Bolt torque chart is based on the component contained in the external thread or the material strength of the bolt. Bolt Torque Chart Templates in word or excel format contains the size of bolt and the torque that is required to fasten it. The torque is recommended according to the grade of the material used and the bolt size.
Bolt torque calculator chart templates are available on this website and can be downloaded for free. You can print them and keep them for future reference. A specific bolt torque specification is based on several factors.
Metric Bolt Torque Chart Template
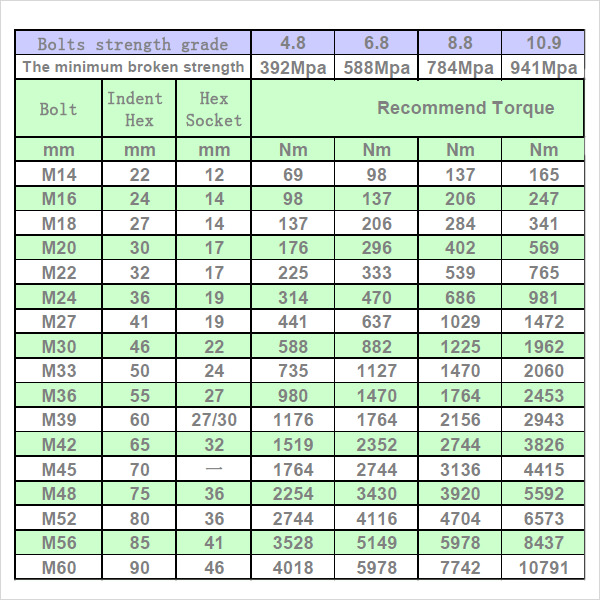
This template has a number of columns and rows. In the left side of the template there are the bolt strength grade specifications, divided in a few columns. On the right side there are the specifications of the torque recommended.
Socket Head Bolt Torque Chart
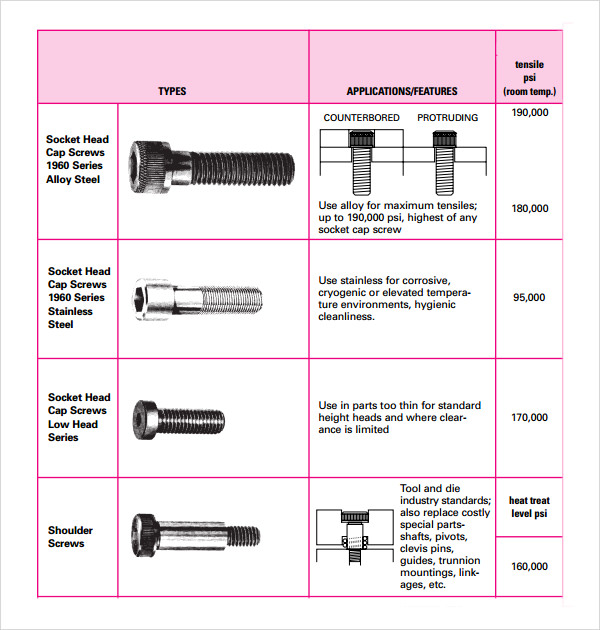
In this template there are the pictures of the various types of sockets on one side and their features and specifications on the other side. There are various types of socket heads which can be seen and their respective applications.
Importance Of A Bolt Torque Chart
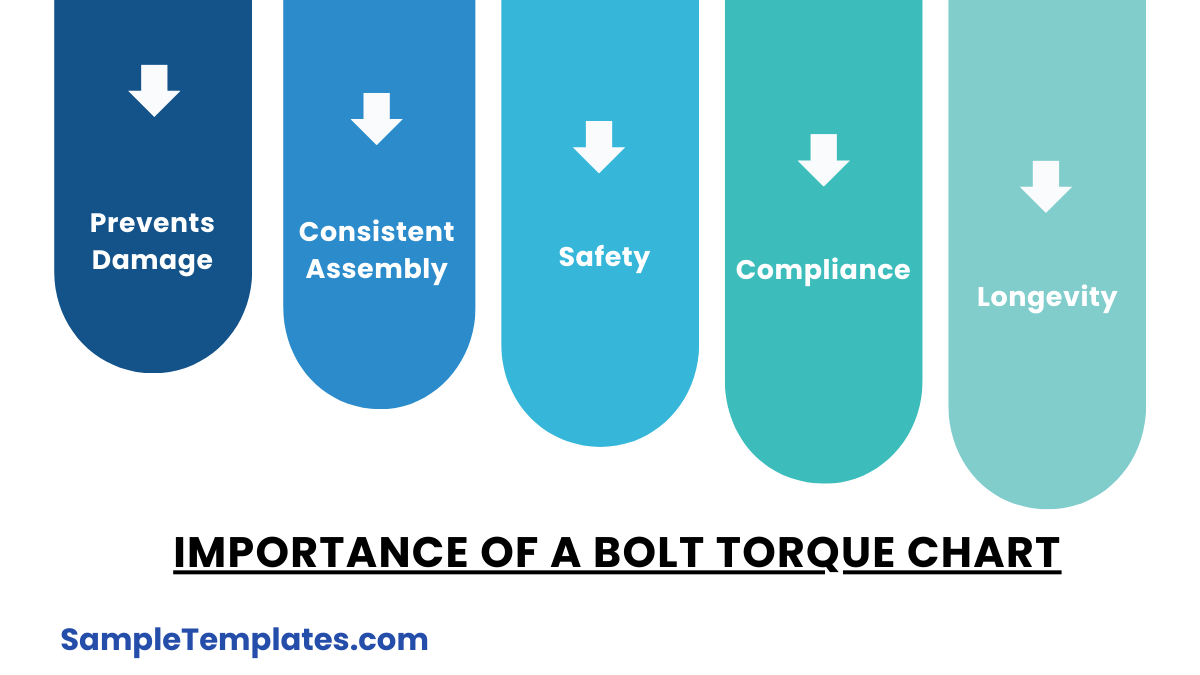
One may wonder as to why a bolt torque chart is needed. There are a number of varieties of bolts and torques available. The specification of each one could be different from the other. Thus it is important because it gives you the specific information about what sort of bolt needs which torque to fit properly. You can also see Baby Growth Chart Templates.
- Ensures Proper Tightening: It provides the recommended torque values for different bolt sizes and materials, ensuring that bolts are neither under-tightened nor over-tightened. Proper tightening is crucial for the integrity and safety of the assembly.
- Prevents Damage: Over-tightening a bolt can strip threads, stretch the bolt, or cause the material being fastened to deform or crack. Under-tightening can lead to bolts loosening over time, leading to potential failures or hazards.
- Consistent Assembly: It helps maintain consistency in assembly processes, which is particularly important in manufacturing and construction where multiple workers may be involved. Consistency ensures that all bolts in an assembly are torqued to the same specification.
- Safety: Properly torqued bolts ensure the safety of the structure or equipment being assembled. This is especially critical in applications like automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery, where bolt failure could lead to catastrophic results.
- Compliance: In many industries, adhering to torque specifications is a regulatory requirement. Using a bolt torque chart ensures compliance with industry standards and regulations.
- Longevity: Properly torqued bolts contribute to the longevity and reliability of the assembled components, reducing maintenance costs and downtime.
For that you need to know more about bolts and torques, such as their size, class among other things. A chart can give you a complete list of the bolts and the torques. When you are using them for any machinery you need to know about their pairing
Stainless Steel Bolt Torque Chart
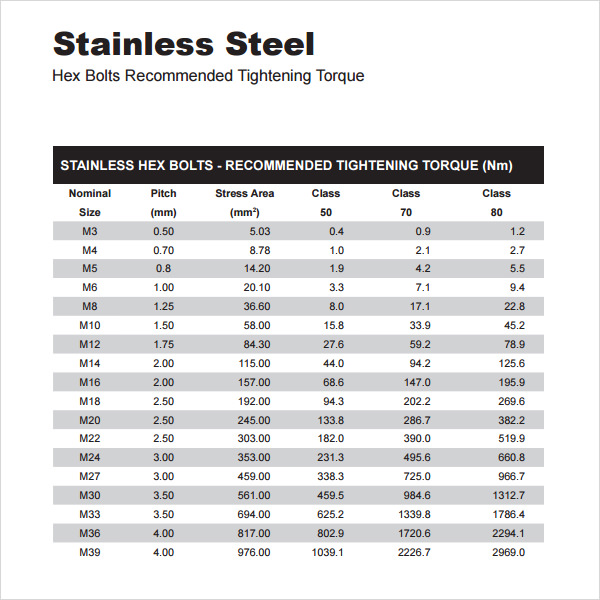
This is a template which mentions various types of hex bolts recommended for tightening torques. In the chart there are mentions of size, class, stress area, etc. for your convenience. The material mentioned in the chart is stainless steel.
Bolt Torque Chart Fine Thread
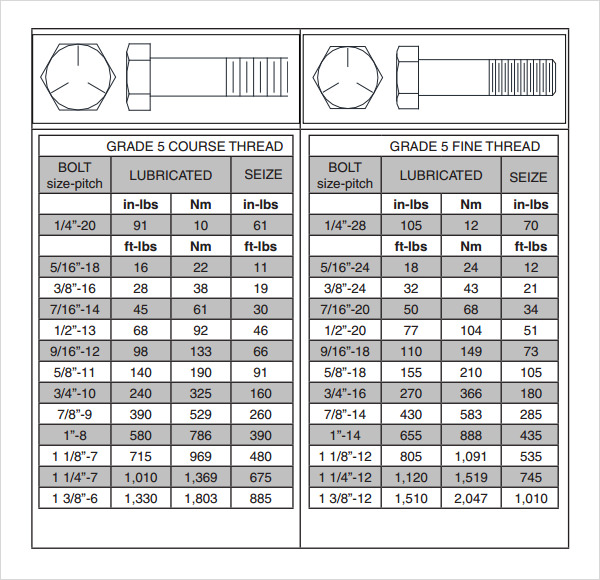
The template is divided into two main columns, one for grade 5 course thread and another for grade 5 fine threads. These two columns are then divided into a few sub columns, which mention the specifications of the bolt torque.
Main Features of a Bolt And Torque Chart
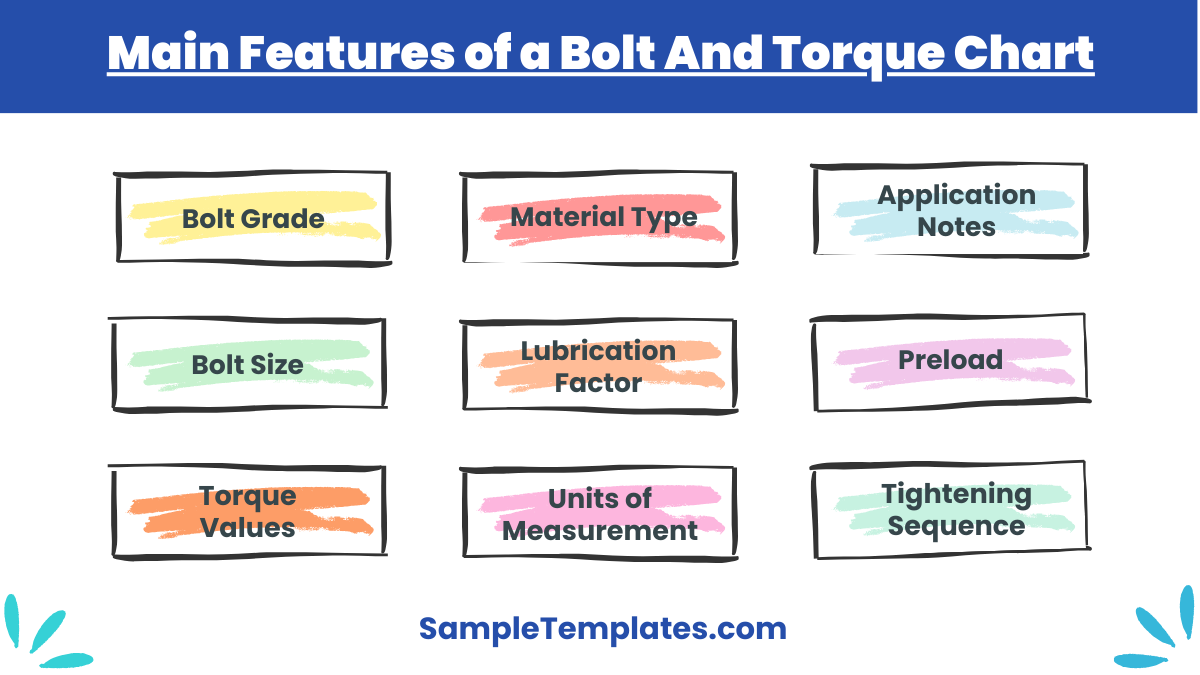
The bolt and torque chart is used by an engineer, a mechanic etc., for making or fixing various machines. Not all bolts can be fixed with all types of torques, and therefore, knowing the specifications are necessary. Thus a good bolt and torque chart should have the important features of the bolts and torques, and preferably also which one suits the other.
- Bolt Size: This includes the diameter and thread pitch of the bolt, usually specified in metric (e.g., M6, M8) or imperial (e.g., 1/4″, 3/8″) units.
- Bolt Grade/Class: This refers to the material and strength of the bolt, which can affect the torque required. Common grades include 8.8, 10.9, and 12.9 for metric bolts, and Grade 5, Grade 8 for imperial bolts.
- Torque Values: The chart provides the recommended torque values for tightening bolts. This is usually presented in units of torque such as Newton-meters (Nm) or foot-pounds (ft-lbs).
- Lubrication Factor: Some charts include different torque values based on whether the bolt is lubricated or dry, as lubrication can significantly affect the friction and thus the torque required.
- Material Type: The chart may specify torque values based on the type of material the bolt is fastening, such as steel, aluminum, or plastic, as different materials have different properties.
- Units of Measurement: The torque values are often given in multiple units, such as Nm, ft-lbs, and inch-lbs, to accommodate different preferences and standards.
- Application Notes: Some charts include additional notes or guidelines for specific applications, such as the type of tools to use or safety precautions to take.
- Preload or Clamp Load: Some charts provide information on the expected preload or clamp load achieved when the bolt is torqued to the specified value, which is important for understanding the force exerted by the bolt.
- Temperature Considerations: In some cases, charts may include adjustments for torque values based on the operating temperature of the assembly, as temperature can affect the materials’ properties and the bolt’s behavior.
- Tightening Sequence: While not always included in basic torque charts, more comprehensive references might suggest a tightening sequence for multiple bolts to ensure even distribution of load and proper assembly.
Moreover, it might also be a good idea to describe the applications of the various types of the bolts, so that people can choose them according to their requirements. These are the main features of a bolt and torque chart. You can also see Element Chart Templates.
Bolt Torque Chart B7
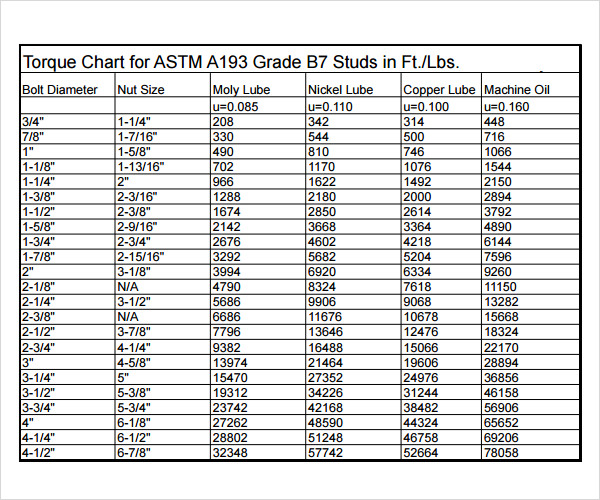
Flange Bolt Torque Chart
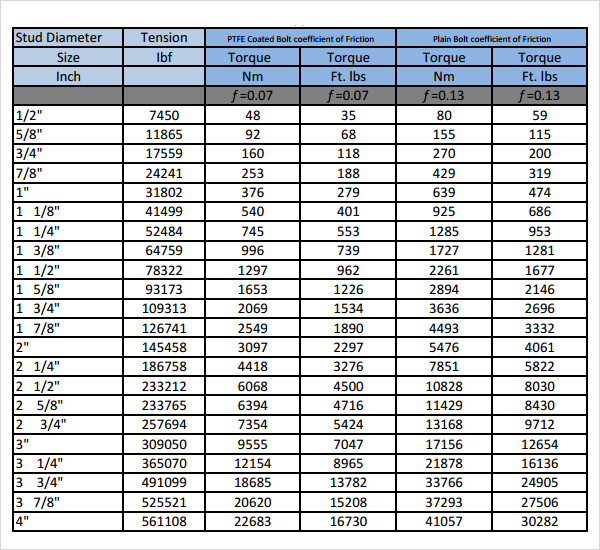
How to Make a Bolt and Torque Chart?
Creating a bolt and torque chart involves several steps to ensure accuracy and reliability. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Gather Necessary Information
- Bolt Specifications: Collect information on different bolt sizes, thread pitches, and bolt grades/classes.
- Material Properties: Gather data on the materials being joined, as this can affect torque values.
- Lubrication Details: Determine if the bolts will be lubricated or dry during assembly.
2. Determine Torque Values
- Reference Standards: Use standard references such as ISO, DIN, or SAE standards that provide torque values for different bolt grades and sizes.
- Manufacturer Guidelines: Refer to torque recommendations provided by bolt manufacturers.
- Engineering Calculations: Perform engineering calculations if necessary to determine specific torque values for unique applications.
3. Create the Chart Layout
- Headers: Decide on the headers for your printable chart. Common headers include:
- Bolt Size (Diameter and Thread Pitch)
- Bolt Grade/Class
- Torque Values (Lubricated and Dry)
- Material Type (if applicable)
- Units (Nm, ft-lbs, etc.)
- Units of Measurement: Ensure the torque values are provided in multiple units if necessary.
4. Populate the Chart
- Fill in the Data: Enter the torque values for each bolt size and grade/class combination.
- Lubrication Factors: Include separate columns for lubricated and dry torque values if applicable.
- Material Considerations: Add rows or columns for different material types if relevant to your application.
5. Include Additional Information
- Preload or Clamp Load: If applicable, include information on the expected preload or clamp load.
- Tightening Sequence: Provide guidelines on the tightening sequence for multiple bolts.
- Application Notes: Add any additional notes or guidelines relevant to specific applications or conditions.
6. Format the Chart
- Ensure Clarity: Format the blank chart for easy readability. Use clear fonts, appropriate spacing, and color coding if necessary.
- Standardization: Ensure the chart adheres to industry standards for torque values and presentation.
7. Validate and Review
- Accuracy Check: Verify the accuracy of the torque values and other data.
- Expert Review: Have the chart reviewed by an engineering expert to ensure correctness.
- Real-World Testing: Conduct real-world testing if possible to validate the torque values.
8. Update and Maintain
- Regular Updates: Keep the chart updated with the latest standards and manufacturer recommendations.
- Feedback Loop: Incorporate feedback from users to improve the chart over time.
Example Layout
| Bolt Size | Thread Pitch | Grade 8.8 (Dry) | Grade 8.8 (Lubricated) | Grade 10.9 (Dry) | Grade 10.9 (Lubricated) | Grade 12.9 (Dry) | Grade 12.9 (Lubricated) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M6 | 1.0 mm | 10 Nm | 8 Nm | 15 Nm | 12 Nm | 20 Nm | 16 Nm |
| M8 | 1.25 mm | 25 Nm | 20 Nm | 35 Nm | 28 Nm | 45 Nm | 36 Nm |
| M10 | 1.5 mm | 45 Nm | 36 Nm | 60 Nm | 48 Nm | 70 Nm | 56 Nm |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
By following these steps, you can create a comprehensive and reliable bolt and torque chart tailored to your specific needs and applications.
Fastenal Bolt Torque Chart
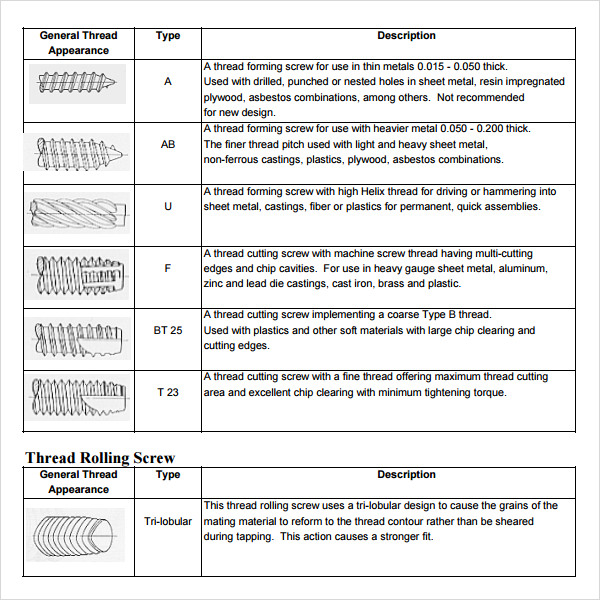
General Bolt Torque Chart
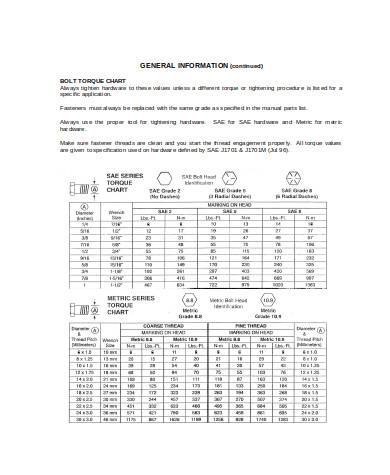
What is the rule of thumb for bolt torque?
A common rule of thumb is to apply torque to 75% of the bolt’s proof load. This ensures sufficient clamping force without over-tightening and damaging the bolt or threads.
How do I know how much to torque my bolts?
Refer to the bolt torque chart specific to the bolt size, grade, and lubrication condition. If unsure, consult manufacturer guidelines or engineering standards for accurate torque values.
How to determine the torque required for a bolt?
To determine required torque, consider bolt size, grade, lubrication, and material being fastened. Use a bolt torque chart or calculation based on these factors, referencing engineering standards or manufacturer recommendations.
How much torque on a 1 inch bolt?
The torque required for a 1-inch bolt depends on its grade and lubrication. For example, a Grade 8.8 dry 1-inch bolt typically requires around 300-400 ft-lbs of torque. Consult specific torque charts for precise values.
How to properly torque bolts?
Use a calibrated torque wrench, applying torque gradually in a crisscross pattern if multiple bolts are involved. Follow the specified torque value from a reliable chart or manufacturer’s guidelines, ensuring even and correct tightening
If you have any DMCA issues on this post, please contact us!
Related Posts
Weekly Schedule Samples & Templates
Contractual Agreement Samples & Templates
FREE 9+ Amazing Sample Church Bulletin Templates in PSD | PDF
Sample Business Card Templates
Sample Cashier Job Descriptions
Questionnaire Samples
FREE 10+ Sample HR Resource Templates in PDF
FREE 10+ HR Consulting Business Plan Samples in MS Word | Google Docs | Pages | PDF
FREE 49+ Sample Job Descriptions in PDF | MS Word
FREE 16+ Nonprofit Budget Samples in PDF | MS Word | Excel | Google Docs | Google Sheets | Numbers | Pages
FREE 13+ Academic Calendar Templates in Google Docs | MS Word | Pages | PDF
FREE 10+ How to Create an Executive Summary Samples in Google Docs | MS Word | Pages | PDF
FREE 23+ Sample Event Calendar Templates in PDF | MS Word | Google Docs | Apple Pages
Company Profile Samples
FREE 10+ Leadership Report Samples [ Development, Training, Camp ]