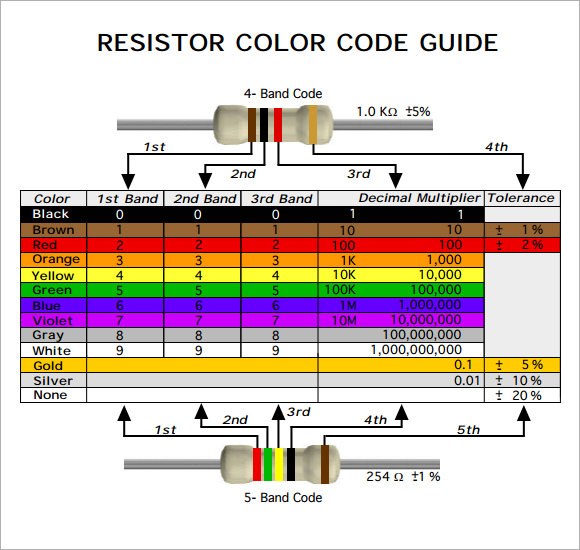
Resistor Color Code Chart Printable
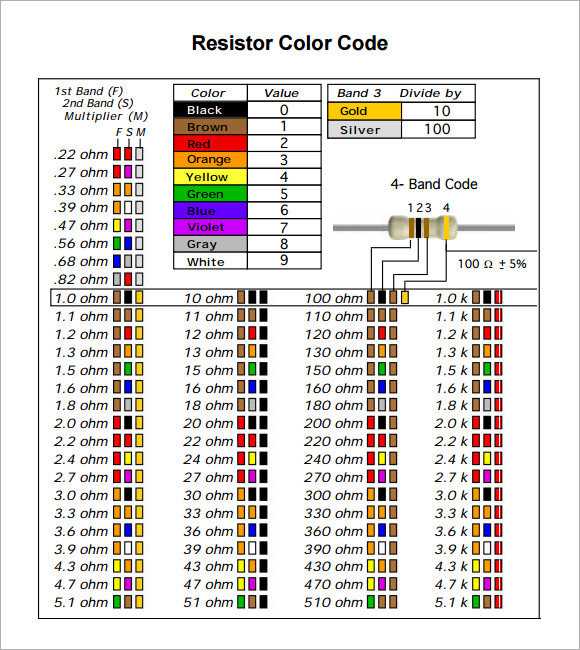
How To Remember Resistor Color Code?
1. Mnemonic Phrase:
Use a mnemonic to remember the color order. A popular one is:
- Black (0), Brown (1), Red (2), Orange (3), Yellow (4), Green (5), Blue (6), Violet (7), Gray (8), White (9).
Mnemonic:
“BB ROY Great Britain Very Good Wife”
(B for Black and Brown, ROY for Red, Orange, Yellow, and so on).
2. Visualize the Colors:
Imagine the colors progressing from darker (black) to lighter (white) in sequence. This can help reinforce the order.
3. Practice with a Chart:
Regularly refer to a resistor color code chart and try decoding resistors, which reinforces memory through repetition.
4. Use an App:
Some mobile apps can quiz you on resistor codes or provide quick lookups to reinforce learning. You can also see more on Decimal To Fraction Chart.
5. Flashcards:
Create flashcards with the color bands on one side and their numerical values on the other, practicing until memorized.
Resistor Color Code Chart Band
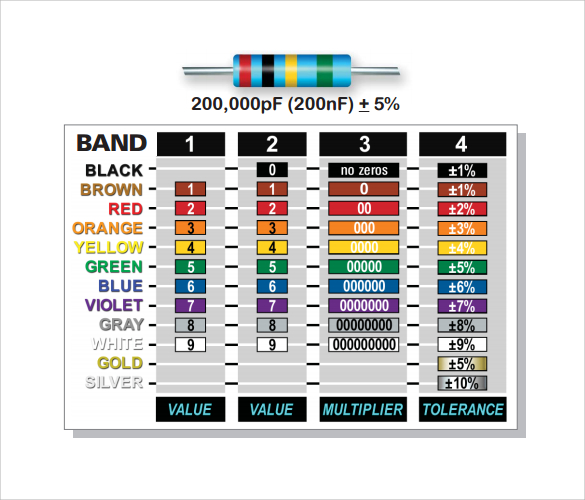
Simple Resistor Color Code Chart

5 Band Resistor Color Code Chart
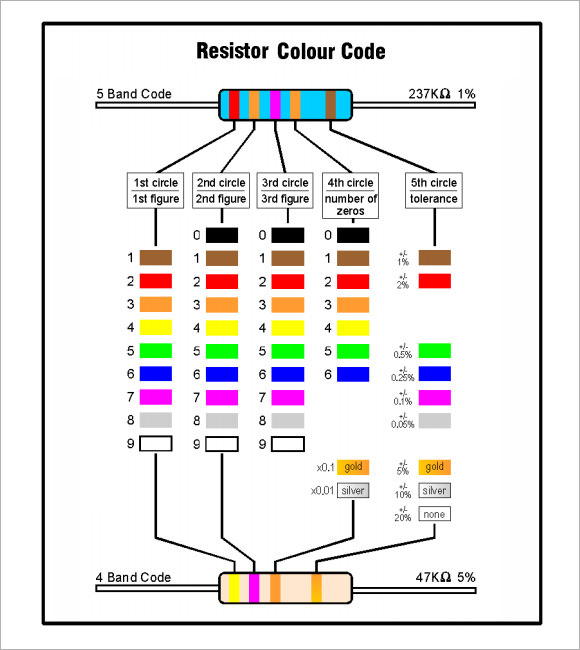
Tips for Reading Resistor Codes
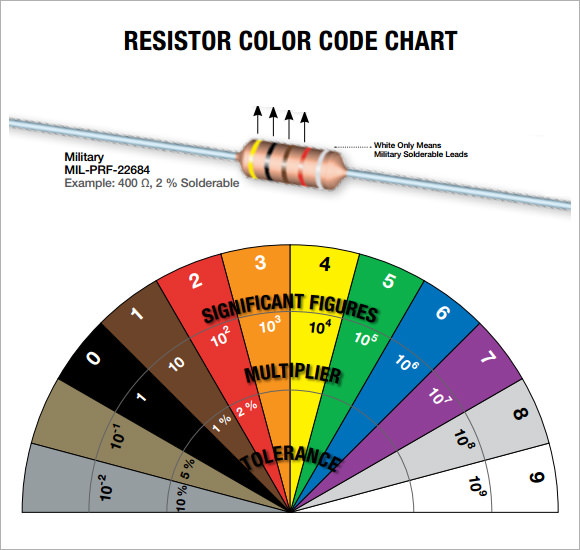
- Understand the band sequence: The first two or three bands represent the significant digits, the next band indicates the multiplier, and the final band denotes tolerance.
- Read from left to right: Start reading from the side with the color band closer to the edge of the resistor.
- Memorize color values: Use mnemonic devices to remember the color values, such as “Black = 0, Brown = 1, Red = 2…” to easily recall the digit each color represents.
- Identify the tolerance band: The last band is typically gold, silver, or no color, representing the tolerance (±5%, ±10%, or ±20%).
- Use a resistor color chart: Keep a resistor color code chart handy for quick reference when you’re unsure of the values.
- Pay attention to precision resistors: Some resistors have 5 or 6 color bands, where three bands indicate the value and additional bands represent a finer tolerance.
- Practice reading codes: Familiarize yourself by practicing on different resistors to get comfortable with identifying the values quickly.
- Check with a multimeter: When in doubt, use a multimeter to verify the resistor’s actual value, as it will confirm the color code reading.
Resistor Color Code Chart Poster

Sample Resistor Color Code
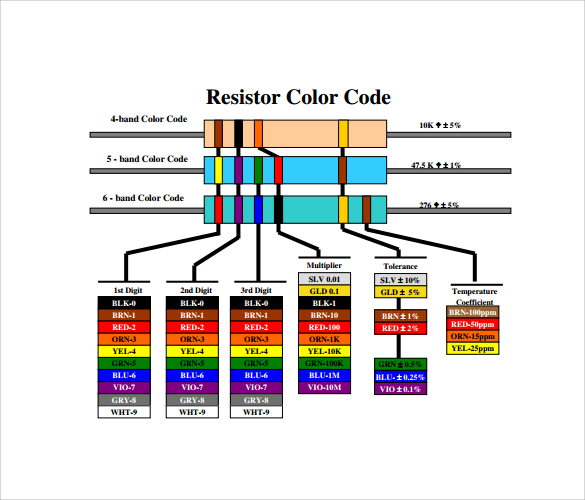
Uses of Resistor Color Code Chart
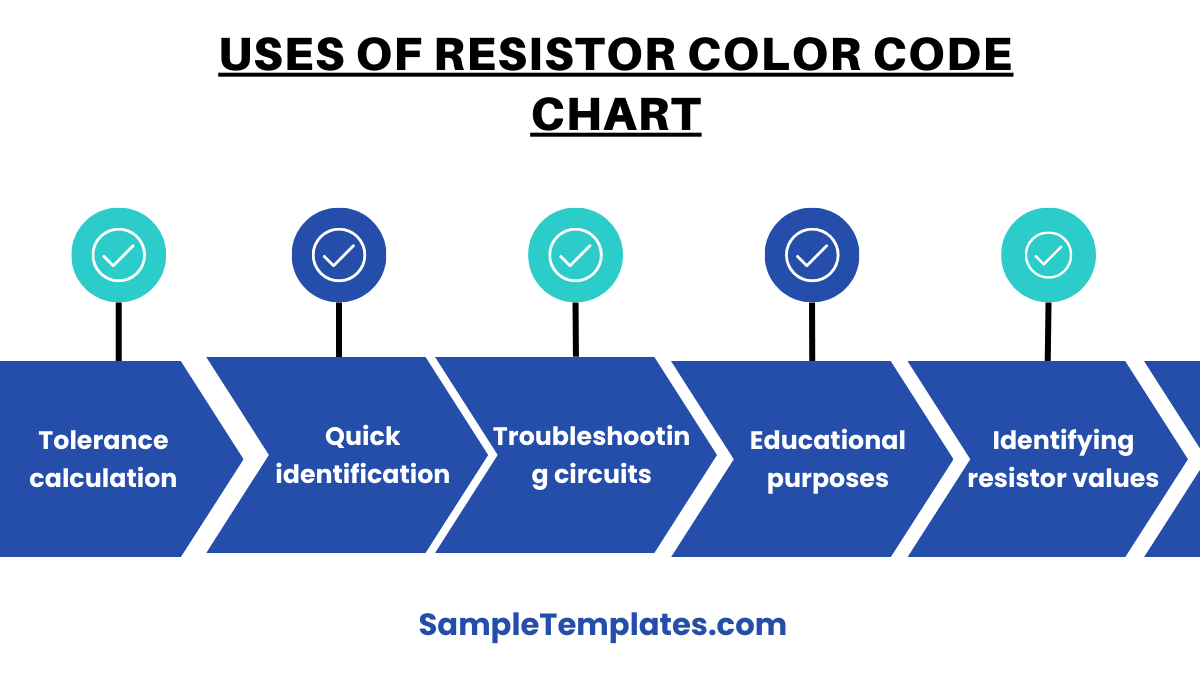
- Identifying resistor values: The color code chart helps determine the resistance value of a resistor based on its color bands.
- Tolerance calculation: It allows users to determine the tolerance, or acceptable range of deviation, in the resistor’s value.
- Reading resistance in different units: The chart assists in converting resistance into ohms, kilo-ohms, or mega-ohms depending on the color bands.
- Quick identification: It provides a fast way for technicians and engineers to visually identify resistor specifications without using electronic testing devices.
- Verifying resistor accuracy: Helps verify if the resistor being used matches the circuit’s design requirements.
- Troubleshooting circuits: When diagnosing faulty circuits, the chart helps identify whether a resistor is functioning within its expected range.
- Educational purposes: It is widely used for teaching electronics and electrical engineering students how to read and interpret resistor values.
- Standardization: It ensures uniformity in resistor labeling, making components easily recognizable and interchangeable across different manufacturers.
Simple Resistor Color Code Free
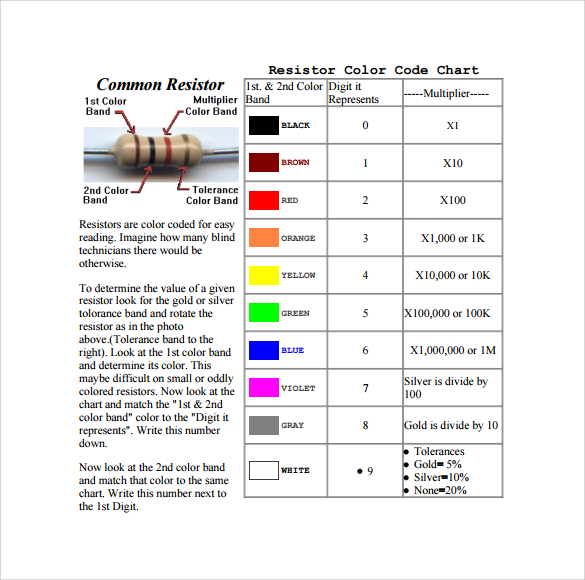
Example of Resistor Color Code Chart
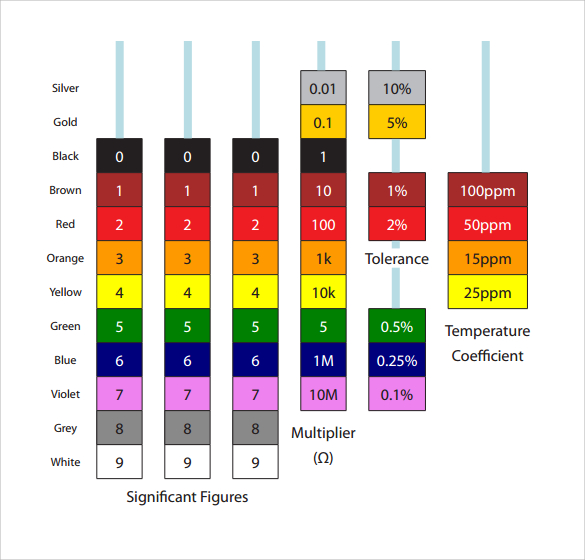
What are the color codes for resistors?
Resistor color codes use black (0), brown (1), red (2), orange (3), yellow (4), green (5), blue (6), violet (7), gray (8), white (9), plus gold and silver for tolerance values.
What color is a 330 ohm resistor?
A 330-ohm resistor typically has orange (3), orange (3), and brown (multiplier of 10) color bands, with an additional gold or silver band indicating a 5% or 10% tolerance.
Does it matter which way a resistor goes?
Resistors are non-polarized components, meaning they can be inserted in any direction in a circuit. The orientation doesn’t affect their function or resistance value.
What is the color mnemonic?
A common mnemonic for resistor color codes is “Black Bears Run On Your Grass But Very Good Weather,” representing Black (0) to White (9) for remembering the digits.
What is the primary color code?
The primary resistor color code starts from black (0), brown (1), red (2), orange (3), yellow (4), green (5), blue (6), violet (7), gray (8), and white (9), followed by tolerance bands.
How to calculate a resistor?
To calculate a resistor’s value, read the first two or three color bands for digits, then multiply by the third or fourth band’s value, which represents the multiplier. Finally, account for the tolerance.
If you have any DMCA issues on this post, please contact us!
Related Posts
Weekly Schedule Samples & Templates
Contractual Agreement Samples & Templates
FREE 9+ Amazing Sample Church Bulletin Templates in PSD | PDF
Sample Business Card Templates
Sample Cashier Job Descriptions
Questionnaire Samples
FREE 10+ Sample HR Resource Templates in PDF
FREE 10+ HR Consulting Business Plan Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | Pages | PDF
FREE 49+ Sample Job Descriptions in PDF | MS Word
FREE 16+ Nonprofit Budget Samples in PDF | MS Word | Excel | Google Docs | Google Sheets | Numbers | Pages
FREE 13+ Academic Calendar Templates in Google Docs | MS Word | Pages | PDF
FREE 10+ How to Create an Executive Summary Samples in Google Docs | MS Word | Pages | PDF
FREE 23+ Sample Event Calendar Templates in PDF | MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages
Company Profile Samples
FREE 10+ Leadership Report Samples [ Development, Training, Camp ]